Understanding the concept of force is essential in physics and engineering. A force diagram, also known as a free-body diagram, is a visual representation that helps us analyze and understand the forces acting on an object. By creating a force diagram, we can identify and quantify the different forces involved.
A force diagram typically consists of a labeled object or system and arrows representing the forces acting on it. The length and direction of the arrows indicate the magnitude and direction of the forces. This visual tool allows us to analyze how different forces interact with each other and the resulting net force on the object.
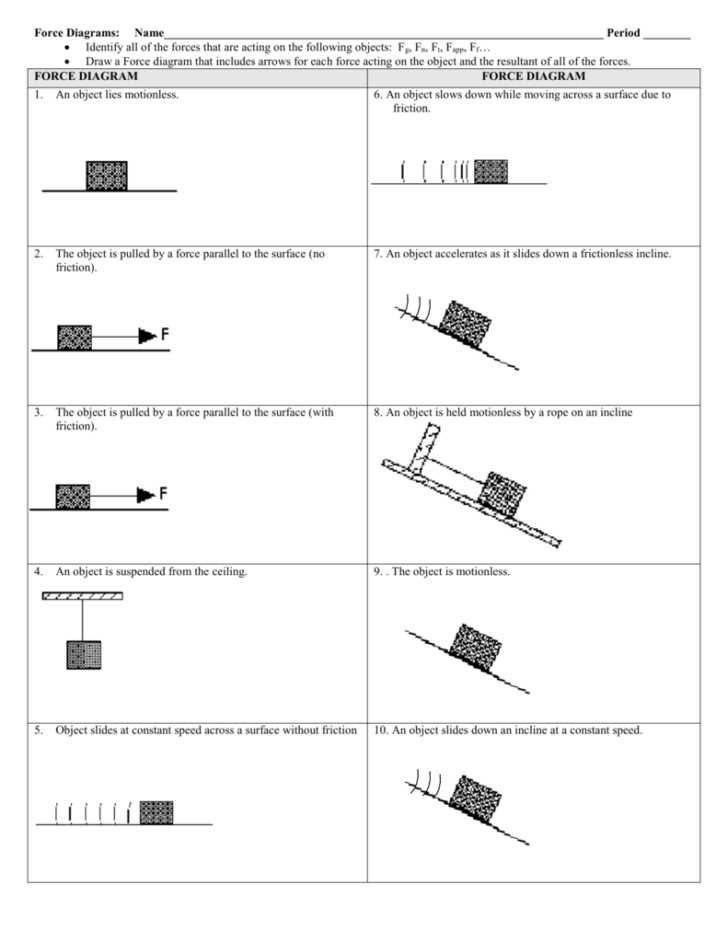
A force diagram worksheet is a valuable tool for students and learners to practice their understanding of force diagrams. It usually presents a scenario or situation where forces are acting on an object, and the task is to correctly identify and represent these forces in a diagram. The worksheet provides answers or solutions to guide students in correcting their diagrams.
By completing a force diagram worksheet with answers, students can actively engage with the concept of forces and improve their problem-solving skills. They can identify misconceptions, check their understanding, and learn from their mistakes. This interactive practice reinforces the learning process and helps students develop a deeper understanding of the principles behind force diagrams.
What is a force diagram?

A force diagram, also known as a free body diagram, is a visual representation of the forces acting on an object in a given situation. It is a simplified drawing that helps to analyze the forces and their directions in order to understand the overall forces acting on the object.
A force diagram typically consists of a labeled object or particle, with arrows representing the forces acting on it. The length and direction of the arrows indicate the magnitude and direction of the forces. The diagram includes all the forces that affect the object, including both applied forces and reaction forces.
Force diagrams are commonly used in physics and engineering to evaluate the forces involved in different scenarios, such as objects on inclined planes, objects in motion, or systems in equilibrium. By visualizing the forces, it becomes easier to determine the net force acting on the object and understand the resulting motion or stability.
It is important to note that force diagrams are not meant to show the physical size or shape of the object, but rather to focus on the forces acting on it. These diagrams are an essential tool in physics and provide a clear and concise representation of the forces involved in a given situation, helping to analyze and understand the forces at play.
Importance of force diagrams in understanding physics
Force diagrams play a crucial role in understanding physics as they provide a visual representation of the forces acting on an object or system. These diagrams help physicists analyze and predict the motion and behavior of objects, allowing them to make accurate calculations and draw conclusions about the underlying principles of physics. By visually representing the forces at play, force diagrams simplify complex physical scenarios and make them more accessible for analysis.
One of the key benefits of force diagrams is their ability to clearly illustrate the direction and magnitude of forces acting on an object. By representing each force as an arrow, with the length of the arrow indicating the magnitude and the direction indicating the direction of the force, physicists can easily see the overall effect of the forces on the object. This visual representation aids in understanding the balance or imbalance of forces and helps determine whether an object will stay at rest, move in a straight line, or accelerate in a particular direction.
Force diagrams also allow physicists to identify and analyze the different types of forces acting on an object. This is important as it helps in recognizing and understanding the fundamental forces of nature, such as gravity, friction, and electromagnetic forces. By delineating the individual forces, physicists can study their interactions, determine their relative strengths, and investigate how they contribute to the overall behavior of the object.
In conclusion, force diagrams are an indispensable tool in understanding physics. Through their visual representation of forces, they simplify complex scenarios and help physicists analyze the behavior and motion of objects. Force diagrams provide a systematic approach to understanding the forces at play and allow for accurate calculations and predictions. Without force diagrams, the study of physics would be much more difficult and less accessible, limiting our understanding of the fundamental laws governing the universe.
Basic Concepts of Force Diagrams
A force diagram, also known as a free-body diagram, is a visual representation of the forces acting on an object in a given situation. It is a valuable tool in physics and engineering, as it allows for the analysis of forces and their effects on objects.
Identifying Forces: The first step in creating a force diagram is to identify all the forces acting on the object. These forces can be classified as either contact forces or non-contact forces. Contact forces occur when objects physically touch each other, while non-contact forces act at a distance, such as gravitational or electrical forces.
Representing Forces: Once the forces have been identified, they are represented using arrows. The length and direction of the arrows indicate the magnitude and direction of the force. The use of arrows allows for a concise and clear representation of the forces acting on the object.
Labeling Forces: Each force on the diagram should be labeled to indicate its nature, such as friction, tension, or gravity. Additionally, the magnitude of each force can be labeled using standard units of measurement, such as Newtons (N).
Applying Newton’s Laws: Force diagrams are used to apply Newton’s laws of motion to the object being analyzed. By summing up the forces in different directions, the net force acting on the object can be determined. This net force can then be used to calculate the object’s acceleration or to determine if the object is at equilibrium.
Iterative Process: Creating a force diagram is often an iterative process, involving the identification of forces, representation of forces, labeling of forces, and application of Newton’s laws. By refining and revising the force diagram, a more accurate analysis of the forces acting on an object can be achieved.
In conclusion, force diagrams are a fundamental tool in physics and engineering for understanding the forces acting on an object. By carefully representing and labeling the forces, and applying Newton’s laws, force diagrams can provide valuable insights into the behavior of objects in various situations.
Definition of force
A force is a physical quantity that can change the state of motion or shape of an object. It is a vector quantity, which means it has both magnitude and direction. Force is measured in newtons (N).
Key terms: force, physical quantity, state of motion, shape, vector quantity, magnitude, direction, newtons.
A force can be thought of as a push or a pull. It is something that causes an object to accelerate or decelerate. Forces can also cause objects to change their shape or deform. The magnitude of a force determines how much it can change the motion or shape of an object, while the direction determines the way in which it changes it.
For example, if a person pushes a car, they apply a force in the direction they want the car to move. The magnitude of the force will determine how fast the car accelerates, while the direction will determine the path it takes.
In physics, force is often represented by a vector arrow. The length of the arrow represents the magnitude of the force, and the direction of the arrow indicates the direction in which the force is acting. Forces can be added together using vector addition to determine the net force on an object.
Summary: A force is a physical quantity that can change the state of motion or shape of an object. It is a vector quantity with magnitude and direction, and is measured in newtons. Forces can be thought of as pushes or pulls, and can cause objects to accelerate, decelerate, or change shape.
Types of forces

Force is a crucial concept in the study of physics and can be defined as a push or pull upon an object. There are several different types of forces that act on objects in various situations. Understanding these different types of forces is essential in order to analyze and interpret the motion and behavior of objects.
1. Contact forces: Contact forces are forces that result from the physical contact between two objects. These forces can be divided into several categories, including:
- Friction: Friction is a force that opposes the motion of an object when it is in contact with another object or surface.
- Weight: Weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. It is the force that causes an object to have weight or mass.
- Tension: Tension is a force that is transmitted through a string, rope, or cable when it is pulled tight.
- Normal force: Normal force is the force exerted by a surface that is perpendicular to the surface. It is the force that supports an object’s weight and prevents it from sinking through the surface.
2. Non-contact forces: Non-contact forces, also known as field forces, do not require physical contact between two objects. These forces can act over a distance and include:
- Gravity: Gravity is the force of attraction between all objects with mass. It is responsible for the motion of the planets, the tides, and the falling of objects.
- Magnetic force: Magnetic force is the force exerted by a magnetic field on a magnetic object or by a moving magnetic object on a non-magnetic object.
- Electrostatic force: Electrostatic force is the force exerted by electric charges on each other. Like charges repel each other, while opposite charges attract each other.
By understanding the different types of forces and how they interact, scientists and engineers can analyze and predict the behavior of objects in a wide range of situations. This knowledge is essential for the development of technology and the advancement of our understanding of the physical world.
Using Force Diagram Worksheet
A force diagram worksheet is a helpful tool used to analyze and understand the forces acting on an object in a given situation. It is particularly useful in physics and engineering to visually represent and calculate the forces involved in a problem or scenario.
The worksheet usually consists of a diagram of the object in question, with arrows indicating the direction and magnitude of each force acting on it. The forces are labeled with relevant information such as the type of force (e.g., tension, gravitational, friction), the objects involved, and any other important details.
By completing the force diagram worksheet, students can develop their understanding of Newton’s laws of motion and gain practice in applying these principles to real-life situations. They can also learn how to break down complex problems into simpler components and analyze the forces acting on each part independently.
The force diagram worksheet can be used in various educational settings, such as classroom discussions, individual or group activities, and homework assignments. It can be a valuable tool for both teachers and students to assess comprehension, identify misconceptions, and provide opportunities for further learning and practice.
To ensure a successful use of the force diagram worksheet, it is important for students to have a solid understanding of the basic concepts of forces, vectors, and motion. It is also beneficial for teachers to provide clear instructions and examples, and to encourage students to think critically and discuss their reasoning when completing the worksheet.
In conclusion, the force diagram worksheet is a practical and effective tool for visualizing and solving problems related to forces. It helps students develop their analytical and problem-solving skills and provides a tangible representation of abstract concepts. By using this worksheet, students can enhance their understanding of forces, motion, and the principles of physics.
Step-by-step Guide to Completing the Force Diagram Worksheet
When completing a force diagram worksheet, it is important to follow a step-by-step approach to ensure accuracy and clarity. This guide will walk you through the process of completing the worksheet effectively.
1. Understand the Scenario
Begin by carefully reading and understanding the scenario provided. Identify the objects or bodies involved and the forces acting upon them. Take note of any given information such as mass, acceleration, or applied forces.
2. Identify the Forces
Next, list all the forces acting on each object or body. This may include weight, tension, friction, normal force, or any other forces specified in the scenario. Remember to label each force and indicate its direction.
3. Determine the Magnitude and Direction

For each force listed, determine its magnitude and direction. If the magnitude is given in the scenario, write it down. If not, use your knowledge of physics principles or any relevant formulas to calculate the magnitude. Indicate the direction of each force using arrows on the diagram.
4. Apply Newton’s Laws
Apply Newton’s laws of motion to determine any additional forces that may be present. Remember that forces are balanced when there is no acceleration, and forces are unbalanced when there is acceleration. Analyze the scenario carefully and consider the resulting motion or equilibrium conditions.
5. Review and Refine
Once you have completed the force diagram, review it for accuracy and clarity. Double-check the direction and magnitude of each force, ensuring they are labeled correctly. If needed, revise or refine the diagram to accurately represent the forces involved.
By following these steps, you will be able to effectively complete a force diagram worksheet, accurately representing the forces acting on objects or bodies in a given scenario. Remember to take your time and carefully analyze the information provided to ensure an accurate depiction of the forces involved.