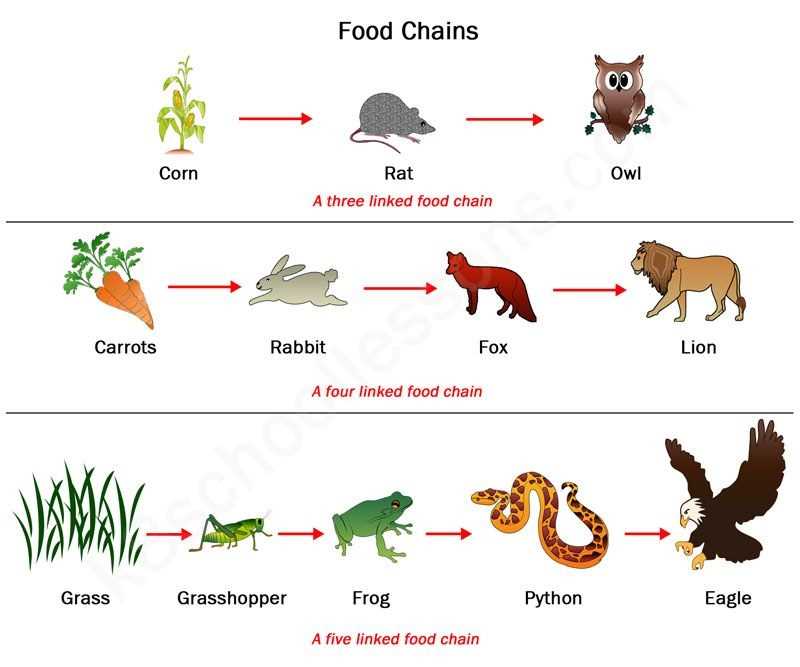
A food chain is a series of organisms that transfer energy through the consumption of other organisms. Understanding the interactions within food chains is essential for studying ecosystems and the balance of nature. Food chain gizmos are tools designed to help students visualize and comprehend these complex relationships. By providing an answer key for the food chain gizmos, educators can guide students through the learning process and ensure they grasp key concepts.
One example of a food chain gizmo is a puzzle set that allows students to match different organisms with their corresponding positions in the food chain. This hands-on activity enables students to manipulate the pieces and see how energy flows from one organism to another. With the answer key, students can check their understanding and ensure they have correctly arranged the puzzle set.
Another food chain gizmo is an interactive simulation that lets students create their own food chains and observe the consequences of changing variables. By altering the population size or introducing a new species, students can witness the effects on the entire food chain. The answer key for this gizmo provides guidance on the potential outcomes and helps students develop a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
Overall, food chain gizmos and their answer keys play a crucial role in enhancing students’ comprehension of ecological relationships. By engaging in hands-on activities and interactive simulations, students can actively explore and learn about the intricate connections within food chains. With the guidance provided by the answer key, educators can facilitate meaningful discussions and ensure students grasp the foundational concepts of ecology.
The importance of food chain gizmos
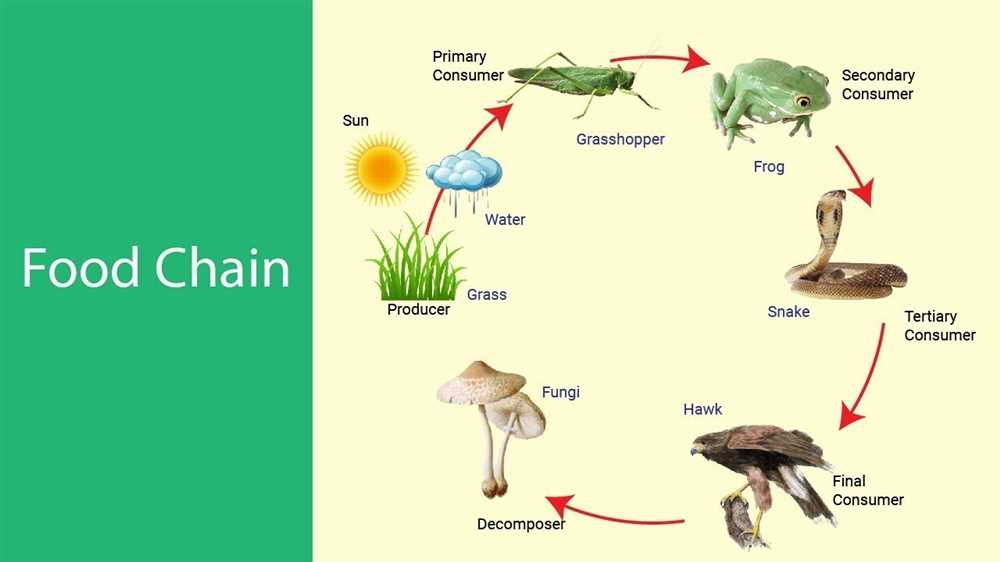
Food chain gizmos play a crucial role in understanding and studying the delicate balance of ecosystems. These gizmos, whether they are models, simulations, or interactive tools, provide a visual and interactive representation of the food chain, showing the complex relationships between different organisms and their energy flow.
One of the key advantages of using food chain gizmos is their ability to simplify and clarify the often complex interactions between organisms in an ecosystem. By visualizing the different trophic levels and the transfer of energy from one organism to another, students and researchers can grasp the dynamics of food chains more easily. This helps in understanding the impact of changes in one part of the food chain on the entire ecosystem.
Food chain gizmos also enable hands-on learning and experimentation. Through these interactive tools, students can explore and manipulate various factors that affect the food chain, such as population size, resource availability, and predator-prey relationships. This experiential learning approach fosters a deeper understanding of ecological concepts and empowers students to become active learners and problem-solvers.
Furthermore, food chain gizmos are invaluable in environmental education and conservation efforts. By using these tools, educators can engage students in discussions about the impact of human activities on ecosystems and the importance of preserving biodiversity. Additionally, gizmos can be used to explore the consequences of disruptions in food chains, such as the extinction of keystone species or the introduction of invasive species.
In conclusion, food chain gizmos are essential tools for understanding, teaching, and researching the intricate relationships within ecosystems. Their ability to simplify complex concepts, enable hands-on learning, and facilitate discussions about environmental issues makes them indispensable in environmental education and conservation efforts. By using these gizmos, we enhance our understanding of the delicate balance of nature and promote a sustainable approach towards our ecosystems.
Understanding food chains
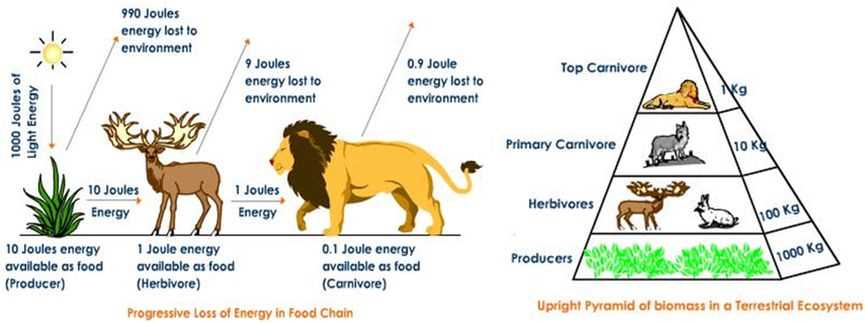
Food chains are an essential part of the ecosystem and are crucial for the survival of all living organisms. They illustrate the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another in a specific environment. By understanding food chains, we can gain insight into the interdependent relationships between different species and recognize the importance of maintaining balance within an ecosystem.
A food chain typically consists of four main components: producers, consumers, decomposers, and the environment. Producers, such as plants and algae, are the primary source of energy in a food chain. They convert sunlight into organic compounds through photosynthesis, which serves as nourishment for other organisms. Consumers, including herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, obtain energy by consuming producers or other consumers. Decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms and organic waste, returning nutrients to the environment.
In a food chain, each organism occupies a specific trophic level, indicating its position in the transfer of energy. Producers are at the base of the food chain, followed by primary consumers, secondary consumers, and so on. The top predator, also known as the apex predator, occupies the highest trophic level.
It is important to note that every organism in a food chain has a specific role and function. If one organism is removed or its population is significantly reduced, it can disrupt the entire food chain and have cascading effects on other species. This emphasizes the delicate balance and interdependence of the ecosystem.
Understanding food chains is crucial for conservation efforts and maintaining a healthy environment. By studying and analyzing food chains, we can identify potential threats and develop strategies to protect endangered species. Additionally, understanding the complex interactions within food chains can help us comprehend the consequences of human impacts, such as pollution and habitat destruction, and work towards sustainable solutions.
Exploring different types of food chain gizmos
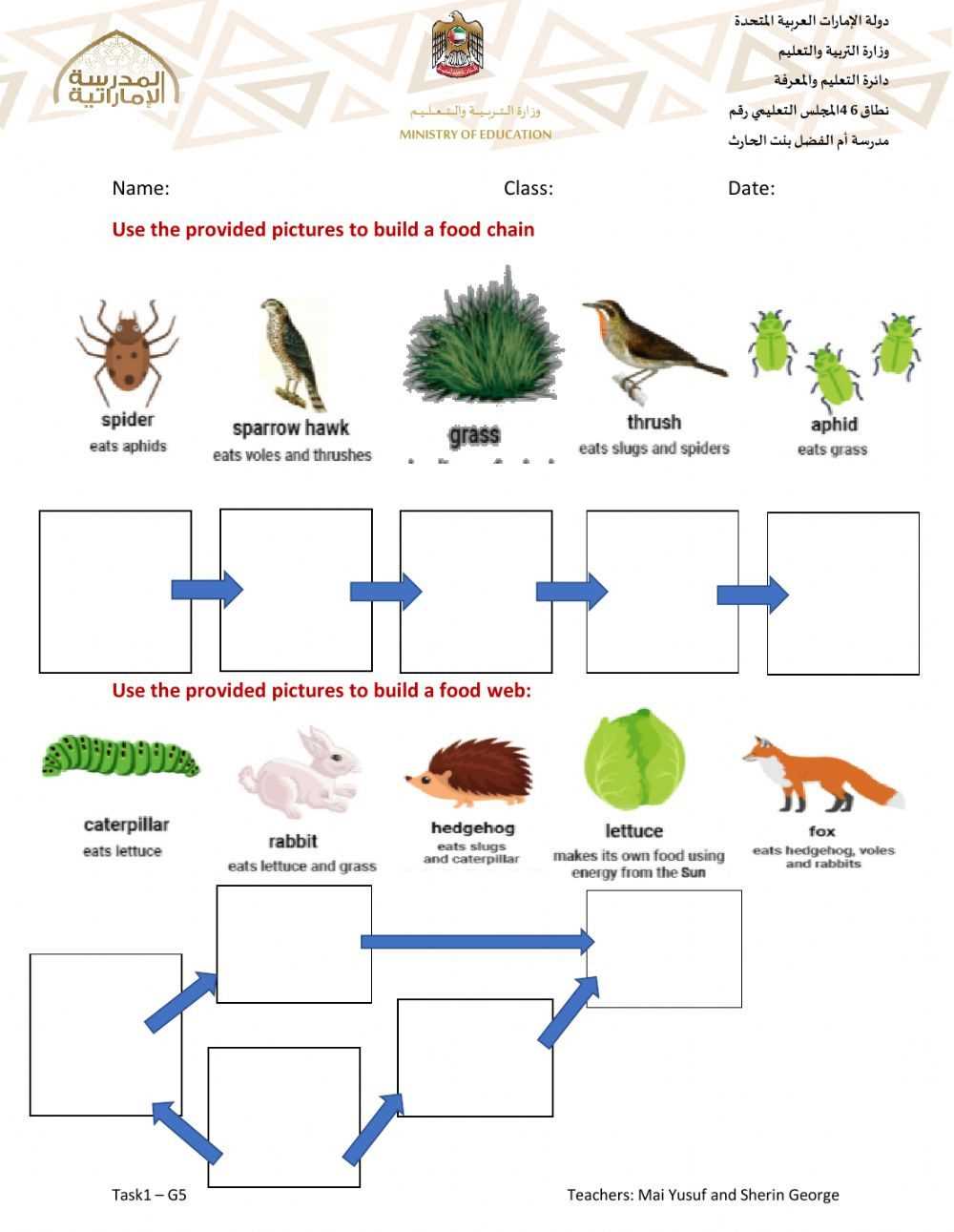
Food chain gizmos are fascinating tools that help us understand the complex relationships between different organisms in an ecosystem. These gizmos come in various forms and serve different purposes, allowing scientists and researchers to study and observe the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem.
1. Food chain models: One type of food chain gizmo is a model that visually represents the feeding relationships among organisms in a particular ecosystem. These models often use arrows to indicate the direction of energy transfer through the food chain. They are useful for illustrating complex interactions and can be used in educational settings to teach students about the concept of food chains.
2. Trophic level analyzers: Trophic level analyzers are devices that measure the energy content of different organisms in a food chain. These analyzers give scientists valuable data about the amount of energy transferred from one trophic level to another. By understanding the energy flow within an ecosystem, researchers can gain insights into the stability and functioning of the food chain.
- 3. GPS tracking devices: GPS tracking devices are not traditional food chain gizmos, but they play an important role in studying predator-prey relationships. By attaching GPS devices to predators, such as wolves or lions, researchers can track their movements and observe their hunting behaviors. This data provides valuable insights into the dynamics of a food chain and can help identify the key players in an ecosystem.
4. Chemical tracers: Chemical tracers are substances that are used to track the flow of nutrients through a food chain. By adding a specific chemical to the diet of an organism at the bottom of the food chain, scientists can trace its movement through higher trophic levels. This technique helps researchers understand the pathways and rates of nutrient transfer within an ecosystem.
5. Stable isotope analysis: Stable isotope analysis is a method that uses isotopes of elements, such as carbon or nitrogen, to determine the source of an organism’s food. By analyzing the isotopic composition of different organisms in a food chain, researchers can infer their position and role within the chain. This technique provides insights into the complexity and interconnectedness of food webs.
In conclusion, food chain gizmos come in various forms and serve different purposes, from models and analyzers to tracking devices and chemical tracers. These tools help scientists explore and understand the intricate relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, shedding light on the flow of energy and nutrients through the food chain.
How food chain gizmos work
Food chain gizmos are innovative devices that help study and understand the complex relationships and interactions between different organisms in an ecosystem. These gizmos simulate the flow of energy and nutrient transfer between different levels of a food chain, allowing scientists and students to observe and analyze the dynamics of ecosystems in a controlled environment.
One key component of food chain gizmos is the use of models to represent different organisms and their roles in the food chain. Each model is designed to accurately depict the physical characteristics and behaviors of a specific organism, from producers to consumers and decomposers. The models are placed in a carefully constructed set-up that replicates the natural environment, complete with habitats and food sources.
Once the gizmo is set up, the flow of energy and nutrients can be observed by watching the movement and interactions of the different models. For example, the model representing a plant will absorb sunlight and convert it into energy through photosynthesis. This energy can then be transferred to herbivorous models when they consume the plant. The herbivorous models, in turn, can be consumed by larger carnivorous models, creating a chain of energy transfer.
Through the use of sensors and data collection tools, food chain gizmos are also able to provide quantitative data on factors such as energy transfer efficiency and biomass production at each level of the food chain. This data can be used for analysis and comparison, allowing scientists to study the effects of various factors on ecosystem dynamics, such as changes in population size or introduction of new species.
In conclusion, food chain gizmos provide a valuable tool for studying and understanding the intricate web of interactions within an ecosystem. By simulating the flow of energy and nutrients, these devices enable scientists and students to observe and analyze complex relationships, ultimately contributing to our knowledge of the natural world.
Benefits of using food chain gizmos

Food chain gizmos offer a range of benefits that make them a valuable tool for studying and understanding the intricacies of food chains and ecosystems. These gizmos are designed to simulate real-life scenarios and allow students to observe and analyze the interactions between different organisms in a food chain. Here are some of the key benefits of using food chain gizmos:
1. Hands-on learning: Food chain gizmos provide a hands-on approach to learning about food chains. Instead of just reading about them in a textbook, students can actively participate in the process of constructing and observing food chains. This hands-on learning experience enhances engagement and understanding.
2. Visual representation: Food chain gizmos offer a visual representation of complex ecological relationships. By using these gizmos, students can see how different organisms are connected in a food chain and how energy flows through the ecosystem. This visual representation helps students grasp the concept more easily.
- Detailed analysis: Food chain gizmos allow students to analyze the various components of food chains in detail. They can observe the predator-prey relationships, energy transfer, and the impact of environmental factors on the food chain. This detailed analysis helps students develop critical thinking skills and a deeper understanding of ecosystem dynamics.
- Interactive exploration: Food chain gizmos encourage interactive exploration. Students can experiment with different combinations of organisms and observe the resulting effects on the food chain. This interactive exploration fosters curiosity and encourages students to ask questions and seek answers.
- Real-world application: Food chain gizmos help students understand the relevance and importance of food chains in real-world scenarios. They can learn about the balance of ecosystems, the impact of human activities, and the conservation of biodiversity. This real-world application enhances students’ awareness and appreciation of the natural world.
In conclusion, food chain gizmos offer a range of benefits that enhance the learning experience and understanding of food chains. They provide a hands-on, visual, and interactive approach to studying ecological relationships. By using these gizmos, students can develop critical thinking skills, explore different scenarios, and understand the real-world relevance of food chains.
Considerations when choosing food chain gizmos
When it comes to choosing the right food chain gizmos, there are several key considerations that need to be taken into account. These considerations will help ensure that the gizmos are effective and efficient in managing food waste and promoting sustainable practices in the food industry.
1. Functionality: One of the most important factors to consider is the functionality of the food chain gizmos. They should be designed to efficiently handle and process food waste, ensuring that it is properly disposed of or transformed into useful byproducts such as compost or biogas. The gizmos should also be easy to operate and maintain, allowing for smooth integration into existing food production systems.
2. Scalability: Another crucial consideration is the scalability of the food chain gizmos. As the food industry continues to grow and evolve, it is essential that the gizmos can accommodate increasing volumes of food waste. Look for gizmos that can be easily scaled up or down to match the needs of different food establishments, from small restaurants to large-scale food processing plants.
3. Sustainability: Sustainability should be at the forefront of the decision-making process when choosing food chain gizmos. Evaluate the environmental impact of the gizmos, considering factors such as energy consumption, water usage, and emissions. Opt for gizmos that prioritize energy efficiency and use environmentally-friendly technologies to minimize their carbon footprint.
4. Cost-effectiveness: Cost-effectiveness is another important consideration, especially for businesses operating on tight budgets. Compare the upfront costs of different gizmos, but also take into account the long-term savings and potential return on investment. Consider factors such as maintenance, operational costs, and potential revenue streams generated by the gizmos, such as the sale of compost or biogas.
5. Integration: Lastly, consider how well the food chain gizmos can integrate with existing food production processes. They should be compatible with existing infrastructure and able to seamlessly fit into the existing workflow without causing disruptions. Look for gizmos that can be easily integrated with other technologies and systems, allowing for efficient management of food waste throughout the entire food chain.