Understanding the foundations of government is crucial for any student of political science or anyone interested in how societies are organized and governed. This article aims to provide answers to a worksheet that explores the foundational principles and structures of government.
In order to understand the foundations of government, it is important to first define some key terms. One of the key terms is sovereignty, which refers to the ultimate authority and power to govern within a specific territory. Another key term is social contract, which is an agreement between the government and the governed that outlines their rights and responsibilities.
The worksheet also explores the different types of government, such as democracy, monarchy, and dictatorship. Democracy is a system of government in which power is vested in the people, who exercise it directly or through elected representatives. Monarchy, on the other hand, is a form of government in which a single individual, usually a king or queen, reigns over the state. Dictatorship, meanwhile, is a form of government in which power is concentrated in the hands of a single leader or a small group of individuals.
Furthermore, the worksheet delves into the concept of separation of powers, which is an important principle in many modern democracies. Separation of powers is the division of government powers among different branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial branches, to prevent the concentration of power in one group or individual. This system of checks and balances ensures that no one branch of government becomes too powerful.
Foundations of Government Worksheet Answers
In this worksheet, we will explore the answers to various questions related to the foundations of government. Understanding the foundations of government is crucial for individuals to comprehend how power and authority are structured within a society.
1. What is the purpose of government?
The purpose of government is to maintain order, provide public services, protect citizens’ rights and freedoms, and promote the general welfare. Government ensures the rule of law and provides a framework for individuals to live in peace and harmony.
2. What is the difference between a monarchy and a democracy?

A monarchy is a form of government in which power is concentrated in the hands of a single ruler, usually a king or queen, who inherits the position. In contrast, a democracy is a system where power is vested in the people, who exercise it directly or through elected representatives. In a democracy, decisions are made through majority rule.
3. What are the main characteristics of a constitutional government?
A constitutional government is a system that is bound by a constitution or a set of fundamental principles and laws that outline the powers and limitations of the government. The main characteristics of a constitutional government include the separation of powers, checks and balances, protection of individual rights, and the rule of law.
4. How does the concept of federalism impact government structure?
Federalism is a system of government in which power is divided between a central government and regional or state governments. This impacts the government structure by creating a dual system of authority, where both the federal and state governments have their own powers and responsibilities. Federalism allows for the distribution of power, enhancing the representation of various interests and promoting a more balanced governance.
5. Why is a system of checks and balances important in a government?

A system of checks and balances is crucial in a government to prevent the abuse of power and ensure that no single branch of government becomes too dominant. It allows each branch of government to check the actions of the other branches and maintain a balance of power. This system helps in promoting accountability and protecting the rights of individuals.
In conclusion, understanding the foundations of government, including its purpose, different forms, characteristics, and systems, is essential for individuals to be well-informed citizens and actively participate in the democratic process. It is through this understanding that citizens can engage in the shaping of their government and society.
Understanding the Structure of Government
The structure of government plays an essential role in ensuring the efficient functioning of a country. It encompasses the various branches and levels of governance that work together to make decisions, enforce laws, and provide essential services to the people. Understanding this structure is crucial for citizens to actively participate in the democratic process and hold their representatives accountable.
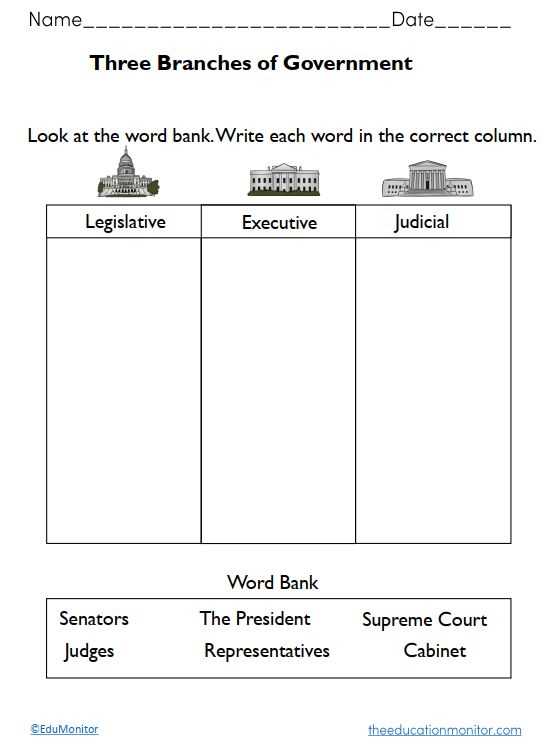
At the federal level, the government is typically divided into three branches: the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. Each branch has separate powers and responsibilities to ensure a system of checks and balances. The executive branch, led by the President or Prime Minister, is responsible for implementing and enforcing laws. The legislative branch, consisting of the elected representatives, has the authority to create and pass laws. The judicial branch, headed by the Supreme Court, interprets the laws and ensures their constitutionality.
Branches of government:
- Executive branch: responsible for implementing and enforcing laws.
- Legislative branch: has the authority to create and pass laws.
- Judicial branch: interprets laws and ensures their constitutionality.
Furthermore, government structure also includes levels of governance, such as local, state, and national governments. Local governments handle issues specific to a particular city or town, such as providing local public services and maintaining infrastructure. State governments have the power to make decisions for an entire state, including education policies and the administration of state laws. The national government oversees matters that affect the entire country, such as defense, foreign affairs, and the economy.
Levels of government:
- Local governments: handle issues specific to a city or town.
- State governments: make decisions for an entire state.
- National government: oversees matters that affect the entire country.
By understanding the structure of government and its various branches and levels, individuals can actively participate in their democratic system. This involvement may include voting for representatives, engaging in political discussions, and advocating for changes in policies or laws. It also allows citizens to hold their government accountable for its actions and ensure that it operates in the best interests of the people it serves.
Key Concepts in Government
In order to understand the foundations of government, it is important to grasp key concepts that shape its structure and function. These concepts encompass the fundamental principles and mechanisms that underpin the governing process. By examining these concepts, we can gain insight into how governments are established and how they function to serve their populations.
Sovereignty is a crucial concept in government, referring to the supreme authority and power that a government holds over its territory and people. Sovereignty allows governments to establish laws, enforce regulations, and make decisions that impact the lives of individuals within their jurisdiction. It also enables governments to represent their country in international affairs, negotiate treaties, and maintain order within their borders.
Separation of powers is another fundamental concept that plays a significant role in government systems. It involves the division of governmental authority among different branches, such as the executive, legislative, and judicial branches. This separation ensures a system of checks and balances, preventing any one branch from becoming too powerful and potentially abusing its authority. The executive branch is responsible for enforcing laws, the legislative branch creates laws, and the judicial branch interprets and applies laws.
Moreover, federalism is a concept that is central to many governments. It refers to the division of power between a central authority and regional or local governments. This allows for the distribution of authority and decision-making among different levels of government, ensuring that power is not concentrated solely at the national level. Federalism can help accommodate diverse regional interests and promote cooperation among different jurisdictions.
The concepts of sovereignty, separation of powers, and federalism are just a few examples of the key principles and mechanisms that shape governments. By understanding these concepts and their applications, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the foundations and functioning of governments worldwide.
The Role of Government in Society
The role of government in society is an essential and multifaceted one. Its primary function is to ensure the well-being and welfare of its citizens by providing them with the necessary services, protection, and infrastructure. Governments have the power to make and enforce laws, maintain order, protect property rights, and promote the common good. They also play a significant role in economic development, education, healthcare, and social welfare.
Laws and Order: One of the crucial roles of the government is to establish and enforce laws to maintain order and protect the rights and freedom of individuals. Laws act as guidelines for behavior and ensure justice and fairness in society. The government provides a system of courts and law enforcement agencies to enforce these laws and ensure public safety and security.
Economic Development: Governments play a crucial role in promoting economic growth and development. They establish fiscal policies, regulate financial institutions, and encourage investments to stimulate economic activity. They also provide funding and support for infrastructure projects, such as roads, bridges, and public transportation, which are essential for business operations and the overall development of the country.
Education and Healthcare: Governments have the responsibility to provide accessible and quality education and healthcare services to their citizens. They establish and regulate educational institutions, develop curriculum standards, and provide financial aid to ensure equal opportunities for all. Similarly, governments create and regulate healthcare systems, provide funding for research and development, and implement policies to ensure access to affordable and quality healthcare for everyone.
Social Welfare: Governments also have a role in promoting social welfare and reducing inequality. They establish social welfare programs, such as unemployment benefits, welfare assistance, and public housing, to provide support for those in need. Governments also implement policies to protect vulnerable groups, such as children, the elderly, and people with disabilities, and to promote equality and social justice.
In conclusion, the role of government in society is diverse and comprehensive. It encompasses ensuring laws and order, promoting economic development, providing education and healthcare services, and promoting social welfare. By fulfilling these roles, governments contribute to the overall well-being and progress of society.
Forms of Government
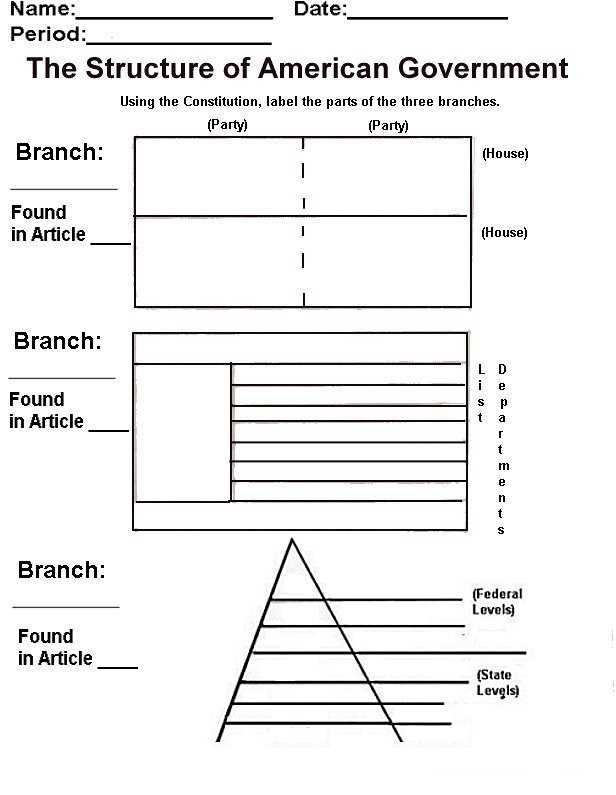
The concept of government and the different forms it can take have been subjects of study and debate throughout history. Governments can be classified into various types based on how power is distributed and exercised within a society. Some of the most common forms of government include monarchy, democracy, oligarchy, and theocracy.
Monarchy: In a monarchy, a single individual, usually a king or queen, holds all the power and authority. This form of government can be hereditary, meaning that power is passed down through generations within a specific family, or it can be an absolute monarchy where the ruler has unlimited power. Monarchies can also be constitutional, where the monarch’s powers are limited by a constitution or parliamentary system.
Democracy: Democracy is a system of government in which power is vested in the people. It allows citizens to participate in decision-making processes and elect representatives who will govern on their behalf. Democratic governments are characterized by the respect for individual rights, the rule of law, and regular elections. There are different types of democracy, such as direct democracy, where citizens directly participate in decision-making, and representative democracy, where citizens elect representatives to make decisions on their behalf.
Oligarchy: Oligarchy is a form of government where power is concentrated in the hands of a few individuals or a small group. These individuals, often referred to as an elite, exercise influence and control over the government and society. Oligarchies can be characterized by wealth, social standing, or specific qualifications that grant a small group authority and power over others. This form of government often lacks transparency and inclusiveness, as decision-making is limited to a select few.
Theocracy: Theocracy is a form of government where religious leaders hold the ultimate authority and govern in accordance with religious principles and laws. In this system, government and religion are intertwined, and religious texts and doctrines often serve as the basis for legislation and governance. Theocracies can vary in how much power religious leaders have and the extent to which religious laws are enforced.
These are just a few examples of the different forms of government that exist. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses and can be influenced by various factors such as history, culture, and the values and beliefs of the people. The study of government and the exploration of different forms are essential for understanding the complexities of political systems and governance.
The Influence of Historical Documents on Government
Historical documents have played a significant role in shaping the foundations of government throughout history. These documents have provided a basis for the establishment of constitutions, laws, and systems of governance in various countries around the world. One such influential historical document is the Magna Carta, which was signed in 1215 by King John of England.
The Magna Carta, or the Great Charter, established the principle that the monarch was not above the law and that individuals had certain rights that the government could not infringe upon. This document laid the groundwork for the development of constitutional law and the protection of individual liberties in England and later in other nations. The ideas expressed in the Magna Carta, such as due process and trial by jury, continue to influence the legal systems of many countries today.
Another seminal historical document is the U.S. Constitution, which was drafted in 1787 and serves as the supreme law of the United States. The Constitution outlines the structure of the government, the powers of its branches, and the fundamental rights of its citizens. It has been the foundation of democratic governance in the United States for over two centuries and has inspired constitution-making efforts worldwide.
Other important historical documents that have influenced government include the Declaration of Independence, the French Declaration of the Rights of Man and of the Citizen, and the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. These documents have articulated fundamental principles such as equality, freedom, and justice, which have guided the development of government systems and the protection of human rights globally.
In conclusion, historical documents have had a profound influence on the establishment and development of governments. They have provided a framework for constitutional law, protected individual liberties, and promoted principles of equality and justice. The ideas and values expressed in these documents continue to shape and guide governments around the world today.