
Studying fossils provides invaluable insights into the Earth’s history and the evolution of life on our planet. Fossils worksheet answer keys are a useful tool for educators to ensure students gain a comprehensive understanding of this fascinating subject. By providing a set of answers to worksheet questions, students can verify their own responses and fill in any knowledge gaps.
Fossils worksheet answer keys typically include detailed explanations for each question, helping students understand the concepts and processes involved in paleontology. These keys often cover a range of topics, such as fossil identification, dating techniques, and fossil formation. By using an answer key, students can compare their own answers and identify any misconceptions they may have had.
Furthermore, fossils worksheet answer keys can serve as a reference guide for educators, facilitating class discussions and providing supplementary information for lessons. Teachers can use these answer keys to reinforce key points, expand on certain concepts, and address common misconceptions. This comprehensive resource ensures that students not only have the correct answers but also a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Fossils Worksheet Answer Key: Your Guide to Understanding Fossils

Fossils Worksheet Answer Key is an essential tool for understanding fossils and their significance in the field of paleontology. Fossils provide valuable clues about the Earth’s past and help scientists reconstruct the history of life on our planet. By answering key questions related to fossils, this worksheet serves as a comprehensive guide to aid in the understanding of this fascinating field.
What are fossils?
Fossils are the remains or traces of organisms that lived in the past. They can include bones, shells, imprints, or even preserved soft tissues. Fossils are formed through a process called fossilization, which occurs when an organism is buried and preserved in sediment or other natural materials. Over time, the organic materials are replaced by minerals, resulting in the formation of a fossil.
How do fossils help us understand the past?
Fossils provide a wealth of information about the history of life on Earth. They can reveal the morphology, behavior, and habitats of ancient organisms, giving scientists insights into their evolutionary relationships. Fossils can also provide evidence of past environmental conditions, such as climate change, and help us understand how ecosystems have evolved over time. By studying fossils, scientists can paint a picture of the past and gain a better understanding of the processes that have shaped life on our planet.
- Fossils Worksheet Answer Key: An overview of the main types of fossils. This section provides definitions and examples of different types of fossils, such as body fossils, trace fossils, and molds and casts. It helps students understand the different ways in which organisms can be preserved in the fossil record.
- Fossils and Evolution: This section explores the role of fossils in understanding the process of evolution. It explains how fossils can be used to trace the evolutionary history of species and understand the patterns of diversification and extinction.
- Interpreting Fossils: This section focuses on the methods and techniques used to interpret fossils. It includes information on dating techniques, such as radiometric dating, and the use of fossil assemblages to reconstruct past environments.
- Fossils and Paleobiology: This section discusses the field of paleobiology, which combines paleontology and biology to study ancient life forms. It explores topics such as paleoecology, paleoethology, and the study of ancient DNA.
In conclusion, the Fossils Worksheet Answer Key is a valuable resource for anyone interested in understanding fossils and their significance in the field of paleontology. It provides a comprehensive guide to the different types of fossils, their role in understanding evolution and past environments, and the methods used to interpret them. By exploring these topics, students can develop a deeper appreciation for the incredible history of life on Earth and the scientific methods used to study it.
What are Fossils?
Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient organisms that have been preserved in rocks or other geological materials. They provide evidence of past life and can range in size from microscopic to large, fossilized bones. Fossils can be formed through a variety of processes, including mineralization, carbonization, and petrification.
Fossils are invaluable to scientists because they provide a unique window into the Earth’s history and the evolution of life on the planet. By studying fossils, scientists can learn about the ancient environments in which organisms lived, their anatomy, behavior, and evolutionary relationships. Fossils allow us to piece together the puzzle of life’s history and gain insights into the biodiversity and ecosystems of the past.
There are different types of fossils, each with its own characteristics and formation processes. Body fossils are the preserved remains of an organism’s body, such as bones, shells, or teeth. Trace fossils, on the other hand, are indirect evidence of an organism’s existence, such as footprints, burrows, or coprolites (fossilized dung). Fossils can also provide information about past climates, as the presence of certain plants or animals can indicate the environmental conditions of a particular time period.
Overall, fossils are a remarkable record of Earth’s history and serve as a vital tool for understanding the past and present biodiversity of our planet. They allow us to glimpse into the ancient worlds that existed long before humans walked the Earth and provide valuable insights into the processes of evolutionary change.
Types of Fossils
Fossils are the remains or traces of ancient organisms that have been preserved in the Earth’s crust. They provide valuable clues about the history of life on our planet. There are several types of fossils, each with its unique characteristics and preservation process.
1. Petrified Fossils: Petrified fossils are formed when the organic material of the organism is replaced by minerals, such as silica or calcite. This process occurs over millions of years, as water containing these minerals seeps into the remains and slowly replaces the original organic material. The result is a fossil that preserves the shape and details of the organism, often turning it into stone.
2. Mold Fossils: Mold fossils are formed when the remains of an organism, such as a shell or bones, are buried in sediment and then dissolved by groundwater. The cavity left behind by the dissolved remains is known as a mold. Mold fossils provide important information about the shape and size of the organism, but they do not preserve any of the original material.
3. Cast Fossils: Cast fossils are formed when a mold fossil is filled with minerals or sediment that harden into a solid replica of the organism. This process creates a cast, which is a three-dimensional representation of the organism. Cast fossils can provide more detailed information about the internal structures of an organism, such as its internal organs or the shape of its bones.
4. Trace Fossils: Trace fossils are not the remains of the actual organism but rather evidence of its activity. They include footprints, burrows, and coprolites (fossilized feces). Trace fossils provide insights into the behavior and ecology of ancient organisms, allowing scientists to reconstruct their interactions with their environment.
5. Amber Fossils: Amber fossils are formed when organisms, such as insects or small animals, become trapped in sticky tree resin and then preserved over millions of years. The resin hardens into amber, which preserves the organism in incredible detail. Amber fossils can provide valuable information about the anatomy and behavior of ancient organisms, as well as insights into the ecosystems they once inhabited.
6. Frozen Fossils: Frozen fossils are formed when the remains of ancient organisms become encased in ice and preserved in an extremely cold environment. These fossils are often exceptionally well-preserved, with soft tissues and even fur or feathers intact. Frozen fossils have provided scientists with unique insights into the appearance and physiology of ancient organisms, such as the famous woolly mammoths.
In conclusion, fossils come in various forms and provide a window into the past. Each type of fossil has its own story to tell, shedding light on the diversity and evolution of life on Earth.
Fossil Formation Process
Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of plants and animals that lived in the past. They provide valuable information about the history of life on Earth and the evolution of different species. Fossil formation is a complex process that involves several steps.
The first step in the fossil formation process is burial. When an organism dies, it must be quickly covered by sediment such as sand, mud, or silt. This prevents the remains from being exposed to scavengers or decomposing rapidly. Over time, the sediment piles up and puts pressure on the remains, turning them into rock.
- Key phrase: Burial
- Related terms: Sediment, pressure, rock
Next, the process of fossilization begins. This involves the replacement of organic materials with minerals. As the remains are buried deeper, groundwater seeps into the rock and carries minerals such as calcium and silica. These minerals gradually replace the original organic materials, preserving the shape and structure of the organism.
- Key phrase: Fossilization
- Related terms: Groundwater, minerals, preservation
Finally, the last step in fossil formation is exposure. This occurs when the rock layer containing the fossil is exposed at the surface due to erosion or other geological processes. Once exposed, the fossil can be discovered and studied by paleontologists, who can learn more about the ancient life forms that once inhabited our planet.
- Key phrase: Exposure
- Related terms: Erosion, geological processes, paleontologists
Overall, the fossil formation process is a slow and intricate one. It requires the right conditions of burial, fossilization, and exposure to create fossils that can withstand the test of time. Through the study of fossils, scientists can gain insights into the history of life on Earth and the processes that have shaped it over millions of years.
Importance of Fossils
Fossils play a crucial role in understanding the history and evolution of life on Earth. They provide scientists with valuable information about the past, allowing them to reconstruct ancient ecosystems, track evolutionary changes, and study the biodiversity that existed long before our time.
One of the key benefits of fossils is their ability to provide evidence for the existence of extinct species. Fossils can tell us how these creatures looked, what they ate, and how they lived. They allow us to piece together the puzzle of the past and gain insights into the diversity of lifeforms that have inhabited our planet.
Reconstructing Ancient Ecosystems
Fossils help in reconstructing ancient ecosystems by providing information about the plants, animals, and environments that existed in the past. By studying the remains of plants and animals found in sedimentary rock layers, scientists can gain insights into the ecological relationships between different species and understand how they interacted with their environment.
Tracking Evolutionary Changes
Fossils also allow scientists to track evolutionary changes over time. By comparing the fossils of different species from different time periods, scientists can observe how organisms have evolved and adapted to changing environmental conditions. This helps in understanding the processes that have shaped life on Earth and provides insights into the mechanisms of evolution.
Studying Biodiversity
Fossils provide a unique window into the rich biodiversity that has existed over millions of years. By examining fossilized remains, scientists can document the variety of species that have lived on Earth and study their adaptations, behavior, and ecological roles. This information is crucial for understanding the history and dynamics of biodiversity and can help in conservation efforts by providing insights into natural processes and patterns.
In conclusion, fossils are invaluable resources that provide a glimpse into the past and help us understand the origins and evolution of life on Earth. By studying fossils, scientists can reconstruct ancient ecosystems, track evolutionary changes, and study biodiversity. Fossils are not just remnants of the past, but windows to understanding our planet’s history and the diversity of life that has inhabited it.
Fossil Dating Methods
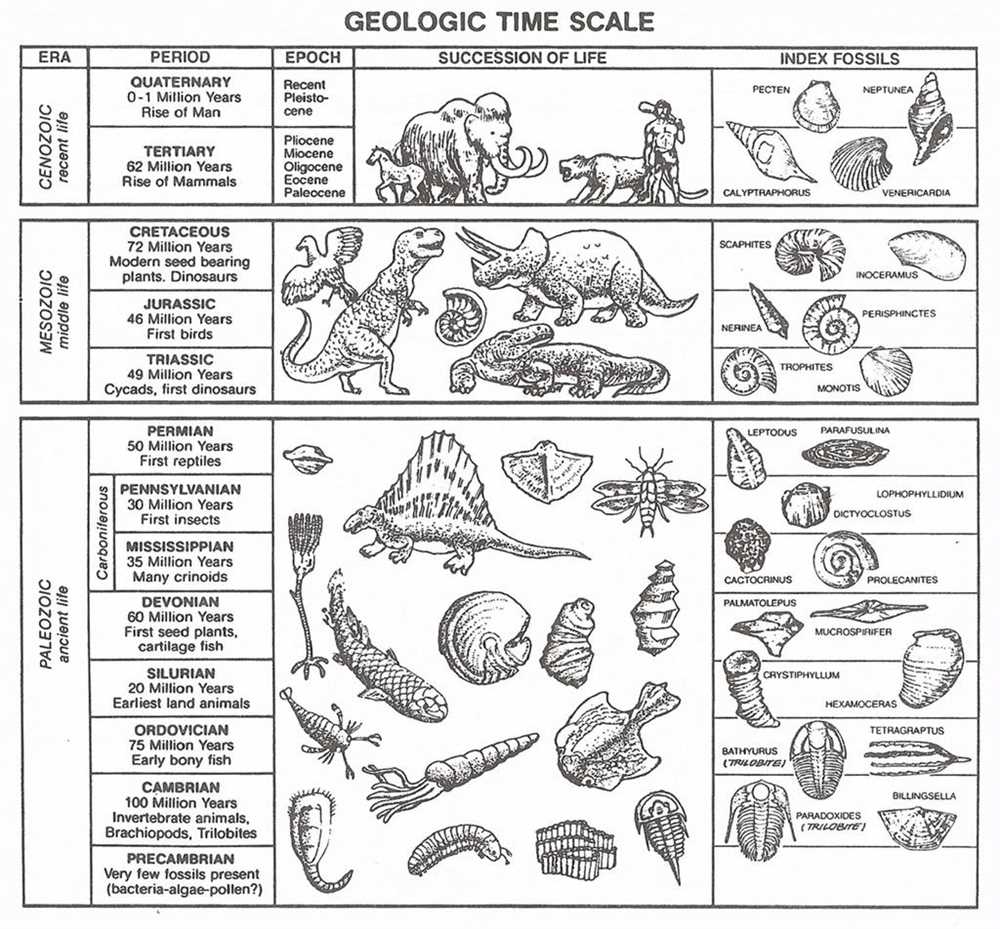
Fossil dating is the process of determining the age of fossils and rocks using various methods. These methods rely on the principles of radioactive decay, fossil succession, and relative dating.
One of the most commonly used methods for dating fossils is radioactive dating. This method uses the decay of radioactive isotopes in rocks and minerals to determine their age. By measuring the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes, scientists can calculate the age of the sample. This method is especially useful for dating rocks and minerals that are hundreds of thousands to billions of years old.
Another method used for dating fossils is fossil succession. This principle states that certain fossils are found only in specific layers of rock, and these layers can be correlated across different locations. By comparing the fossils found in different layers, scientists can determine the relative age of the rocks and fossils. For example, if a fossil of a certain species is found in a layer of rock that is known to be older than another layer containing a different species, it can be inferred that the first species is older than the second species.
In addition to radioactive dating and fossil succession, scientists also use other dating methods such as carbon dating, which uses the decay of carbon-14 isotopes in organic materials, and luminescence dating, which measures the amount of stored energy in minerals. These methods provide additional tools for dating fossils and rocks, and they can be used in combination with other methods to obtain more accurate age estimates.
In conclusion, fossil dating methods are essential for determining the age of fossils and rocks. These methods rely on principles such as radioactive decay, fossil succession, and relative dating, and they provide valuable insights into the Earth’s history and the evolution of life on our planet.