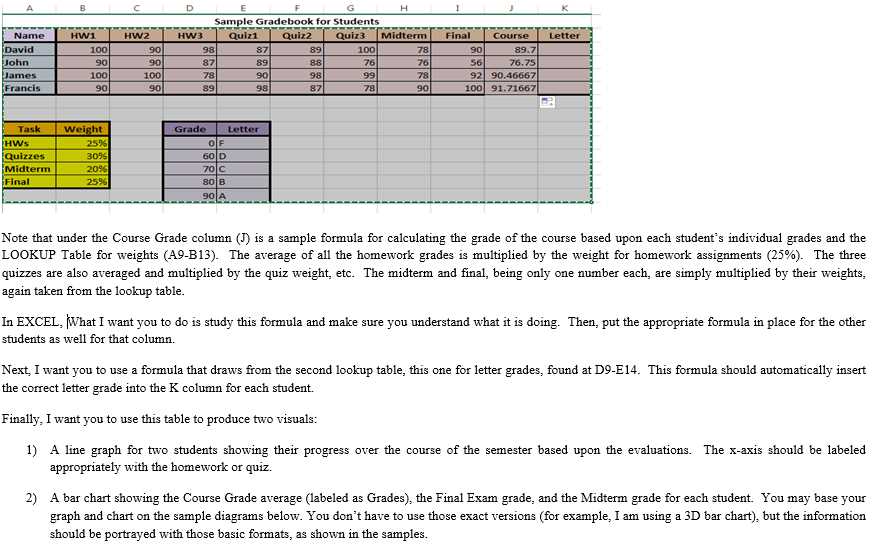
As the end of the semester approaches, it is time for students to start preparing for their final exam in biology. This exam is a culmination of everything they have learned throughout the semester, and it is important to approach it with the right mindset and study strategies.
To excel in the final exam, students need to review the key concepts and topics covered in the course so far. This includes understanding cell biology, genetics, evolution, and ecology, among other things. It is crucial to have a solid understanding of these fundamental principles in order to succeed in the exam.
One effective way to study for the final exam is to create a study schedule and stick to it. This will help students allocate enough time to review each topic thoroughly and avoid last-minute cramming. Additionally, using flashcards, practice quizzes, and past exam papers can also be useful tools to test one’s knowledge and identify areas that need further revision.
Importance of the final exam
The final exam in biology is an essential component of the semester as it evaluates students’ understanding and knowledge of key concepts covered throughout the course. It serves as a comprehensive assessment tool that allows both students and teachers to gauge the level of mastery achieved in the subject. The final exam covers a wide range of topics, including cellular biology, genetics, ecology, and physiology, requiring students to demonstrate their ability to apply critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
The final exam holds great importance as it not only determines students’ grades but also serves as an opportunity for them to showcase their learning outcomes. It provides a platform for students to consolidate and synthesize the information they have learned throughout the semester and apply it in practical scenarios. By testing their knowledge and understanding, the final exam enables students to identify areas of improvement and further enhance their comprehension of complex biological concepts.
Preparing for the final exam requires students to review and revise material covered in class, which promotes active learning and retention. It encourages students to engage in self-directed study, enhancing their ability to organize and assimilate information effectively. Additionally, the final exam promotes discipline and time management skills as students must allocate sufficient time for studying and practice.
In conclusion, the final exam plays a vital role in assessing students’ comprehension of biology and provides an opportunity for them to showcase their learning outcomes. It promotes active learning, self-directed study, and critical thinking skills, helping students to consolidate their understanding and identify areas for improvement. Therefore, the final exam serves as a crucial evaluation method that contributes to the overall growth and development of students in the field of biology.
Topics covered in the final exam for Biology semester 1
In the final exam for Biology semester 1, students will be tested on a wide range of topics that have been covered throughout the course. These topics include:
- Cellular Structure and Function: Students will be expected to demonstrate a deep understanding of the structure and function of cells. This includes knowledge of cell organelles, their functions, and how they work together to carry out essential processes such as metabolism and protein synthesis.
- Genetics and Heredity: This topic covers the principles of inheritance and how traits are passed down from one generation to the next. Students will need to be familiar with concepts such as Punnett squares, Mendelian genetics, and the role of DNA in determining an organism’s characteristics.
- Evolution and Natural Selection: Understanding evolution is crucial in the field of biology. Students will need to have a solid grasp of the principles of natural selection, speciation, and the evidence for evolution. They should also be able to explain the process of adaptation and how it contributes to the survival of species.
- Ecology and Ecosystems: This topic explores the interrelationships between organisms and their environment. Students should be able to describe the different levels of ecological organization, such as populations, communities, and biomes. They should also understand energy flow and nutrient cycling within ecosystems.
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration: These processes are vital for all living organisms. Students will be expected to explain the chemical reactions involved in photosynthesis and cellular respiration, as well as their importance in maintaining the balance of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
These are just a few of the key topics that students can expect to be assessed on in the final exam for Biology semester 1. It is important for students to review and study these topics thoroughly in order to be well-prepared for the exam. Additionally, understanding the connections between these topics and their real-world applications will enhance students’ overall understanding of biology.
Cellular structure and function
The cellular structure and function play a crucial role in the study of biology. The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is composed of various components that work together to perform vital functions necessary for life. One of the key components of a cell is the cell membrane, which acts as a protective barrier and controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. The cell membrane is made up of a double layer of phospholipids and proteins that enable selective permeability.
Within the cell, there are various organelles with specific functions. The nucleus, often referred to as the control center of the cell, contains the genetic material and regulates the cell’s activities. The endoplasmic reticulum is an extensive network of membranes involved in protein and lipid synthesis. The Golgi apparatus processes, packages, and transports proteins and lipids to their designated locations within the cell or for secretion. The mitochondria are responsible for energy production through cellular respiration, while the chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis in plant cells.
The cytoskeleton, made up of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments, provides structure, support, and movement within the cell. It allows for cellular transport, cell division, and maintains cell shape. The cytoplasm, the fluid matrix inside the cell, houses the organelles and facilitates various chemical reactions necessary for cellular functions.
In conclusion, understanding the cellular structure and function is essential in comprehending the intricate processes that occur within living organisms. The cell’s components and organelles work together to maintain homeostasis, carry out metabolic activities, and ensure the survival and reproduction of the organism. Through studying cellular biology, scientists can gain insights into disease mechanisms, develop new treatments, and further advance our understanding of life itself.
Genetics and Inheritance

Genetics is the scientific study of genes, heredity, and the variation of organisms. It plays a crucial role in understanding how traits are passed from one generation to another. Through the study of genetics, scientists have been able to unravel the mysteries behind inheritance and the mechanisms of genetic diseases.
One of the key concepts in genetics is the idea of inheritance. Inheritance refers to the process by which genetic information is passed from parents to offspring. This information is carried by molecules called DNA, which are found in the cells of all living organisms. DNA contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism, and it is these instructions that determine an individual’s traits.
- Genes are segments of DNA that contain the instructions for building proteins, which are the building blocks of life.
- Each individual has two copies of each gene, one inherited from each parent.
- Genes come in different versions called alleles, which can be dominant or recessive.
- Dominant alleles are always expressed in an individual’s phenotype, while recessive alleles are only expressed if the individual has two copies.
Understanding genetics and inheritance is essential not only for understanding how traits are passed down in families but also for studying and treating genetic disorders. By studying the inheritance patterns of genetic diseases, scientists can gain insights into the underlying causes and develop new treatments or preventative measures. Genetics has revolutionized the field of medicine, allowing for personalized treatments and targeted therapies based on an individual’s genetic makeup.
Evolution and Natural Selection

The theory of evolution, proposed by Charles Darwin in the 19th century, is one of the fundamental principles in biology. It explains how species change over time and how new species arise. The process of evolution is driven by natural selection, which is the mechanism through which organisms with advantageous traits are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing those traits onto future generations.
Natural selection occurs when individuals with certain traits have a higher chance of surviving and reproducing compared to individuals without those traits. This leads to a change in the frequency of those traits in the population over time. The traits that are favored by natural selection are typically those that increase an organism’s fitness, or its ability to survive and reproduce in its environment.
For example, in a population of bird species where food is scarce, individuals with longer beaks may have an advantage over individuals with shorter beaks. The longer beak allows them to reach food sources that are deep within flowers or tree bark, giving them a higher chance of survival and reproductive success. As a result, the frequency of the long-beaked trait increases in the population over time.
Natural selection can also result in the formation of new species. This occurs when a population becomes geographically isolated and the different environments or selection pressures in each location favor different traits. Over time, these populations may accumulate enough genetic differences that they can no longer interbreed and produce fertile offspring. This process, known as speciation, leads to the formation of two separate species.
In conclusion, evolution and natural selection are intricately linked and play a crucial role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth. They explain how species change and adapt to their environments over time, ultimately leading to the emergence of new species.
Ecology and ecosystems
Ecology is the study of how organisms interact with each other and with their environment. It encompasses a wide range of topics, including the relationships between different species, the flow of energy and nutrients in ecosystems, and the effects of human activities on the natural world.
At the core of ecology is the concept of ecosystems. An ecosystem is a community of organisms and their physical environment, functioning as a unit. It includes all the living organisms in an area, as well as the non-living elements such as air, water, and soil. Ecosystems can be as small as a puddle or as large as an entire forest.
In an ecosystem, organisms interact with each other and with their environment in various ways. These interactions can be classified into three main categories:
- Competition: Organisms within an ecosystem often compete for limited resources such as food, water, and territory. This competition can lead to changes in population sizes and the distribution of species within the ecosystem.
- Symbiosis: Symbiotic relationships occur when two or more species live together in close association. These relationships can be mutually beneficial (mutualism), beneficial to one species and neutral to the other (commensalism), or beneficial to one species and harmful to the other (parasitism).
- Trophic interactions: Trophic interactions refer to the transfer of energy and nutrients between different levels of a food chain or food web. Producers, such as plants, capture energy from the sun and convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then passed on to consumers at higher trophic levels.
Understanding ecology and ecosystems is essential for addressing environmental issues and conserving biodiversity. By studying how organisms interact and depend on each other, scientists can develop strategies for sustainable resource management and habitat conservation.
Study Tips and Strategies for the Final Exam
In order to prepare effectively for the final exam in biology, it is important to adopt a systematic approach to studying and make use of proven strategies. These tips will help you maximize your learning and retention of important concepts.
Create a Study Schedule
First and foremost, create a study schedule that allows you to allocate specific time slots for each topic or chapter. This will help you stay organized and ensure that you cover all the material before the exam. Make sure to prioritize challenging topics and allocate more time for them.
Review Lecture Notes and Textbooks
Reviewing your lecture notes and textbooks is crucial for building a solid foundation of knowledge. Go through your notes and highlight key points. Summarize the information in your own words to ensure that you understand it fully. Pay close attention to any diagrams or visuals as they often provide valuable insights into complex concepts.
Utilize Flashcards and Diagrams
Flashcards and diagrams are great tools for studying biological terms, definitions, and processes. Create flashcards for important terms and concepts and use them for quick review sessions. Diagrams can help you visualize complex processes, such as cellular respiration or photosynthesis, making it easier to understand and remember them.
Practice with Past Exams
Obtaining and practicing with past exams is an excellent way to familiarize yourself with the exam format and the types of questions that may be asked. Analyze the questions and identify any patterns or recurring themes. This will give you a better idea of what to expect and allow you to focus your studying accordingly.
Form Study Groups
Forming study groups with classmates can be extremely beneficial. Discussing concepts, explaining them to others, and answering questions can deepen your understanding and solidify your knowledge. Additionally, studying with others can help motivate and inspire you to stay focused and committed to your studying goals.