Understanding the process of fetal development is crucial for expecting parents and healthcare professionals alike. This webquest provides detailed answers to key questions about the various stages of fetal development, from conception to birth.
During the first trimester, the fertilized egg undergoes rapid cell division and develops into an embryo. By week 10, the embryo is fully formed and is referred to as a fetus. At this stage, major organs and systems, including the heart, brain, and limbs, have begun to develop.
Throughout the second trimester, the fetus experiences significant growth. Its size increases, and its features become more defined. The mother may begin to feel fetal movements, known as quickening, during this time. Additionally, the fetus’s senses, such as hearing and taste, start to develop.
In the third trimester, the fetus’s growth continues, and it gains significant weight. The lungs and other vital organs fully mature, preparing the fetus for life outside of the womb. The fetus also acquires antibodies from the mother, which help protect against infections after birth.
By exploring this webquest and gaining insight into the fascinating process of fetal development, individuals can better understand the miracles of life and the important milestones that occur before a baby is born.
Fetal Development Webquest Answers
In the Fetal Development Webquest, we explored the different stages of human fetal development and the changes that occur during each stage. We learned that fetal development begins at fertilization with the formation of a zygote, which then undergoes rapid cell division to form an embryo. This embryonic period is crucial for the development of all major organs and body systems. The embryo then develops into a fetus, which is characterized by continued growth and maturation of organs and tissues.
During the webquest, we also discovered the different structures and organs that develop in the fetus. For example, we learned that during the first trimester, the fetus develops a primitive heart, brain, and spinal cord. By the end of the first trimester, the fetus has developed all major organs and body systems, although they are not fully functional yet. In the second trimester, the fetus continues to grow, and its movements become more coordinated. By the third trimester, the fetus has reached a size and maturity where it can survive outside of the womb with medical support.
Throughout the webquest, we also discussed the importance of prenatal care in supporting healthy fetal development. We learned that proper nutrition, regular prenatal check-ups, and avoiding harmful substances such as tobacco and alcohol are all crucial for the well-being of the developing fetus. We also explored the various factors that can impact fetal development, such as genetic disorders, maternal health conditions, and exposure to environmental toxins. Overall, the Fetal Development Webquest provided us with a comprehensive understanding of the different stages and factors influencing human fetal development.
Stages of Fetal Development
The process of fetal development can be divided into three main stages: the germinal stage, the embryonic stage, and the fetal stage. Each stage is characterized by significant changes and milestones in the development of the unborn baby.
Germinal Stage
The germinal stage is the earliest stage of pregnancy, starting from fertilization and lasting for about two weeks. During this stage, the fertilized egg, called a zygote, begins to divide and multiply rapidly. It travels down the fallopian tube and attaches itself to the uterine wall in a process known as implantation.
Over the course of the germinal stage, the zygote develops into a blastocyst, which consists of two main parts: the inner cell mass and the outer cell layer. The inner cell mass will eventually develop into the embryo, while the outer cell layer will form the placenta.
Embryonic Stage
The embryonic stage begins at around the third week of pregnancy and lasts until the end of the eighth week. This is a crucial stage of fetal development, as the major organs and body systems begin to form. The embryo grows rapidly in size and starts resembling a human being.
During the embryonic stage, the neural tube, which will later become the brain and spinal cord, begins to develop. The heart starts beating and blood circulation begins. The limb buds appear, and the basic structure of the face, eyes, and ears starts to form. By the end of this stage, the embryo has all its major organs, although they are not fully developed.
Fetal Stage
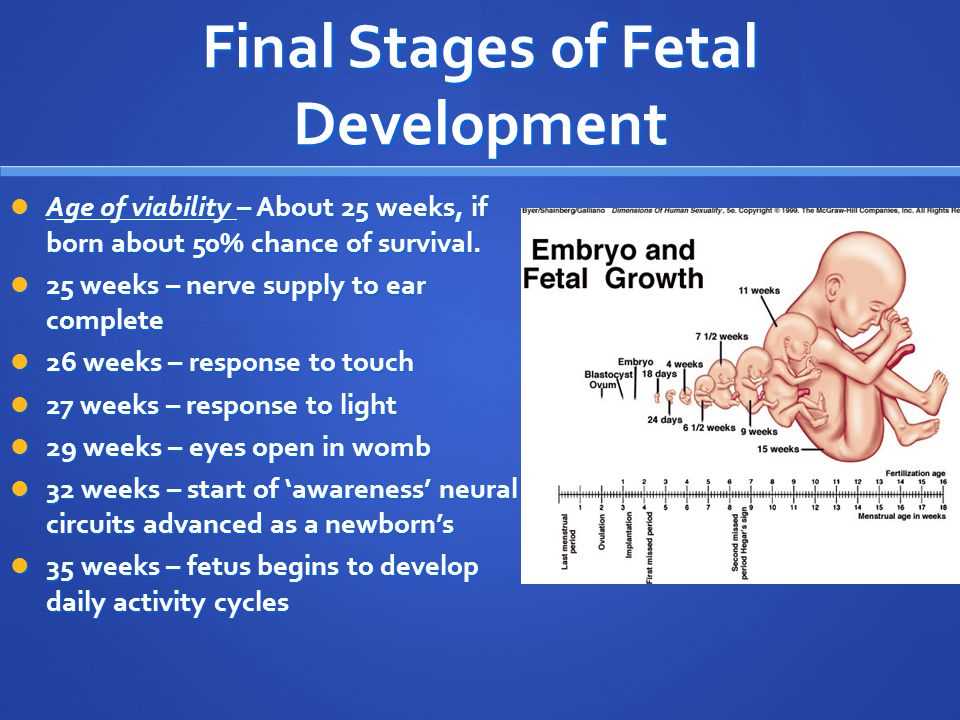
The fetal stage begins at the ninth week of pregnancy and lasts until birth. During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and refine its body structures. It also becomes more active, with noticeable movements such as kicking and stretching.
The organs and body systems continue to mature during the fetal stage. The fetus develops a more distinct appearance, with fully formed facial features, limbs, and fingers. It also develops a layer of fat to help regulate body temperature and prepares for life outside the womb.
By the end of the fetal stage, the baby is ready for birth and is considered fully developed. However, the final weeks of pregnancy are crucial for continued growth and development to ensure a healthy and fully matured baby.
Fertilization of the Egg
The process of fertilization is a crucial step in the development of a new life. It occurs when a sperm cell successfully meets and penetrates an egg. This remarkable event takes place in the fallopian tube, where the egg waits for fertilization after being released from the ovary during ovulation.
Once a sperm enters the woman’s body through sexual intercourse, it travels through the cervix and into the uterus. From there, it continues its journey towards the fallopian tube. Only a small fraction of the millions of sperm that are ejaculated manage to survive this long and arduous journey.
When a sperm successfully reaches the fallopian tube, it must navigate through the protective layers surrounding the egg. The sperm uses its tail to propel itself forward and overcomes various barriers to reach the egg’s surface. Once a sperm makes contact with the egg, it releases enzymes that help it penetrate the protective layer surrounding the egg.
Finally, when a single sperm successfully penetrates the egg, fertilization occurs. This momentous event triggers the activation of the egg and prevents any other sperm from entering. The genetic material from the sperm combines with the genetic material from the egg, resulting in the formation of a zygote, which is the earliest stage of human development.
In conclusion, fertilization is a complex and remarkable process that involves the successful meeting and penetration of an egg by a sperm. It is a crucial step in the development of a new life and marks the beginning of human embryonic development.
Implantation and Embryonic Development
Implantation is a crucial step in the development of a fetus. Once the fertilized egg, known as a zygote, attaches itself to the lining of the uterus, it begins to develop into an embryo. This process, which occurs approximately 6-9 days after fertilization, is essential for the continued growth and survival of the developing fetus.
During implantation, the zygote burrows into the lining of the uterus, also known as the endometrium. This process is facilitated by the presence of special enzymes released by the developing embryo, which help to break down the uterine lining and create a suitable environment for implantation. Once attached, the zygote is able to receive nutrients and oxygen from the mother’s bloodstream, allowing it to grow and develop.
Following implantation, the embryonic stage begins. This stage is characterized by rapid cell division and differentiation, as the cells of the embryo start to specialize and form the various tissues and organs of the body. The embryo develops a primitive circulatory system, and the beginnings of the nervous system and other vital organs start to form.
By the end of the embryonic stage, which lasts from about week 3 to week 8 of pregnancy, the basic structures of the body are in place. The embryo is now referred to as a fetus, and it enters the fetal stage of development. During this stage, the fetus continues to grow and develop, with organs becoming more complex and functional.
In conclusion, implantation and embryonic development are critical stages in the early development of a fetus. Implantation allows for the attachment of the fertilized egg to the uterine lining, enabling the embryo to receive necessary nutrients and oxygen. The embryonic stage is a period of rapid cellular division and differentiation, laying the foundation for the development of the body’s organs and systems. Understanding the process of implantation and embryonic development is essential for comprehending the complex journey from conception to birth.
Formation of Major Organs
The development of major organs is a crucial process during fetal development. It begins during the embryonic stage, which is characterized by rapid cell division and differentiation. During this stage, the three primary germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm) are formed.
From these germ layers, the major organs of the body start to develop. For example, the ectoderm gives rise to the nervous system, skin, and hair. The mesoderm contributes to the development of muscles, bones, and the circulatory system. The endoderm forms the digestive system, respiratory system, and other internal organs.
As development progresses, these major organs undergo further specialization and morphological changes. For instance, the heart begins as a simple tube and gradually develops into a complex organ with four chambers. The brain also undergoes extensive development, with different regions and structures forming over time.
This process of organ formation is tightly regulated by genetic factors, signaling molecules, and cellular interactions. Any disruptions or abnormalities during this period can result in congenital abnormalities or malformations. Therefore, understanding the formation of major organs is vital for identifying potential issues and developing interventions to ensure healthy fetal development.
Development of the Nervous System
The development of the nervous system is a complex and fascinating process that occurs during fetal development. It begins early in embryogenesis and continues throughout gestation. The nervous system is derived from a specialized group of cells called neuroectodermal cells, which undergo a series of intricate processes to form the intricate network of neurons, synapses, and glial cells that make up the nervous system.
During fetal development, the nervous system undergoes several critical stages, including neural induction, neural proliferation, neural migration, axon guidance, and synaptogenesis. Neural induction is the process by which the neuroectodermal cells are specified to become neural tissue. This is followed by neural proliferation, during which the neuroectodermal cells divide and multiply to increase their numbers. Neural migration then occurs, where the newly formed neurons migrate to their specific locations in the developing brain and spinal cord.
Once the neurons have reached their appropriate locations, axon guidance takes place. This process involves the growth of axons, the long projections of neurons, to reach their target cells. The axons are guided by various molecular cues and signals present in the developing nervous system. This intricate process ensures that the axons reach their appropriate targets and establish proper connections. Finally, synaptogenesis occurs, whereby the synapses, the connections between neurons, are formed. Synaptic connections are essential for the transmission of signals within the nervous system and are crucial for various brain functions.
In summary, the development of the nervous system is a complex and highly regulated process that occurs during fetal development. It involves a series of intricate steps, including neural induction, neural proliferation, neural migration, axon guidance, and synaptogenesis. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these processes is critical for unraveling the mysteries of brain development and function.
Development of the Musculoskeletal System
The musculoskeletal system plays a crucial role in the overall development and functionality of the human body. It is responsible for providing support, stability, and movement to the body, enabling individuals to perform various activities. The development of the musculoskeletal system begins early in embryonic life and continues throughout fetal development.
Formation of the bones: The development of bones, which are the main structural component of the musculoskeletal system, starts during the embryonic period. The mesenchymal cells, which are the building blocks of bone tissue, begin to condense and differentiate into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts secrete a matrix of collagen and minerals, which eventually form the framework for the bone. Over time, this initial framework undergoes remodeling and ossification, forming fully developed bones.
Growth of muscles: Muscles are essential for movement and require proper development during fetal life. They arise from the mesoderm layer of the embryo and begin to form muscle fibers. These fibers elongate and differentiate into specific types of muscle tissue, such as skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles. As the fetus grows, muscles continue to develop and mature, gaining strength and coordination.
Development of joints: Joints are vital for the mobility and flexibility of the musculoskeletal system. They are formed when two or more bones come together. During fetal development, the joint cavities start to form as the mesenchymal cells differentiate into cartilage. Over time, this cartilage transforms into various types of joints, such as hinge joints, ball-and-socket joints, and pivot joints. The development of joints is essential for the proper movement and function of the musculoskeletal system.
In conclusion, the development of the musculoskeletal system involves the formation and growth of bones, muscles, and joints. These processes begin during embryonic life and continue throughout fetal development. Proper development of the musculoskeletal system is crucial for the overall functionality and mobility of the human body.