Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationship between the sides and angles of triangles. It is an important concept in various fields such as physics, engineering, and navigation. To solve trigonometric problems, it is crucial to understand the trigonometric ratios, which are the values that describe the relationship between the angles and sides of a triangle.
The trigonometric ratios include sine, cosine, and tangent. Each of these ratios is represented by a specific formula and can be used to find the values of the sides and angles in a right triangle. For example, the sine ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse. By knowing this ratio, you can calculate the value of the sine of an angle in a right triangle.
Understanding these trigonometric ratios is essential for solving trigonometric equations and problems. However, finding their values can sometimes be challenging. That is why having an answer key that provides the correct values of each trigonometric ratio can be extremely helpful. It allows students and learners to check their calculations and verify if they are on the right track.
With the answer key for the value of each trigonometric ratio, students can confidently practice solving trigonometric problems and gain a better understanding of the subject. It provides them with a reliable reference to ensure they are using the correct values and formulas. This answer key serves as a valuable tool to support learning and success in trigonometry.
Overview of Trigonometric Ratios
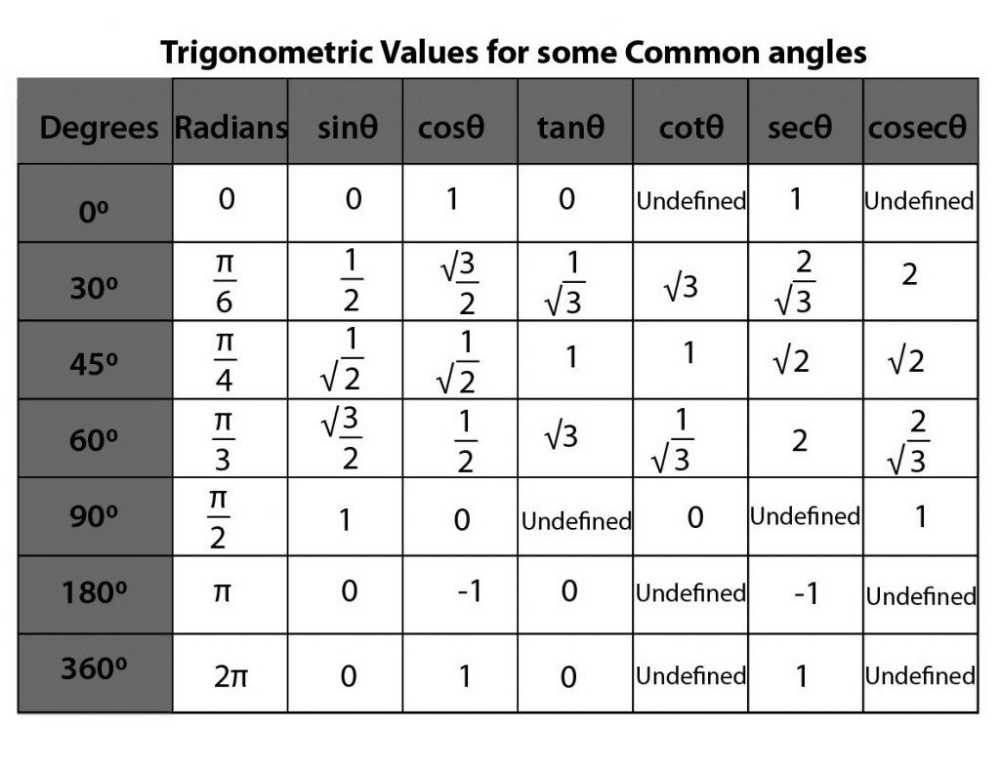
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. Trigonometric ratios are mathematical expressions that relate the angles of a right triangle to the lengths of its sides. There are six trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent.
The sine function, abbreviated as sin, is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the hypotenuse of the right triangle. It is represented as sinθ = opposite/hypotenuse. The cosine function, abbreviated as cos, is defined as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the hypotenuse. It is represented as cosθ = adjacent/hypotenuse. The tangent function, abbreviated as tan, is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the side adjacent to the angle. It is represented as tanθ = opposite/adjacent.
The cosecant function, abbreviated as csc, is the reciprocal of the sine function. It is defined as cscθ = 1/sinθ. The secant function, abbreviated as sec, is the reciprocal of the cosine function. It is defined as secθ = 1/cosθ. The cotangent function, abbreviated as cot, is the reciprocal of the tangent function. It is defined as cotθ = 1/tanθ.
To find the value of each trigonometric ratio, you need to know the length of the sides of a right triangle and the measurement of the angles. Trigonometric ratios are used in various fields such as physics, engineering, and navigation to solve problems involving angles and distances. Understanding and applying trigonometric ratios is essential in many real-life situations and in advanced mathematical concepts.
Understanding the concept of trigonometric ratios
The concept of trigonometric ratios is a fundamental concept in mathematics and plays a crucial role in various disciplines such as physics, engineering, and navigation. Trigonometric ratios are used to relate the angles of a right triangle to the lengths of its sides.
There are six trigonometric ratios: sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent. These ratios are defined based on the sides of a right triangle. The sine ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the hypotenuse of the triangle. The cosine ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the hypotenuse. The tangent ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the adjacent side. The other three trigonometric ratios are the reciprocals of these three ratios.
To find the value of each trigonometric ratio, a triangle with known angles is necessary. The ratios can be determined by using the lengths of the sides of the triangle. The values of these ratios can be calculated using a calculator or by referring to trigonometric tables. Understanding trigonometric ratios is essential in solving various mathematical problems involving angles and distances.
The six trigonometric ratios are:
- Sine: opposite/hypotenuse
- Cosine: adjacent/hypotenuse
- Tangent: opposite/adjacent
- Cosecant: hypotenuse/opposite
- Secant: hypotenuse/adjacent
- Cotangent: adjacent/opposite
By understanding and being able to use these trigonometric ratios, one can solve problems involving angles and distances, such as finding the height of a building using the angle of elevation or finding the length of a shadow using the angle of depression. Trigonometric ratios are also used in navigation and satellite positioning systems to determine the location of an object based on the angles measured from different satellite signals.
Overall, understanding the concept of trigonometric ratios is essential in various fields of study and can be applied to solve real-world problems. It provides a mathematical foundation for understanding the relationship between angles and sides of a right triangle, allowing for precise calculations and measurements.
The Importance of Finding the Value of Each Trigonometric Ratio
Trigonometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the relationships between the angles and sides of triangles. Trigonometric ratios, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, play a crucial role in solving problems related to angles and distances. Finding the value of each trigonometric ratio is essential in various fields such as engineering, physics, navigation, and astronomy.
1. Engineering: Trigonometry is extensively used in engineering to calculate distances, heights, and angles. Architects and structural engineers rely on trigonometric ratios to design buildings, bridges, and other structures. By determining the value of trigonometric ratios, engineers can accurately analyze forces, measure distances, and determine the stability of structures.
2. Physics: Trigonometry is fundamental in physics, especially in studying the motion of objects. By finding the value of trigonometric ratios, physicists can analyze the path, velocity, and acceleration of moving objects. Trigonometry is also used in optics to calculate the angle of refraction and reflection, enabling the design and optimization of lenses, mirrors, and other optical devices.
3. Navigation: Trigonometry plays a key role in navigation, both on land and at sea. By using trigonometric ratios, navigators can determine their position, track their course, and calculate distances between locations. Trigonometry is crucial for celestial navigation, which involves using the position of celestial bodies, such as the sun, moon, and stars, to determine latitude and longitude.
4. Astronomy: Trigonometry is essential in astronomy for measuring distances between celestial objects and calculating their sizes. By measuring the angles and distances, astronomers can determine the positions and movements of celestial bodies. Trigonometric ratios are also used in determining the inclination and eccentricity of orbits, as well as the brightness and temperature of stars.
In conclusion, finding the value of each trigonometric ratio is of utmost importance in various fields, such as engineering, physics, navigation, and astronomy. Trigonometry allows us to make accurate calculations and solve complex problems related to angles, distances, and motion. Without an understanding of trigonometric ratios, many advancements in science, engineering, and technology would not be possible.
Sin, Cos, and Tan Ratios
The sin, cos, and tan ratios are fundamental trigonometric functions used to find the value of an angle in a right triangle. These ratios are defined based on the sides of the triangle and vary depending on the angle.
To understand these ratios, let’s consider a right triangle with an angle θ. The side opposite θ is called the opposite side, the side adjacent to θ is called the adjacent side, and the hypotenuse is the longest side. These terms are important when determining the trigonometric ratios.
Sine Ratio (sin θ)
The sine ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is denoted as sin θ. Mathematically, sin θ = opposite/hypotenuse.
Cosine Ratio (cos θ)

The cosine ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. It is denoted as cos θ. Mathematically, cos θ = adjacent/hypotenuse.
Tangent Ratio (tan θ)
The tangent ratio is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. It is denoted as tan θ. Mathematically, tan θ = opposite/adjacent.
These three ratios are useful in solving various trigonometric problems, such as finding missing side lengths or angles in right triangles. By knowing the lengths of two sides, you can use the ratios to calculate the value of the unknown angle.
Explaining the sine ratio
The sine ratio is a trigonometric ratio that relates the length of the opposite side of a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse. It is one of the fundamental ratios used in trigonometry and is represented by the equation sin(theta) = opposite/hypotenuse, where theta is the angle of interest.
The sine ratio can be used to find the value of an unknown side length or angle in a right triangle, given the lengths of the other sides. It is particularly useful in solving problems involving height or distance, such as finding the height of a tree or the distance between two points.
To find the value of the sine ratio, you first need to identify the angle of interest and label the sides of the triangle accordingly. The opposite side is the side that is opposite to the angle of interest, while the hypotenuse is the longest side of the triangle. Once you have identified the sides, you can use the equation sin(theta) = opposite/hypotenuse to calculate the sine ratio.
For example, if you have a right triangle with an angle of 30 degrees and a hypotenuse of 10 units, you can use the sine ratio to find the length of the opposite side. By rearranging the equation sin(theta) = opposite/hypotenuse, you get opposite = sin(theta) * hypotenuse. Substituting the values, you get opposite = sin(30) * 10, which equals 5 units.
By understanding and applying the sine ratio, you can solve various trigonometric problems involving right triangles and accurately calculate unknown side lengths or angles. It is an essential concept in trigonometry and forms the foundation for more advanced trigonometric functions and identities.
Calculation of the cosine ratio
The cosine ratio is one of the trigonometric ratios used to calculate the relationship between the angles and sides of a right triangle. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of the hypotenuse. The cosine ratio is denoted as cos(theta), where theta is the angle in consideration.
To calculate the value of the cosine ratio, we first need to know the length of the adjacent side and the length of the hypotenuse. These values can be obtained either through measurement or given in a problem statement. Once we have these values, we can use the cosine function or the cosine table to find the cosine value.
The cosine function is defined as:
cos(theta) = adjacent/hypotenuse
For example, if the length of the adjacent side is 5 and the length of the hypotenuse is 13, we can calculate the cosine ratio as follows:
- cos(theta) = 5/13
- cos(theta) ≈ 0.385
If we have a cosine table, we can find the cosine value by looking up the angle in the table. The table provides the cosine value for different angles, allowing us to easily find the corresponding value for our given angle.
It is important to note that the cosine ratio can vary depending on the angle. For acute angles (less than 90 degrees), the cosine ratio will always be positive. However, for obtuse angles (greater than 90 degrees), the cosine ratio will be negative. This is because the adjacent side may be negative, depending on the orientation of the triangle.
Understanding the tangent ratio
The tangent ratio is one of the fundamental trigonometric ratios used in solving for unknown angles or side lengths in right triangles. It is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite an angle to the length of the side adjacent to the angle. The tangent ratio is represented as tanθ, where θ is the angle of interest.
To understand the tangent ratio, let’s consider an example. Suppose we have a right triangle ABC, where angle A is 45 degrees and side AC is the hypotenuse. The side opposite to angle A is BC, and the side adjacent to angle A is AB.
Using the tangent ratio, we can calculate the value of tanθ by dividing the length of the side opposite the angle by the length of the side adjacent to the angle. In this case, tan45° = BC/AB. Since angle A is 45 degrees and BC and AB are both equal to the square root of 2 (as the triangle is isosceles), we can simplify the expression to tan45° = √2/√2 = 1.
The value of the tangent ratio can also be expressed as a decimal or a fraction. For example, if the side opposite angle A is 4 and the side adjacent to angle A is 3, then tanθ = 4/3 ≈ 1.333. This means that the angle A in the right triangle has a tangent of approximately 1.333.
The tangent ratio is essential in various fields such as engineering, physics, and navigation. It helps in determining distances and angles in real-world applications, such as surveying land, calculating the height of buildings, or plotting the course of airplanes or ships.
In conclusion, the tangent ratio is a crucial tool in trigonometry that allows us to find the value of an unknown angle or side length in a right triangle. It is calculated as the ratio of the length of the side opposite the angle to the length of the side adjacent to the angle. Understanding and applying the tangent ratio is essential in many practical applications and mathematical problems.