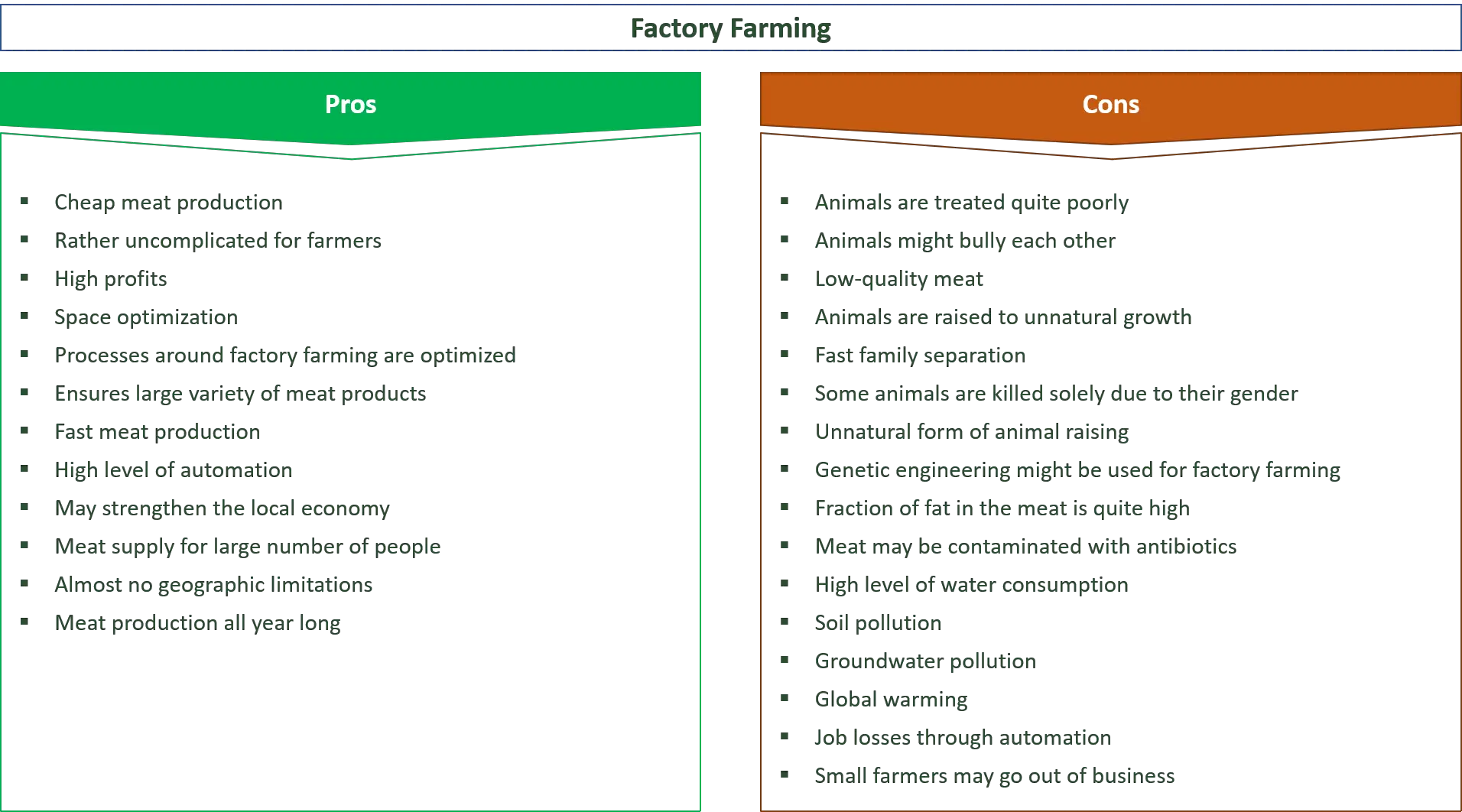
Factories and plantations were integral parts of the industrial development in the past centuries. Both types of establishments played significant roles in shaping the economic and social fabric of societies. However, they differed in various ways, including their rules and regulations. Understanding these differences is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of work and life in factories and plantations. In this article, we will delve into an answer key that compares the rules governing these two types of workplaces.
One of the essential contrasts between factories and plantations lies in their structures. Factories were often large-scale industrial centers where machinery and technology were employed to produce goods. In contrast, plantations primarily focused on agricultural production, such as growing crops like cotton or sugarcane. The diverse nature of their operations demanded distinct sets of rules to maintain order and efficiency.
When examining the rules in factories, one can observe a strong emphasis on productivity and discipline. Workers were required to adhere to strict schedules and perform repetitive tasks with precision. Furthermore, factory rules often prohibited interactions among workers to maximize productivity. On the other hand, plantation rules had a slightly different approach. While productivity was still crucial, the hierarchical structure of plantations allowed for more social interaction among workers. The rules in plantations were designed to maintain discipline but also foster a sense of community among the labor force.
Factory and Plantation Rules Compared Answer Key
In the context of factory and plantation rules, there are several key differences to consider. Factory rules typically apply to industrial settings where goods are manufactured, whereas plantation rules are specific to agricultural estates where crops are cultivated.
One major difference between factory and plantation rules is the type of labor involved. In factories, workers are usually employed in a more structured and specialized manner. They may have specific roles and responsibilities, such as operating machinery or assembling products. On the other hand, plantation labor tends to be more decentralized and manual, with workers involved in various tasks related to crop cultivation, such as planting, harvesting, and processing.
- Working Hours:
- Factory rules often include strict working hours, with set schedules and shifts to ensure maximum productivity. Workers in factories may be required to work long hours, sometimes even overnight or on weekends. This is not the case with plantation labor, as agricultural activities are often dependent on natural factors such as daylight and seasonality. Workers on plantations may have more flexible working hours, depending on the needs of the crops.
- Living Conditions:
- Factory rules may not address living conditions, as workers usually commute to and from work. In contrast, plantation rules often include provisions for housing and accommodation, as workers may need to live on-site to tend to crops and animals.
- Supervision and Discipline:
- Factories typically have a hierarchical structure with clear lines of supervision and strict discipline to maintain order and efficiency. Plantations, on the other hand, may have a more informal hierarchy, with supervision focused on overseeing specific tasks rather than a strict chain of command.
In conclusion, factory and plantation rules differ in terms of labor type, working hours, living conditions, and supervision. Factory rules are more structured and specialized, with stricter working hours and less emphasis on living conditions. On the other hand, plantation rules are more decentralized, with flexible working hours and provisions for on-site living. Understanding these key differences is important for analyzing the distinct nature of work and labor regulations in factory and plantation settings.
Understanding Factory and Plantation Rules
Factory and plantation rules are sets of guidelines and regulations that govern the operations and behaviors of workers within these specific work environments. These rules aim to maintain order, productivity, and safety within the factory or plantation, while also ensuring that workers’ rights are protected.
Key differences between factory and plantation rules:
- Working hours: In factories, there are typically fixed working hours, usually in shifts, which are strictly enforced. Plantations, on the other hand, often have longer working hours, as agricultural work may require more time and flexibility.
- Work conditions: Factory rules often prioritize safety measures, such as providing protective gear, ensuring well-maintained machinery, and minimizing exposure to harmful substances. Plantations, on the other hand, may have rules regarding working in open fields, exposure to weather conditions, and handling of agricultural tools.
- Supervision: Factories usually have a more structured system of supervision and hierarchy, with managers overseeing the work of employees. In plantations, supervisors may be present, but there is often less direct supervision due to the nature of the work being spread out across vast areas.
- Breaks and rest periods: Factory rules typically allocate specific break times and rest periods for workers to ensure they have adequate time to rest and recharge. Plantations may have flexible break times, as the work may require continuous attention without fixed intervals for breaks.
These are just a few examples of the differences between factory and plantation rules. Ultimately, the specific rules and regulations can vary across different countries, industries, and individual workplaces. It is important for both employers and employees to understand and comply with these rules to create a harmonious and productive work environment.
Key Differences between Factory and Plantation Rules
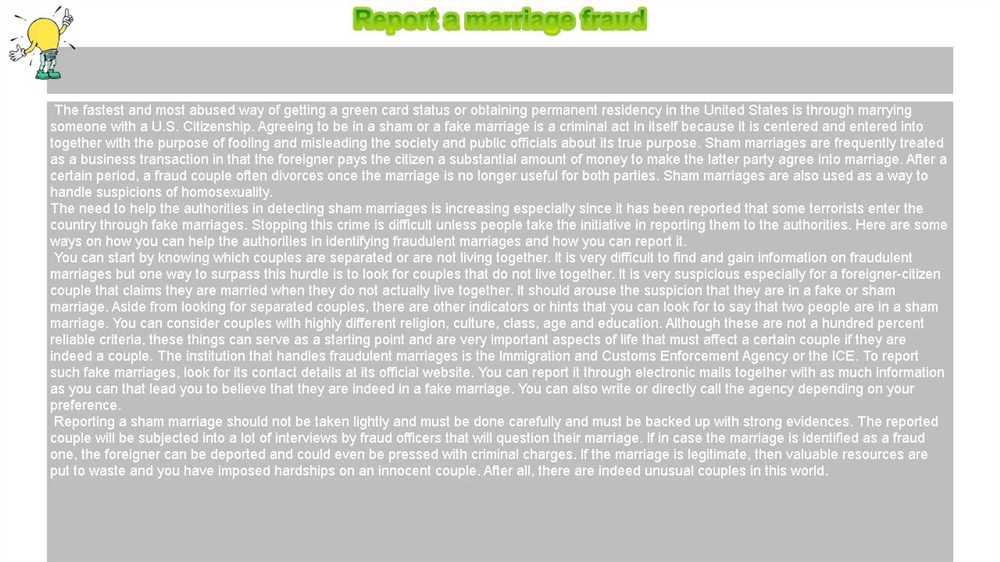
The rules and regulations in factories and plantations differ in several key aspects, reflecting the unique nature of each industry. Firstly, in terms of working conditions, factory rules tend to be stricter compared to plantation rules. This is because factories involve complex machinery and hazardous processes, requiring employees to adhere to strict safety protocols. On the other hand, plantations primarily involve manual labor, allowing for more relaxed rules regarding personal protective equipment and safety procedures.
Another significant difference is the organization of working hours. In factories, workers are usually required to follow a strict schedule and work set shifts. This ensures the continuous operation of the production line and efficient management of resources. In contrast, plantation workers often have more flexible working hours, as their tasks are typically tied to seasonal activities such as planting or harvesting crops.
Furthermore, the level of supervision and control varies between factories and plantations. Factory employees are closely monitored by supervisors and managers to ensure productivity and quality standards are met. This stricter hierarchical structure is necessary to maintain efficiency in a fast-paced manufacturing environment. In plantations, however, because of the nature of the work, supervision may be less intense, allowing workers more autonomy in carrying out their tasks.
Additionally, the role of labor unions and collective bargaining is another point of contrast between factories and plantations. Factory workers have historically been more successful in organizing labor unions and negotiating for better wages, working conditions, and benefits. Plantation workers, on the other hand, face additional challenges due to the seasonal nature of their work and the often remote locations of plantations, which can limit their ability to collectively bargain.
In summary, while both factories and plantations have specific rules and regulations governing their operations, the key differences lie in the level of strictness regarding working conditions and safety, the organization of working hours, the level of supervision and control, and the role of labor unions. These variations reflect the unique characteristics and demands of each industry.
Similarities between Factory and Plantation Rules
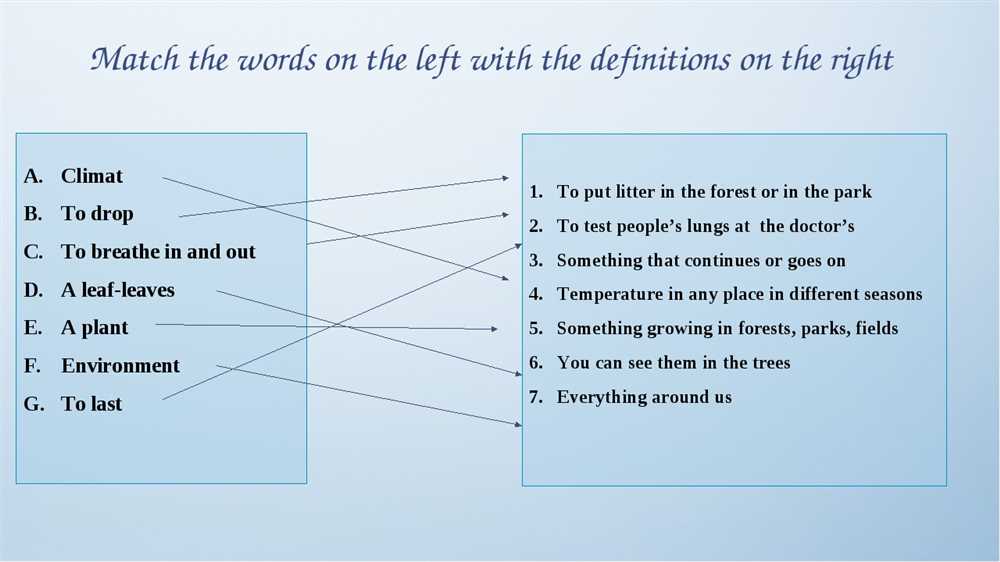
Both factory and plantation rules shared several similarities in their regulations and treatment of workers. These similarities highlight the ways in which both types of establishments were designed to exert control over their workers and maximize productivity.
1. Strict disciplinary measures: In both factories and plantations, strict disciplinary measures were implemented to maintain order and discipline among the workers. This often involved imposing fines or withholding wages for various infractions, such as tardiness or insubordination.
2. Long working hours: Both factories and plantations required their workers to work long hours. This meant that workers often had to endure physically demanding and exhausting shifts that extended well beyond the typical 8-hour workday.
3. Limited breaks and rest time: In both settings, workers were granted limited breaks and rest time. This meant that workers had little time for rest and relaxation during their shifts, further contributing to their physical and mental exhaustion.
4. Rigid hierarchy and supervision: Factories and plantations both had a rigid hierarchical structure in which workers were subordinated to supervisors and overseers. This hierarchy was enforced through strict supervision and surveillance, ensuring that workers followed instructions and maintained productivity.
5. Inadequate living and working conditions: Both factories and plantations often provided inadequate living and working conditions for their workers. Workers in both settings were often subjected to cramped and poorly ventilated spaces, unsanitary conditions, and meager accommodations.
Overall, the similarities between factory and plantation rules highlight the ways in which both types of establishments were designed to exert control over their workers and maximize productivity. These similarities underscore the exploitative nature of these labor environments and the harsh conditions that workers had to endure.
Compliance Requirements for Factory Rules
Factory rules are essential for maintaining a safe and efficient working environment. These rules ensure that employees follow proper protocols and procedures to prevent accidents and maintain productivity. Compliance with factory rules is crucial for both the well-being of employees and the success of the factory as a whole.
Education and Training: In order to comply with factory rules, employees must receive proper education and training. This includes learning about the specific safety measures and procedures that are required in the factory. It is important for employees to understand how to operate machinery and equipment safely, as well as the proper use of personal protective equipment.
Regular Inspections: Regular inspections are another compliance requirement for factory rules. These inspections are conducted to ensure that all equipment and machinery is in proper working condition. Inspections help identify potential hazards and allow for the implementation of necessary maintenance or repairs. Inspecting safety equipment such as fire extinguishers and first aid kits is also important to ensure their effectiveness in case of an emergency.
Reporting and Documentation: Factory rules often require employees to report any accidents, incidents, or near misses that occur within the workplace. This helps identify areas of improvement and allows for necessary action to be taken. Documentation of incidents and any corrective actions taken is also necessary for compliance. Proper record-keeping ensures that all incidents are properly addressed and can be used for future reference or analysis.
Compliance Training Programs: To ensure ongoing compliance with factory rules, it is important to have regular compliance training programs in place. These programs can help reinforce the importance of following factory rules and educate employees about any updates or changes to the rules. Training programs can include workshops, presentations, or online courses that provide employees with the necessary knowledge and skills to comply with factory rules.
- Educate and train employees on factory safety measures
- Conduct regular inspections to ensure equipment and machinery are in proper working condition
- Require employees to report any accidents or incidents
- Maintain proper documentation of incidents and corrective actions
- Implement ongoing compliance training programs
In conclusion, compliance with factory rules is a critical aspect of maintaining a safe and efficient working environment. By educating and training employees, conducting regular inspections, requiring incident reporting, and implementing compliance training programs, factories can ensure adherence to rules and promote a culture of safety and productivity.
Compliance Requirements for Plantation Rules
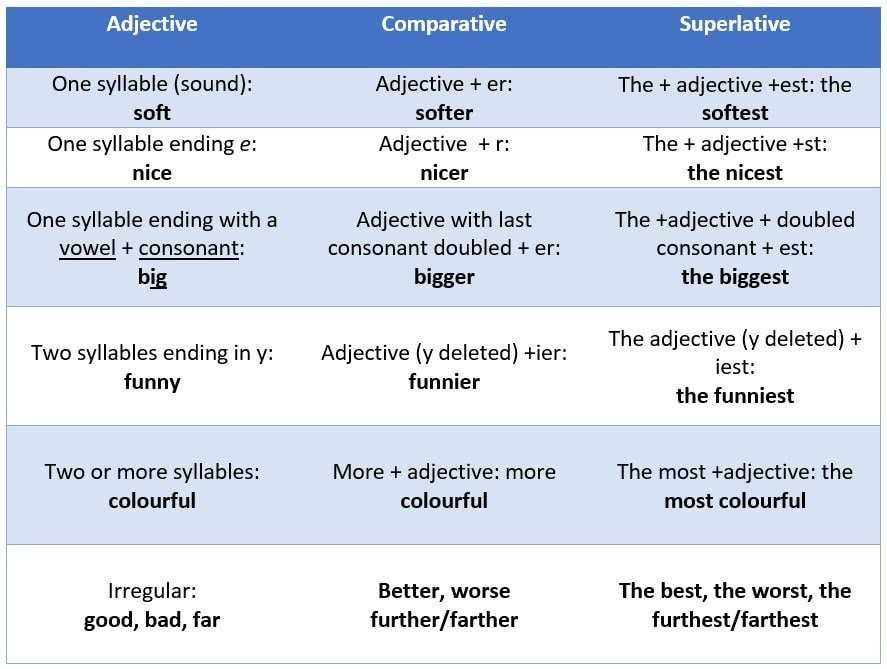
Plantation rules are a set of regulations that govern various aspects of working conditions and employee welfare in plantations. These rules aim to ensure the safety, well-being, and fair treatment of plantation workers. Compliance with plantation rules is necessary to prevent exploitation, protect workers’ rights, and maintain a healthy work environment.
One essential compliance requirement for plantation rules is the provision of adequate housing for workers. Plantation owners must provide suitable living quarters that meet basic standards of cleanliness, comfort, and safety. These accommodations should have proper ventilation, lighting, sanitation facilities, and protection against the elements. Employers must also ensure that the housing conditions are regularly monitored and maintained to ensure the well-being of workers.
Furthermore, plantation rules mandate the provision of fair wages and working hours for employees. Employers must establish and adhere to fair wage structures that meet or exceed legal minimum wage requirements. Additionally, working hours should be reasonable and conform to industry standards to prevent overwork and employee exhaustion. It is crucial for employers to keep accurate records of employee wages and working hours to demonstrate compliance with these regulations.
- Provision of suitable housing for workers
- Ensuring fair wages and working hours
- Maintaining adequate safety measures
- Providing access to healthcare facilities
- Implementing effective grievance redressal mechanisms