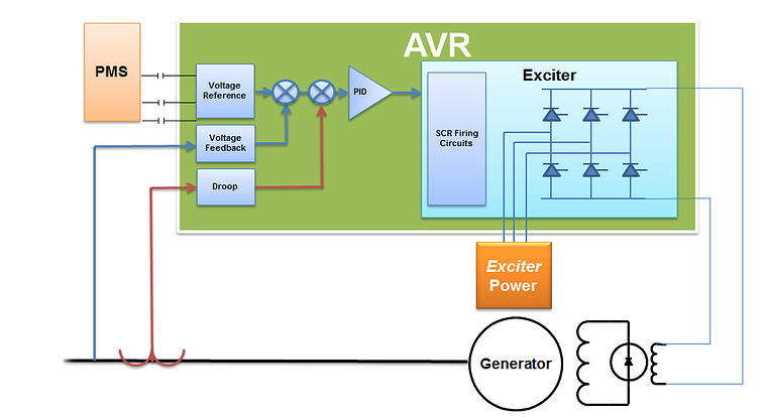
A generator AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator) is an essential component for ensuring the stable operation of a generator. It regulates the voltage output of the generator to maintain a constant and reliable level of power. However, over time, the AVR may deteriorate or malfunction, leading to voltage fluctuations and potential damage to connected appliances and equipment. This is why regular testing of the generator AVR is crucial to ensure proper functioning and prevent costly repairs.
Testing the generator AVR involves several steps to evaluate its performance and identify any issues. First, it is important to check the physical condition of the AVR for any signs of damage or loose connections. Any visible problems should be addressed before proceeding with further testing.
Next, a voltage output test is conducted by connecting a voltmeter to the generator output terminals. The generator is then started, and the voltage reading is observed. The AVR should regulate the voltage output to a stable level within the specified range. Any significant fluctuations or deviations from the desired voltage indicate a potential problem with the AVR.
Another important aspect of generator AVR testing is the load test. This involves connecting various electrical devices to the generator and observing how the AVR handles the load. The AVR should maintain a constant voltage output even under different load conditions. Fluctuations or voltage drops during the load test may indicate an issue with the AVR’s ability to handle varying loads.
In conclusion, regular testing of the generator AVR is essential for ensuring its proper functioning and preventing electrical damage to connected equipment. By following the necessary testing procedures and addressing any issues promptly, generator owners can maintain the reliability and longevity of their power supply.
Generator Avr Test: A Comprehensive Guide
The generator AVR test is an essential step in ensuring the proper functioning of a generator’s Automatic Voltage Regulator (AVR). The AVR plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable output voltage, protecting the generator and its connected devices from voltage fluctuations. Conducting a comprehensive AVR test helps identify any issues or malfunctions in the system, allowing for timely repairs and maintenance.
Why is the AVR test necessary?
The AVR is responsible for regulating the generator’s output voltage and maintaining it within a specified range, regardless of changes in the load or input conditions. If the AVR malfunctions, it can result in voltage spikes or drops, which can damage electrical equipment and disrupt power supply. Therefore, performing regular AVR tests is crucial to ensure the overall reliability and performance of the generator.
How is the AVR test conducted?
There are various methods to conduct an AVR test, depending on the type and model of the generator. One common approach is to use a load bank to simulate variable loads and measure the response of the AVR. This helps assess the AVR’s ability to maintain a stable voltage output under different load conditions. Additionally, voltage and frequency measurements are taken to ensure compliance with the generator’s specifications.
Key parameters to consider during the AVR test:
- Voltage regulation: The AVR should maintain the generator’s output voltage within a specified tolerance range, typically around ±5%. Deviations beyond this range indicate a potential AVR malfunction.
- Response time: The AVR should respond quickly to load changes, adjusting the voltage output to maintain stability. Slow response times can lead to voltage fluctuations and affect the performance of connected devices.
- Overload protection: The AVR should have built-in protection mechanisms to prevent excessive loads from damaging the generator. During the test, load conditions should gradually increase, and the AVR’s response to overload situations should be observed.
- Harmonics and waveform distortion: The AVR should ensure a clean and stable voltage waveform, free from distortions and harmonics. Measurements should be taken to verify the overall waveform quality.
Conclusion:
The generator AVR test is a crucial part of generator maintenance and troubleshooting. By conducting regular tests, generator owners can ensure the longevity and optimal performance of their equipment. The comprehensive nature of the test allows for the identification of any AVR issues, enabling prompt repairs and minimizing the risk of voltage-related damages. Therefore, investing time and resources in AVR testing is vital for any generator owner or operator.
What is a Generator AVR?
A Generator AVR (Automatic Voltage Regulator) is an essential component of a generator that ensures a stable output voltage. It regulates the voltage produced by the generator to protect sensitive electrical equipment from damage due to voltage fluctuations. The AVR monitors the output voltage and makes necessary adjustments to maintain a constant voltage level.
Generators are often used in situations where continuous and reliable power supply is required, such as during power outages or in remote locations. However, the voltage produced by generators can fluctuate due to variations in the engine speed or load changes. These voltage fluctuations can be harmful to electrical devices and may cause them to malfunction or even get damaged.
The Generator AVR acts as a control system that stabilizes the output voltage of the generator. It does so by adjusting the excitation current supplied to the generator’s alternator. When the output voltage drops below the desired level, the AVR increases the excitation current to raise the voltage, and vice versa when the voltage is too high.
The AVR constantly monitors the generator’s output voltage and makes rapid adjustments to maintain a steady voltage within a specified range. This ensures that the electrical devices connected to the generator receive a constant and stable voltage supply, protecting them from potential damage. Generator AVRs are available in various types and models, each designed to suit specific generator setups and requirements.
The Importance of Testing Generator AVR
Generator AVR, or Automatic Voltage Regulator, is a crucial component in a generator system as it ensures stable and reliable electricity output. Testing the generator AVR is essential to ensure its proper functioning and prevent any potential issues that may arise during operation.
One of the primary reasons for testing generator AVR is to ensure that it maintains a steady voltage output regardless of the load variations. Voltage fluctuations can cause damage to sensitive electronic devices or appliances connected to the generator. By testing the AVR, it can be determined if it is functioning correctly and maintaining the desired voltage level.
Testing the generator AVR also helps in identifying any potential faults or defects in the system. This allows for timely maintenance and repair, preventing any major breakdowns or power outages. Regular testing and inspection of the AVR can help in detecting small issues early on before they turn into more significant problems.
In addition, testing the generator AVR enables performance analysis and optimization. By conducting tests under different load conditions, the efficiency and overall performance of the AVR can be evaluated. This can help in identifying areas where improvements can be made, such as adjusting the voltage regulation settings or optimizing the control algorithm.
Overall, the importance of testing generator AVR cannot be overstated. It ensures the stability and reliability of the electricity output, helps in detecting and addressing any faults or defects, and allows for performance analysis and optimization. Regular testing and maintenance of the AVR are essential for efficient and trouble-free operation of generator systems.
Common Issues with Generator AVR
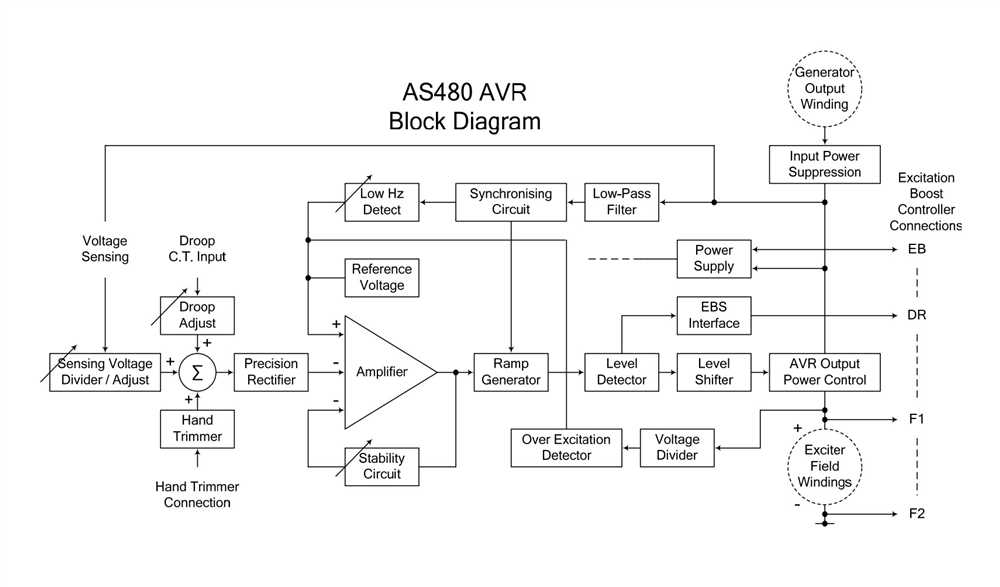
Automatic voltage regulators (AVRs) play a crucial role in ensuring a stable and constant supply of electricity from generator systems. However, like any other component, AVRs can experience issues that can impact their performance. Understanding these common issues can help in diagnosing and resolving problems effectively.
1. Overvoltage Protection Failure: One common issue with generator AVRs is a failure in overvoltage protection. This can occur when the AVR fails to regulate the voltage properly, leading to excessive voltage supplied to connected equipment. Overvoltage can damage sensitive electronics and appliances, so it is essential to address this issue promptly.
2. Underfrequency Protection Failure: Another common issue with generator AVRs is a failure in underfrequency protection. This occurs when the AVR fails to regulate the frequency of the generated electricity, resulting in a frequency below the optimal range. Underfrequency can cause electrical equipment to malfunction or operate inefficiently, so resolving this issue is crucial to maintain smooth operations.
3. Voltage Instability: Generator AVRs can also face issues related to voltage instability. This can manifest as voltage fluctuations or voltage drops. These issues can lead to equipment malfunctions, especially in sensitive electronics. Voltage instability can be caused by various factors, including faulty AVR components, improper wiring, or load imbalances. Identifying the root cause of voltage instability is essential for resolving this issue effectively.
4. Overloading: Overloading the generator AVR is another common issue that can occur when the connected load exceeds the generator’s capacity. This can lead to overheating of the AVR and potentially cause damage to the generator system. Monitoring the load and ensuring that it stays within the generator’s rated capacity can help prevent overloading issues.
5. Faulty Connections: Faulty connections can also cause issues with generator AVRs. Loose or damaged connections can disrupt the flow of electricity, affecting the AVR’s ability to regulate voltage and frequency effectively. Regular inspection and maintenance of connections can help prevent this issue and ensure proper functioning of the AVR.
- Summary:
- – Overvoltage and underfrequency protection failures
- – Voltage instability
- – Overloading
- – Faulty connections
How to Prepare for the Test
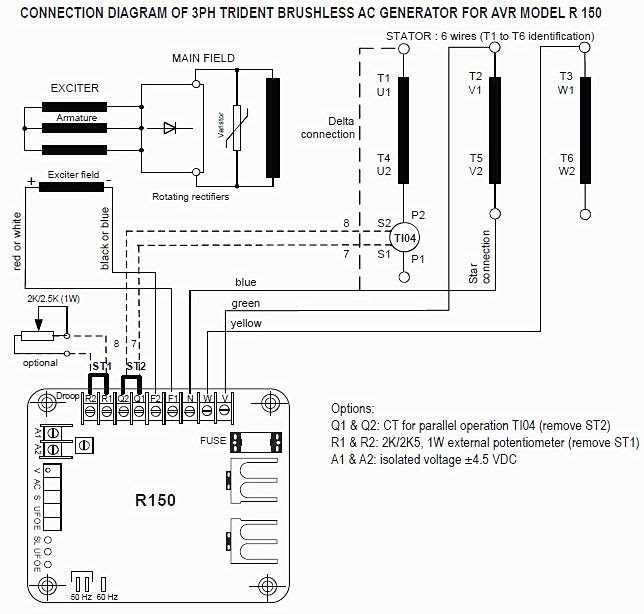
Preparing for a generator AVR test is essential if you want to perform well and ensure the proper functioning of your generator. Here are some steps you can take to effectively prepare for the test:
1. Familiarize yourself with the generator AVR: Take the time to understand the basic principles of how the generator AVR works and its various components. This will help you grasp the test requirements and troubleshoot any potential issues during the test.
2. Review the test specifications: Obtain the test specifications and guidelines provided by the manufacturer or testing authority. These documents will outline the specific procedures, parameters, and performance requirements for the generator AVR test. Understanding these details will help you tailor your preparation efforts accordingly.
3. Gather the necessary tools and equipment: Make sure you have all the required tools and equipment for the test. This may include a multimeter, oscilloscope, load bank, and appropriate safety gear. Ensure that your tools are in good working condition and calibrated properly to obtain accurate test results.
4. Perform a pre-test inspection: Before conducting the test, inspect the generator AVR for any visible damage or signs of wear. Check the electrical connections, wiring, and overall condition of the AVR. Address any issues or concerns found during the inspection to avoid potential complications during the test.
5. Create a testing environment: Set up a proper testing environment that is safe and conducive to accurate measurements. Ensure that the generator is properly grounded and isolated from any potential hazards. Create a checklist of safety protocols and adhere to them throughout the testing process.
6. Practice test procedures: Familiarize yourself with the test procedures by practicing them beforehand. This can include connecting the generator to the load bank, measuring voltage and frequency outputs, and adjusting the AVR parameters. Practicing the procedures will help you become comfortable with the steps involved and improve your efficiency during the actual test.
7. Keep documentation and records: Maintain a logbook or record of all your test preparations and results. This will help you track your progress, identify any recurring issues, and compare the performance of the generator AVR over time. It will also serve as a valuable reference for future test preparations.
By following these steps and investing time in proper preparation, you can increase your chances of success in the generator AVR test. Remember to stay focused, adhere to safety protocols, and consult experts or relevant resources if you encounter any challenges along the way.
Tools and Equipment Needed for Testing
When it comes to testing generator AVR, there are a few essential tools and equipment that are necessary to ensure accurate and reliable results. These tools are designed to measure and assess the various components of the AVR system, helping to identify any issues or malfunctions that may be affecting its performance.
One of the most important tools needed for testing generator AVR is a multimeter. This device is used to measure electrical voltage, current, and resistance, allowing technicians to check the output levels of the AVR system. By using a multimeter, it is possible to identify any deviations from the expected values and troubleshoot potential problems.
- Signal generator: A signal generator is used to generate various electrical signals that simulate different operating conditions. This is beneficial for testing the response and functionality of the AVR system under different scenarios.
- Load bank: A load bank is a device that provides an artificial load to the generator, simulating real-world conditions. This is important for testing the AVR’s ability to regulate and maintain a steady output voltage under different load conditions.
- Oscilloscope: An oscilloscope is a tool that allows technicians to visualize and analyze electrical waveforms. It can be used to monitor and record the output voltage of the generator AVR, providing valuable insights into its performance and stability.
- AVR test bench: An AVR test bench is a specialized piece of equipment that is designed specifically for testing and calibrating AVR systems. It provides a controlled environment for conducting tests and allows for precise adjustments and measurements to be made.
In addition to these tools, it is also important to have a good understanding of the generator AVR system and its operation. This includes knowledge of the different components, their functions, and common issues that may arise. With the right tools and expertise, technicians can effectively diagnose and resolve any problems with the generator AVR, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.