
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy levels, and behavior. It is a chronic condition that affects millions of people around the world. The disorder is often marked by episodes of mania, where individuals experience heightened excitement, energy, and impulsivity, followed by episodes of depression, during which they feel sad, hopeless, and sluggish. These mood swings can have a significant impact on a person’s daily life, relationships, and overall well-being.
When conducting a focused exam on someone with bipolar disorder, it is essential to assess their current mood state, as well as any changes in their behavior, sleep patterns, and thought processes. The healthcare provider should also inquire about the individual’s history of manic and depressive episodes, including their duration, frequency, and severity. Understanding these details can help determine the appropriate treatment plan and support strategies for the patient.
Furthermore, it is crucial to assess the individual’s risk for self-harm or suicide, as individuals with bipolar disorder are at a higher risk for these outcomes. This assessment should involve asking direct questions about suicidal thoughts, making a safety plan with the patient, and involving their support network if necessary. Additionally, evaluating the patient’s physical health, such as any potential medication side effects or comorbidities, is also important as it can impact their overall well-being and treatment options.
Focused Exam Bipolar Disorder Shadow Health
In the context of the “Focused Exam Bipolar Disorder Shadow Health” topic, we will discuss the examination and assessment of bipolar disorder. Bipolar disorder is a mental illness characterized by extreme mood swings, from manic episodes of elevated energy, euphoria, and impulsiveness to depressive episodes of intense sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities. The focused exam for bipolar disorder involves evaluating the patient’s mood, behavior, thoughts, and physical symptoms to determine the presence and severity of bipolar disorder.
During the focused exam, the healthcare provider will assess the patient’s mood stability, looking for signs of both manic and depressive episodes. They will ask about the duration and frequency of these episodes, as well as any triggers or stressors that may contribute to their onset. The healthcare provider will also evaluate the patient’s behavior, looking for signs of impulsivity, irritability, and changes in sleep patterns. Additionally, they will inquire about any thoughts of self-harm or suicide, as these are common in depressive episodes of bipolar disorder.
Furthermore, the healthcare provider will conduct a physical examination to rule out any medical conditions that may mimic the symptoms of bipolar disorder, such as thyroid dysfunction or substance abuse. They will check the patient’s vital signs and perform a neurological examination to assess for any physical abnormalities or signs of cognitive impairment. Laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count and thyroid function tests, may also be ordered to provide additional information about the patient’s overall health and rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Key components of the focused exam for bipolar disorder include:
- Evaluating the patient’s mood stability and episodes of mania and depression
- Assessing any behavioral changes, impulsivity, or changes in sleep patterns
- Inquiring about thoughts of self-harm or suicide
- Conducting a physical examination to rule out medical conditions
- Performing a neurological examination for any abnormalities or cognitive impairment
- Ordering laboratory tests to rule out underlying medical conditions
By performing a focused exam for bipolar disorder, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Early detection and intervention are essential in managing bipolar disorder and improving the patient’s quality of life.
Understanding Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic depression, is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings. Individuals with bipolar disorder experience episodes of mania, which are periods of intense excitement, heightened energy levels, and an elevated mood. These episodes are then followed by periods of depression, where individuals feel hopeless, sad, and experience a lack of interest or pleasure in daily activities.
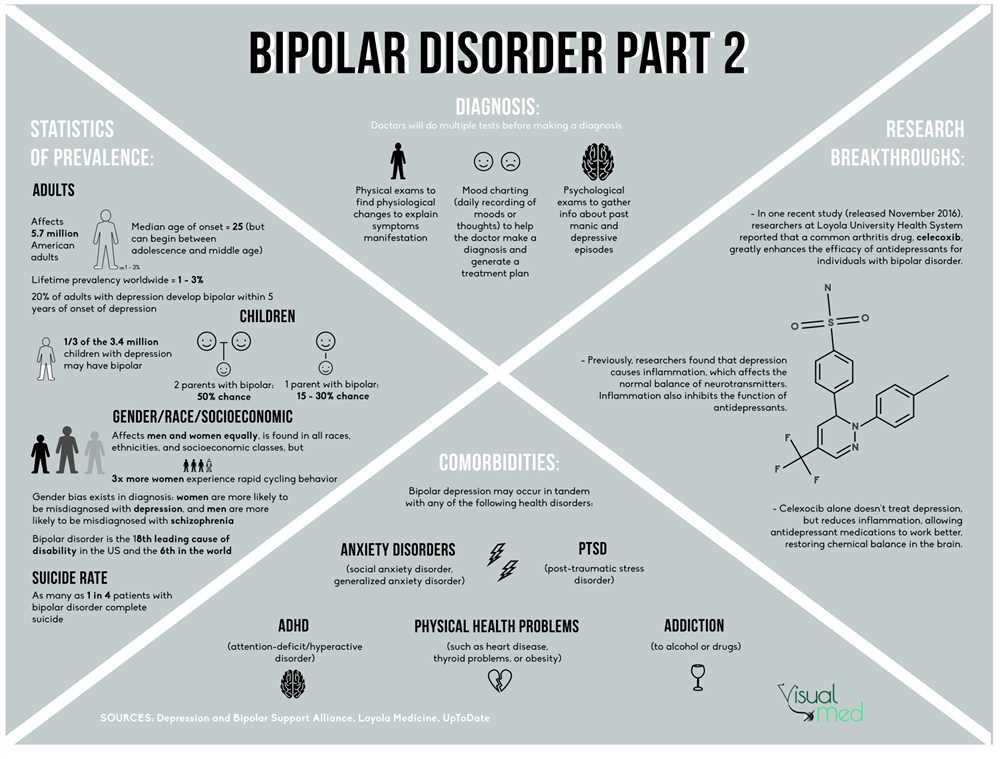
Bipolar disorder is a chronic condition that affects approximately 2.8% of the population. It often manifests in late adolescence or early adulthood and can have a significant impact on a person’s daily functioning. During manic episodes, individuals may engage in risky behaviors, have racing thoughts, exhibit excessive talkativeness, and have difficulty sleeping. On the other hand, during depressive episodes, individuals may feel extremely fatigued, have difficulty concentrating, experience changes in appetite, and have thoughts of self-harm or suicide.
Bipolar disorder is often misdiagnosed as other mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety. It is crucial to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of bipolar disorder. A thorough evaluation and understanding of the person’s medical history, symptoms, and family history is necessary to accurately diagnose and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
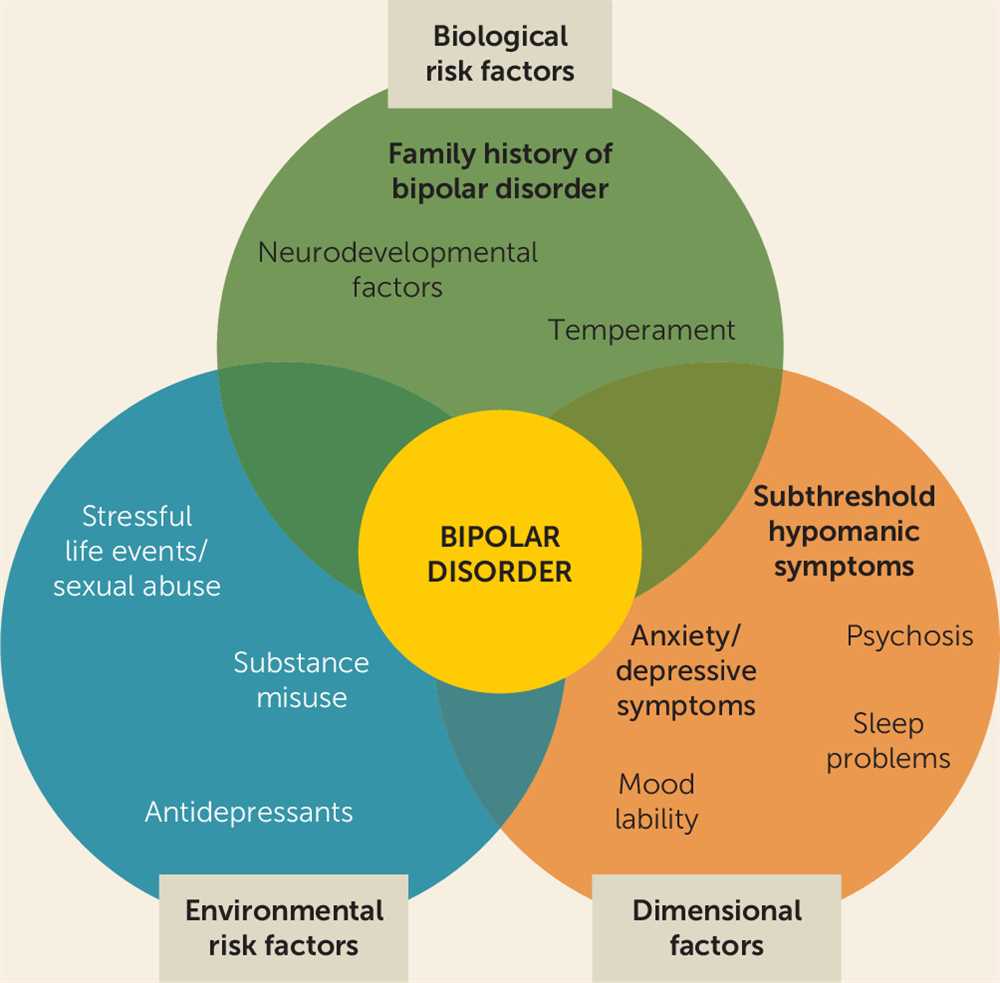
- There is no known single cause of bipolar disorder, but factors such as genetics, brain chemistry, and environmental factors may contribute to its development.
- Treatment for bipolar disorder typically involves a combination of medication, psychotherapy, and the development of coping strategies to manage symptoms and prevent relapses.
- Without proper treatment, bipolar disorder can significantly affect a person’s relationships, work performance, and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings between mania and depression. It is essential to seek professional help for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. With proper management and support, individuals with bipolar disorder can lead fulfilling lives and effectively manage their symptoms.
Symptoms of Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that can range from manic episodes to depressive episodes. These shifts in mood can be severe and can significantly impact a person’s daily functioning and overall quality of life. It is important to recognize the symptoms of bipolar disorder in order to seek appropriate treatment and support.
One of the key symptoms of bipolar disorder is a persistent and pervasive instability in mood. This can manifest in periods of excessive elation and energy during manic episodes, where individuals may engage in risky behavior, experience racing thoughts, and have an inflated sense of self-confidence. On the other hand, during depressive episodes, individuals may feel overwhelming sadness, fatigue, and loss of interest in activities they once enjoyed. These mood swings can last for days, weeks, or even months.
Other symptoms of bipolar disorder can include disrupted sleep patterns, changes in appetite and weight, difficulty concentrating, irritability, restlessness, and feelings of guilt or worthlessness. It is also common for individuals with bipolar disorder to experience difficulties in their relationships, work, and school, as the extreme mood swings can interfere with their ability to function effectively in these areas.
It is important to note that the symptoms of bipolar disorder can vary from person to person and can also change over time. It is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an individualized treatment plan that may include a combination of medication, therapy, and lifestyle changes to manage the symptoms and promote overall well-being.
Diagnostic Criteria for Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, also known as manic-depressive disorder, is a chronic mental illness characterized by extreme shifts in mood, energy, and activity levels. The diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder are established by the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5), which is widely used by healthcare professionals for diagnosing mental disorders.
To meet the criteria for a diagnosis of bipolar disorder, an individual must exhibit specific symptoms for a specified period of time. The DSM-5 outlines several criteria that must be met, including the presence of manic or hypomanic episodes, as well as depressive episodes. These episodes must be distinct periods of abnormally elevated, expansive, or irritable mood, accompanied by an increase in goal-directed activity or energy.
A manic episode is characterized by an elevated mood, racing thoughts, grandiosity, decreased need for sleep, excessive involvement in pleasurable activities with high potential for painful consequences, and an overall sense of euphoria. A hypomanic episode is similar to a manic episode but with less severe symptoms that do not significantly impair functioning or require hospitalization.
In addition to manic or hypomanic episodes, a diagnosis of bipolar disorder also requires the presence of depressive episodes. These episodes involve a persistent feeling of sadness, loss of interest or pleasure in activities, changes in appetite or weight, disturbances in sleep, fatigue or loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating, and suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
The diagnostic criteria for bipolar disorder help healthcare professionals accurately identify and classify the illness, enabling appropriate treatment and support for individuals living with this challenging condition. It is important for individuals experiencing symptoms of bipolar disorder to seek professional help to receive an accurate diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan.
The Importance of Focused Exam for Bipolar Disorder
Performing a focused exam for bipolar disorder is crucial in accurately diagnosing and treating this complex mental health condition. Bipolar disorder is a chronic illness characterized by extreme mood swings and fluctuations in energy levels. It is essential for healthcare professionals to conduct a comprehensive and focused exam to understand the specific symptoms and patterns of the individual, as well as to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
The focused exam allows healthcare providers to evaluate the patient’s history of manic and depressive episodes, identifying key triggers, symptoms, and their impact on daily functioning. This information is vital in diagnosing bipolar disorder, as it differentiates it from other mental health conditions. By collecting data on the patient’s mood patterns, behavior changes, and interpersonal relationships, healthcare providers can form a clearer understanding of the individual’s experiences and tailor treatment plans accordingly.
During the focused exam, healthcare professionals should carefully assess the patient’s mental state, looking for signs of mania (excessive energy, grandiosity, impulsivity) and depression (low mood, hopelessness, lack of interest). The exam may also include evaluating the patient’s sleep patterns, appetite changes, and any history of suicidal thoughts or self-harm. Additionally, a thorough physical examination may be necessary to rule out any underlying medical conditions that could be contributing to the patient’s symptoms.
A focused exam for bipolar disorder not only aids in proper diagnosis but also serves as a foundation for developing an individualized treatment plan. Depending on the patient’s specific symptoms and needs, treatment may involve a combination of medication, therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy), lifestyle changes, and support systems. By conducting a focused exam, healthcare providers can gather the necessary information to create a holistic treatment approach that addresses the patient’s unique circumstances and improves overall quality of life.
In conclusion, a focused exam for bipolar disorder is vital in understanding the nuances of this complex mental health condition. By carefully assessing the patient’s history, symptoms, and functional impact, healthcare professionals can accurately diagnose bipolar disorder and develop tailored treatment plans. The focused exam serves as a critical component in managing bipolar disorder, allowing for targeted interventions and improved outcomes for individuals living with this condition.
Physical Examination for Bipolar Disorder
When conducting a physical examination for bipolar disorder, it is important for healthcare providers to be thorough and observant. Physical signs and symptoms may not always be prominent, but they can provide valuable clues to support a diagnosis.
Vital Signs: Monitoring the patient’s vital signs, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and temperature, is crucial in evaluating their overall physical health. Fluctuations in these vital signs may indicate underlying medical conditions or imbalances that could contribute to bipolar symptoms.
Appearance and Behavior: Observing the patient’s appearance and behavior can provide insights into their mental state. Signs of restlessness, overactivity, or agitation can suggest mania, while a lack of energy, slowed movements, and lack of interest in surroundings may indicate depression. Additionally, noting any changes in grooming or hygiene can be helpful in understanding the patient’s overall functioning.
Neurological Examination: Assessing the patient’s neurological function is crucial in ruling out other potential causes of their symptoms. This may involve evaluating their coordination, muscle strength, reflexes, and sensory responses. Any abnormalities in these areas may warrant further investigation.
Musculoskeletal Examination: Examining the patient’s musculoskeletal system can uncover signs of physical discomfort or pain that may be contributing to their mood disturbances. Assessing joint mobility, muscle strength, and overall posture can help identify any underlying musculoskeletal issues.
Skin Examination: Taking note of the patient’s skin condition, such as any rashes, lesions, or abnormalities, is important for ruling out physical causes of psychiatric symptoms. Certain dermatological conditions may be associated with bipolar disorder, so it is essential to thoroughly examine the patient’s skin.
Gastrointestinal Examination: Symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or changes in appetite and weight can be associated with bipolar disorder. Conducting a gastrointestinal examination can help identify any underlying issues in this system that may be contributing to these symptoms.
Cardiovascular Examination: Bipolar disorder can be associated with increased risk factors for cardiovascular disease, such as obesity, hypertension, and dyslipidemia. Evaluating the patient’s cardiovascular system, including heart sounds and peripheral pulses, is important to identify any potential cardiovascular concerns.