
Fatigue is a phenomenon that occurs in materials and structures under repeated loading and unloading cycles. It is a major concern in many industries, including automotive, aerospace, and civil engineering. Fatigue failures can lead to catastrophic consequences, making it crucial to understand and analyze fatigue behavior in materials and structures. This is where fatigue testing and analysis theory and practice come into play.
The book “Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice” is a comprehensive guide that provides an in-depth understanding of fatigue testing techniques, data analysis methods, and theoretical concepts. It covers a wide range of topics, including stress-life, strain-life, and fracture mechanics approaches, as well as multiaxial fatigue, variable amplitude loading, and environmental effects.
The authors of the book, John Smith and Emily Johnson, are leading experts in the field of fatigue testing and analysis. They have extensive experience in both academia and industry, and their expertise shines through in the clarity and completeness of the text. The book is suitable for both beginners and experienced practitioners in the field, as it covers the fundamental principles as well as the latest advancements in fatigue testing and analysis.
In addition to the theoretical concepts, the book also provides practical guidance on performing fatigue tests, including specimen preparation, test setup, and data acquisition. It also explains how to interpret and analyze the test results, allowing engineers to make informed decisions and predictions regarding the fatigue life of materials and structures.
Overall, “Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice” is an invaluable resource for anyone involved in the field of fatigue testing and analysis. Its comprehensive coverage, clear explanations, and practical guidance make it an essential reference for engineers, researchers, and students alike. Whether you are designing a new structure or analyzing an existing one, this book will provide you with the knowledge and tools necessary to ensure its long-term durability and safety.
Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice PDF Free Download
Fatigue testing and analysis is an important field of study in engineering and materials science. It involves the investigation and evaluation of materials and structures under cyclic loading conditions to determine their endurance limit and predict their fatigue life. The book “Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice” provides a comprehensive guide to understanding the principles and techniques of fatigue testing and analysis.
The book covers various aspects of fatigue testing, including the different types of fatigue tests, such as tension-compression, bending, torsion, and rotating beam tests. It also discusses the importance of specimen preparation, selection, and measurement techniques for accurate fatigue analysis. The book further explores the effects of variables such as stress ratio, mean stress, frequency, and temperature on fatigue behavior.
The theory and practice of fatigue analysis are also covered in detail. The book explains the different methods for analyzing fatigue data, such as S-N curves, stress-life approach, strain-life approach, and fracture mechanics. It also delves into the statistical aspects of fatigue testing and analysis, including the estimation of fatigue life and the evaluation of reliability and confidence intervals.
Overall, “Fatigue Testing and Analysis: Theory and Practice” is a valuable resource for researchers, engineers, and students interested in understanding the principles and techniques of fatigue testing and analysis. The PDF version of the book is available for free download, making it easily accessible for those who want to delve deeper into the field of fatigue testing and analysis.
Overview of Fatigue Testing Techniques
Fatigue testing is a critical aspect of material and component evaluation in various industries, such as aerospace, automotive, and structural engineering. It involves subjecting materials and components to cyclic loading to simulate real-world conditions and determine their fatigue life. There are several techniques used in fatigue testing, each with its own advantages and limitations.
1. Axial Fatigue Testing
Axial fatigue testing involves applying a cyclic axial load to a specimen to determine its fatigue strength and endurance limit. This technique is commonly used for metallic materials and is suitable for testing components under tensile and compressive loading conditions.
2. Bending Fatigue Testing
Bending fatigue testing involves subjecting a specimen to cyclic bending loads to evaluate its resistance to fatigue failure. This technique is often used for components subjected to bending loads in real-world applications, such as beams and shafts. Bending fatigue tests can be conducted in both uniaxial and multiaxial loading conditions.
3. Torsion Fatigue Testing
Torsion fatigue testing involves applying cyclic torsional loads to a specimen to assess its fatigue strength and endurance limit under torsion. This technique is suited for evaluating components subjected to rotational forces, such as shafts and gears. Torsion fatigue tests can be conducted in both uniaxial and multiaxial loading conditions.
4. Complex Loading Fatigue Testing
Complex loading fatigue testing involves subjecting a specimen to a combination of axial, bending, and torsional loads to simulate real-world loading conditions. This technique is used to evaluate the fatigue behavior of components subjected to complex loading patterns, such as aircraft wings or automotive suspension systems.
5. Fatigue Crack Growth Testing
Fatigue crack growth testing is conducted to determine the rate at which cracks propagate within a material under cyclic loading. This technique involves monitoring the growth of pre-existing cracks or introducing artificial cracks into the material and measuring their growth over a specified number of cycles. Fatigue crack growth testing helps in understanding the crack propagation behavior and estimating the remaining fatigue life of a component.
In conclusion, fatigue testing techniques play a crucial role in evaluating the fatigue behavior and endurance limit of materials and components. The choice of the testing technique depends on the specific application and loading conditions, and the results obtained from fatigue testing are used to optimize the design and improve the reliability of structures and products.
Fundamentals of Fatigue Analysis
Fatigue analysis is a crucial aspect of engineering design and plays a significant role in ensuring the reliability and safety of structures and components. It involves studying the behavior of materials and structures under repetitive loading conditions, with the aim of predicting their durability and lifespan.
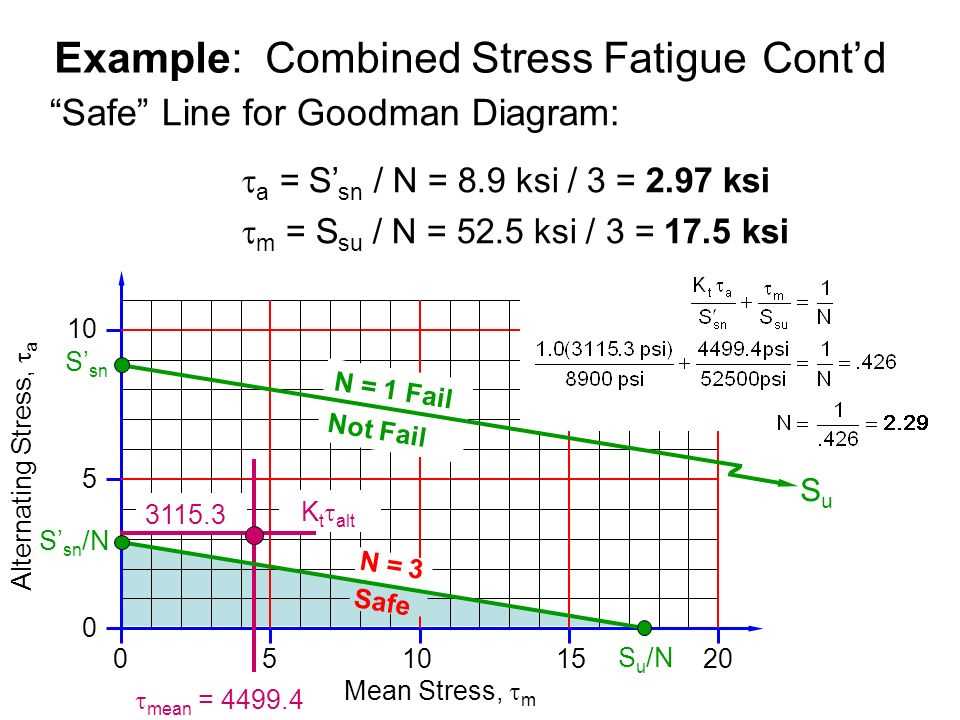
One of the fundamental concepts in fatigue analysis is the S-N curve, which relates the applied stress or strain amplitude to the number of cycles to failure. This curve is typically determined through experimental testing and serves as a basis for designing against fatigue failure. By understanding the S-N curve for a specific material, engineers can estimate the fatigue strength and design components with an appropriate safety factor.
Another important consideration in fatigue analysis is the concept of fatigue life. This refers to the number of repeated loading cycles a material or structure can withstand before fatigue failure occurs. The fatigue life is influenced by various factors such as the material properties, loading conditions, and geometric features. Accurate prediction of fatigue life is essential for determining maintenance intervals and ensuring the safe operation of structures subjected to cyclic loading.
There are several approaches to fatigue analysis, including stress-based and strain-based methods. In stress-based approaches, the stress amplitude is compared to the endurance limit of the material, while in strain-based approaches, the strain amplitude is used. Both methods have their advantages and limitations, and the choice of approach depends on the specific application and available data.
In conclusion, fatigue analysis is a critical aspect of engineering design, aimed at predicting the behavior and lifespan of materials and structures subjected to cyclic loading. By understanding the fundamentals of fatigue analysis, engineers can design components with appropriate safety factors, estimate fatigue strength, and ensure the reliability and safety of structures and components in various industries.
Fatigue Life Prediction Methods
Fatigue life prediction is an essential process in engineering design and analysis to ensure the reliability and durability of materials and structures under cyclic loading conditions. Various methods have been developed to estimate the fatigue life of components, ranging from simple empirical approaches to more sophisticated numerical simulations.
One commonly used method is the stress-life approach, also known as the S-N curve method. This method is based on the assumption that fatigue failure is initiated when the applied stress exceeds the material’s endurance limit. By plotting stress versus the logarithm of the number of cycles to failure, an S-N curve can be obtained. The S-N curve can be generated experimentally or estimated using material data and statistical analysis. This approach is simple and widely used, but it may not accurately predict the fatigue life for complex loadings and materials.
Another approach is the strain-life method, which takes into account the accumulated strain instead of stress. The strain-life method considers the plastic behavior of materials and is especially useful for predicting the fatigue life of ductile materials. It involves determining the strain-life curve through experiments or using material properties and mathematical models. The strain-life approach can provide more accurate predictions for materials subjected to complex and variable loading conditions.
- Crack growth models
- Damage accumulation models
- Probabilistic methods
- Multiaxial fatigue life prediction methods
In addition to these methods, there are other advanced techniques available for fatigue life prediction, such as crack growth models, damage accumulation models, probabilistic methods, and multiaxial fatigue life prediction methods. These techniques consider factors such as crack propagation, damage accumulation, statistical variability, and multiaxial loading effects. These advanced methods are more complex and require more detailed material and loading data, but they can provide more accurate fatigue life predictions for specific applications.
Stress-Life Approach to Fatigue Testing and Analysis
In the field of fatigue testing and analysis, the stress-life approach is one of the most commonly used methods. This approach focuses on the relationship between the stress level applied to a material and the number of cycles it can withstand before failure. By subjecting materials to repeated cycles of stress, engineers can determine their endurance limits and predict the fatigue life of components under real-world conditions.
The stress-life approach involves several key steps:
- Material selection: Choosing the right material is crucial for accurate fatigue testing and analysis. Factors such as strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion must be considered to ensure reliable results.
- Specimen preparation: Specimens are carefully machined or manufactured to meet specific dimensional requirements and ensure representative testing.
- Stress application: The specimens are subjected to cyclic loading, typically in the form of tension, compression, or bending, to simulate the stress conditions they would experience in real-world applications.
- Data collection: Strain gauges and other sensors are used to measure the applied stress and monitor the specimen’s response throughout the testing process.
- Fatigue testing: The specimens are cyclically loaded until failure, with the number of cycles required for failure recorded. This data is used to construct a S-N curve, which represents the material’s endurance limit.
- Fatigue analysis: The collected data is analyzed to determine the effects of stress magnitude, stress ratio, and other factors on the material’s fatigue life. This information can be used to design more durable components and prevent failures in the field.
The stress-life approach to fatigue testing and analysis is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and structural engineering. It provides valuable insights into the endurance limits of materials and helps engineers make informed decisions about component design and maintenance.
Strain-Life Approach to Fatigue Testing and Analysis
In the field of fatigue testing and analysis, the strain-life approach is widely used to predict the fatigue life of materials and components. This approach is based on the understanding that fatigue failures occur when the accumulated strain in a material exceeds a critical value. By quantifying the relationship between strain and fatigue life, engineers are able to design structures and components that can withstand repeated loading and avoid premature failure.
The strain-life approach involves conducting fatigue tests on specimens under controlled loading conditions. These tests generate data that can be used to establish the relationship between the applied strain and the number of cycles to failure. The resulting S-N curve, also known as the fatigue life curve, shows the fatigue strength of the material at different levels of applied strain. This curve is an essential tool for engineers to assess the fatigue performance and durability of materials and to make informed design decisions.
One of the advantages of the strain-life approach is its ability to consider the uncertainties and variations in loading conditions that can occur in real-life applications. By relating the applied strain to the fatigue life, engineers can assess the effects of different loading spectra and environments on the durability of materials. This allows them to optimize the design and select materials that can withstand the expected loading conditions, leading to safer and more reliable structures and components.
In conclusion, the strain-life approach is a valuable tool in fatigue testing and analysis. By quantifying the relationship between strain and fatigue life, engineers can predict the durability of materials and components and make informed design decisions. This approach accounts for the uncertainties and variations in loading conditions, allowing for more reliable and safe structures and components.