In statistics, variance is a measure of how spread out the data points in a dataset are. It is used to understand the variability and dispersion of the data. Calculating the variance is an important step in analyzing data and making informed decisions.
To find the variance, you need to follow a specific formula. First, calculate the mean (average) of the data set. Then, for each data point, subtract the mean and square the result. Finally, calculate the average of these squared differences.
Once you have obtained the average of the squared differences, you have found the variance. It is important to remember that the variance is always a positive value, as it represents the squared differences from the mean. To round your answer to one decimal place, simply round the variance to the nearest tenth.
Understanding and calculating the variance is essential in many fields, such as finance, biology, and social sciences. It provides valuable insights into the data and allows for more accurate analysis and predictions. So, next time you come across a dataset, remember to find the variance to get a better understanding of its dispersion and variability.
What is variance and why is it important?
Variance is a statistical term that measures the spread or dispersion of a set of data points around their mean. It provides information about the variability and diversity within a dataset. Variance is a crucial concept in statistical analysis and has various applications in different fields.
One of the key reasons why variance is important is that it helps in understanding the distribution and pattern of data. By calculating the variance, we can determine how much the individual data points deviate from the average value. This information is essential for researchers, analysts, and decision-makers to make informed decisions based on the data.
Moreover, variance plays a significant role in hypothesis testing and assessing the reliability of statistical results. It allows us to determine the level of confidence in the data and provides a measure of the accuracy of our calculations. High variance indicates a greater level of uncertainty, while low variance suggests a more precise and consistent dataset.
Furthermore, variance is used in financial modeling and risk analysis. In the field of finance, variance is used to assess the volatility of returns on investments. It helps investors and portfolio managers to evaluate the level of risk associated with different assets and make informed investment decisions.
In summary, variance is an important statistical metric that provides valuable insights into the data’s distribution, variability, and reliability. It is widely used in various fields such as research, decision-making, finance, and risk analysis. Understanding and interpreting variance can help in making informed decisions and evaluating the accuracy of statistical results.
Definition of variance
Variance is a statistical measure that quantifies the spread or dispersion of a set of data points. It measures how far each number in the set is from the mean and thus provides an indication of the variability of the data. In essence, variance tells us how spread out the data is around the average. It is an important concept in statistics and is widely used in various fields, including finance, economics, and social sciences.
To calculate the variance, we first need to find the mean of the data set. Then, for each data point, we subtract the mean and square the result. These squared differences are then averaged to obtain the variance. The variance is typically denoted by the symbol σ^2 for a population or s^2 for a sample.
The variance is an important measure because it provides insights into the data distribution and can be used to make comparisons between different sets of data. A small variance indicates that the data points are closer to the mean, while a large variance suggests that the data points are more spread out. Understanding the variance helps in making predictions, identifying patterns, and drawing conclusions from the data.
It is also worth noting that the square root of the variance gives us the standard deviation, which is another commonly used statistical measure of dispersion. Both the variance and standard deviation are important in analyzing data and interpreting statistical results.
Importance of variance in statistics
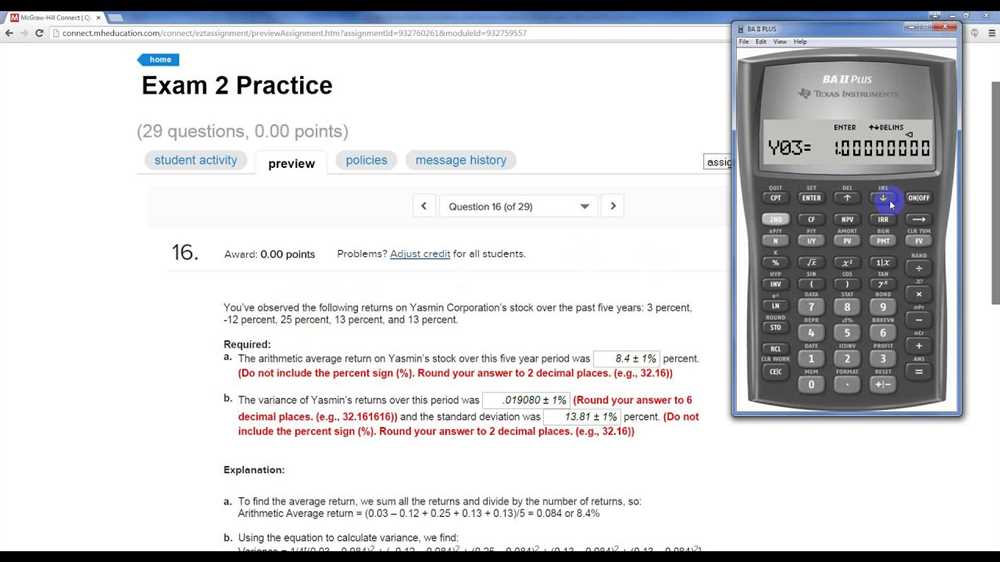
Variance is a crucial concept in statistics that measures the dispersion or variability of a set of data. It provides valuable information about how spread out the individual values in a dataset are from the mean or average value. Understanding variance is essential for making meaningful interpretations and drawing accurate conclusions.
One of the main reasons why variance is important is that it helps in assessing the reliability and consistency of data. By calculating the variance, we can determine how closely the data points cluster around the mean. A small variance indicates that the data points are relatively close together, suggesting that the dataset is consistent and reliable. In contrast, a large variance indicates that the data points are more spread out, suggesting greater variability and potential inconsistencies.
Another importance of variance in statistics is its role in hypothesis testing and decision making. When conducting statistical tests to determine if there are significant differences between groups or variables, variance plays a crucial role. It allows us to compare the variability within groups and assess the significance of differences. For example, if the variance between two groups is significantly different, it suggests that there is a meaningful distinction between them.
Variance also helps in identifying outliers and influential data points. Outliers are extreme values that deviate significantly from the majority of data points. By examining the variance, we can identify such outliers, which may indicate errors in data collection or be important in understanding the underlying phenomenon being studied.
In summary, variance is an important statistical measure that provides insights into the spread and consistency of data. It plays a crucial role in assessing data reliability, making comparisons, and identifying influential observations. By understanding variance, statisticians are able to draw valid conclusions and make informed decisions based on the data they analyze.
How to Calculate Variance
Variance is a statistical measure that quantifies the spread between numbers in a dataset. It provides a mathematical representation of the degree of dispersion in the values of a set of numbers. To calculate variance, you need to follow a set of steps:
Step 1: Calculate the Mean
To begin, you need to calculate the mean of the dataset. The mean, also known as the average, is found by summing up all the numbers in the dataset and dividing the sum by the total number of data points. This gives you a representative value of the dataset.
Step 2: Subtract the Mean from Each Data Point
Next, subtract the mean from each data point in the dataset. This step helps to center the data points around the mean, making it easier to measure the dispersion. The result of this subtraction will give you a set of numbers representing the deviation from the mean.
Step 3: Square the Deviations
After subtracting the mean from each data point, square the resulting deviations. Squaring the deviations eliminates the negative values and emphasizes the differences between the data points and the mean. The squared deviations will give you a set of positive numbers.
Step 4: Calculate the Mean of the Squared Deviations
Calculate the mean of the squared deviations. This can be done by summing up all the squared deviations and dividing the sum by the total number of data points. The result is the variance of the dataset.
Step 5: Determine the Variance
Finally, determine the variance by rounding the calculated mean of the squared deviations. The variance is typically expressed in squared units, such as square meters or square dollars. Rounding the variance helps to simplify the value and make it more easily interpretable.
By following these steps, you will be able to calculate the variance of a dataset and gain insights into the spread and dispersion of the values. Variance is a valuable statistical tool that is widely used in various fields, such as finance, economics, and research.
Formula for calculating variance
Variance is a statistical measure that quantifies the spread or dispersion of a set of data points. It provides an indication of how far each value in the dataset is from the mean. The formula for calculating variance depends on whether the dataset represents a population or a sample.
For a population: The formula for population variance is:
Var(X) = (∑(X – μ)^2) / N
where Var(X) is the population variance, X represents each individual value in the dataset, μ is the population mean, and N is the total number of data points.
For a sample: The formula for sample variance is:
Var(X) = (∑(X – x̄)^2) / (n – 1)
where Var(X) is the sample variance, X represents each individual value in the dataset, x̄ is the sample mean, and n is the sample size.
To calculate the variance, you need to calculate the difference between each data point and the mean, square these differences, sum them up, and then divide by the appropriate denominator based on whether you are dealing with a population or a sample.
Understanding the variance of a dataset is important in various fields, including finance, statistics, and quality control. It helps in analyzing the spread of data, identifying outliers, and making informed decisions based on the variability of the dataset.
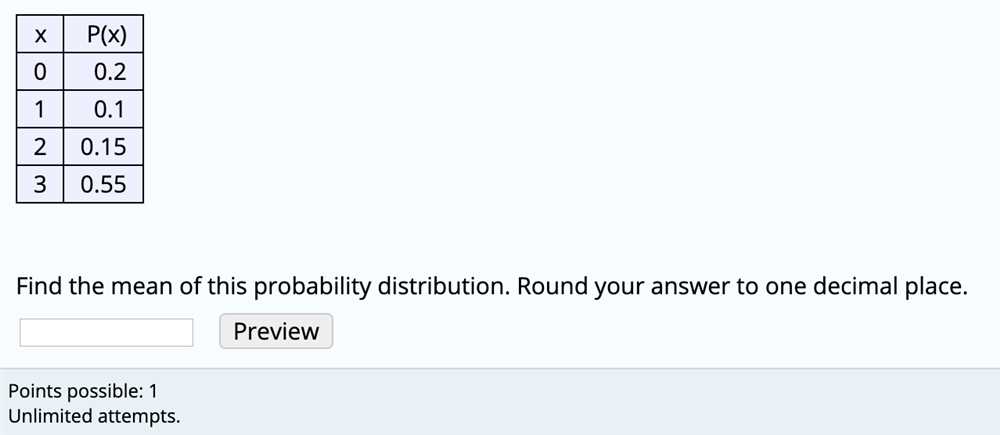
Example calculation of variance
In statistics, variance is a measure of how spread out a set of data is. It quantifies the variability between individual data points and their mean. To calculate the variance, several steps need to be followed.
Step 1: Calculate the mean
Before calculating the variance, it is necessary to find the mean of the data set. The mean is the average value of all the data points. To find the mean, add up all the values and divide the sum by the total number of data points.
Step 2: Determine the differences from the mean
Next, calculate the difference between each individual data point and the mean. These differences are known as deviations. Subtract the mean from each data point.
Step 3: Square the deviations
To eliminate negative values and emphasize the spread, square each deviation. This step ensures that all deviations contribute positively to the variance calculation.
Step 4: Calculate the sum of squared deviations
Add up all the squared deviations calculated in the previous step. This sum is known as the sum of squared deviations.
Step 5: Divide by the number of data points
Divide the sum of squared deviations from step 4 by the total number of data points. This step averages the squared deviations and gives the variance of the data set.
Step 6: Round the result to one decimal place
To ensure consistency and reduce the number of decimal places, round the calculated variance to one decimal place.
Following these steps will yield the calculated variance, which provides a measure of how spread out the data is and helps in understanding the variability within the dataset.
Why is rounding the answer to one decimal place necessary?
When calculating the variance of a dataset, it is important to round the answer to one decimal place. This rounding is necessary because it provides a more manageable and concise representation of the data. Without rounding, the variance can be a long and cumbersome number, making it difficult to interpret and compare with other statistics.
Rounding the answer to one decimal place allows for easier communication and understanding of the data. People are generally more comfortable working with and discussing numbers that are rounded to a specific decimal place. It provides a level of precision that is sufficient for most practical purposes, while still maintaining a reasonable level of accuracy.
Additionally, rounding the answer to one decimal place helps to reduce the impact of small random variations in the data. When calculating the variance, these small variations can sometimes result in decimal places that are insignificant and do not contribute much to the overall understanding of the data. Rounding the variance to one decimal place eliminates these insignificant decimal places, providing a more focused and meaningful result.
Furthermore, rounding the answer to one decimal place can help prevent the misinterpretation or misuse of the data. When dealing with decimals, there is always the potential for rounding errors or confusion. By rounding the variance to one decimal place, it minimizes the chances of miscommunication or misrepresentation, ensuring that the data is accurately and appropriately used.
In conclusion, rounding the answer to one decimal place when calculating the variance is necessary for practicality, communication, accuracy, and to minimize the impact of insignificant decimal places. It provides a more manageable and concise representation of the data, allowing for easier interpretation and comparison.
Importance of rounding in statistical analysis
In statistical analysis, rounding plays a crucial role in ensuring accuracy and reliability of the results. Round is used to reduce the level of detail in a number, while still maintaining a reasonable level of precision.
Rounding is particularly important when reporting summary statistics, such as means, variances, and standard deviations. These measures are often used to describe the central tendency and variability of a dataset, and rounding them to an appropriate decimal place helps in simplifying the values without losing important information.
For example, when calculating the variance of a dataset, it is essential to round the result to a reasonable decimal place. Rounding the variance to the nearest tenth ensures that it is more easily interpretable and makes comparisons between different datasets more straightforward. This rounded value can then be used to make informed decisions or draw conclusions based on the analysis.
Furthermore, rounding also helps to minimize the impact of measurement errors and uncertainties in real-world data. In many cases, the raw data collected may contain slight variations or errors due to various factors. Rounding can help to smooth out these irregularities and provide a clearer picture of the underlying patterns and trends in the data.
In summary, rounding is an important technique in statistical analysis as it improves the readability and interpretability of summary statistics, reduces the impact of measurement errors, and facilitates comparisons between datasets. By carefully choosing an appropriate decimal place to round to, researchers can ensure that their analysis is accurate, reliable, and easily understandable.