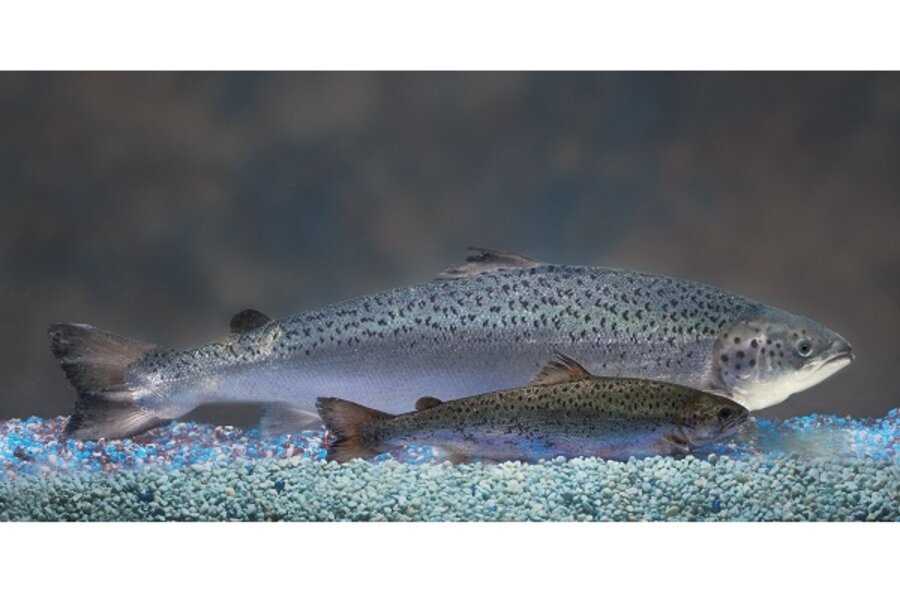

Genetically modified salmon, commonly referred to as “frankenfish,” is a highly controversial topic in the realm of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) and food production. This article aims to provide an answer key for the questions surrounding this genetically engineered fish, shedding light on the key aspects and concerns associated with its production and consumption.
Firstly, it is essential to understand the process behind genetically modifying salmon. Scientists use advanced biotechnology techniques, such as gene splicing and genetic engineering, to introduce specific desirable traits into the DNA of salmon. These traits can include faster growth rates, increased disease resistance, and enhanced tolerance to environmental conditions.
The development of genetically modified salmon offers potential benefits, including increased food production to meet the growing global demand for fish. These modified fish can grow more quickly, resulting in shorter production cycles and reduced pressure on wild salmon populations. However, critics argue that these potential benefits come with significant risks and concerns.
One of the main concerns surrounding genetically modified salmon is the potential environmental impact. Escapees from fish farms could compete with wild salmon for resources and disrupt natural ecosystems. There are also concerns about the spread of modified genes to wild populations, which could have long-term consequences for biodiversity and the overall health of aquatic ecosystems. Another concern is the impact on human health, as the health effects of consuming genetically modified salmon are still not fully understood.
Genetically Modified Salmon Food or Frankenfish Answer Key
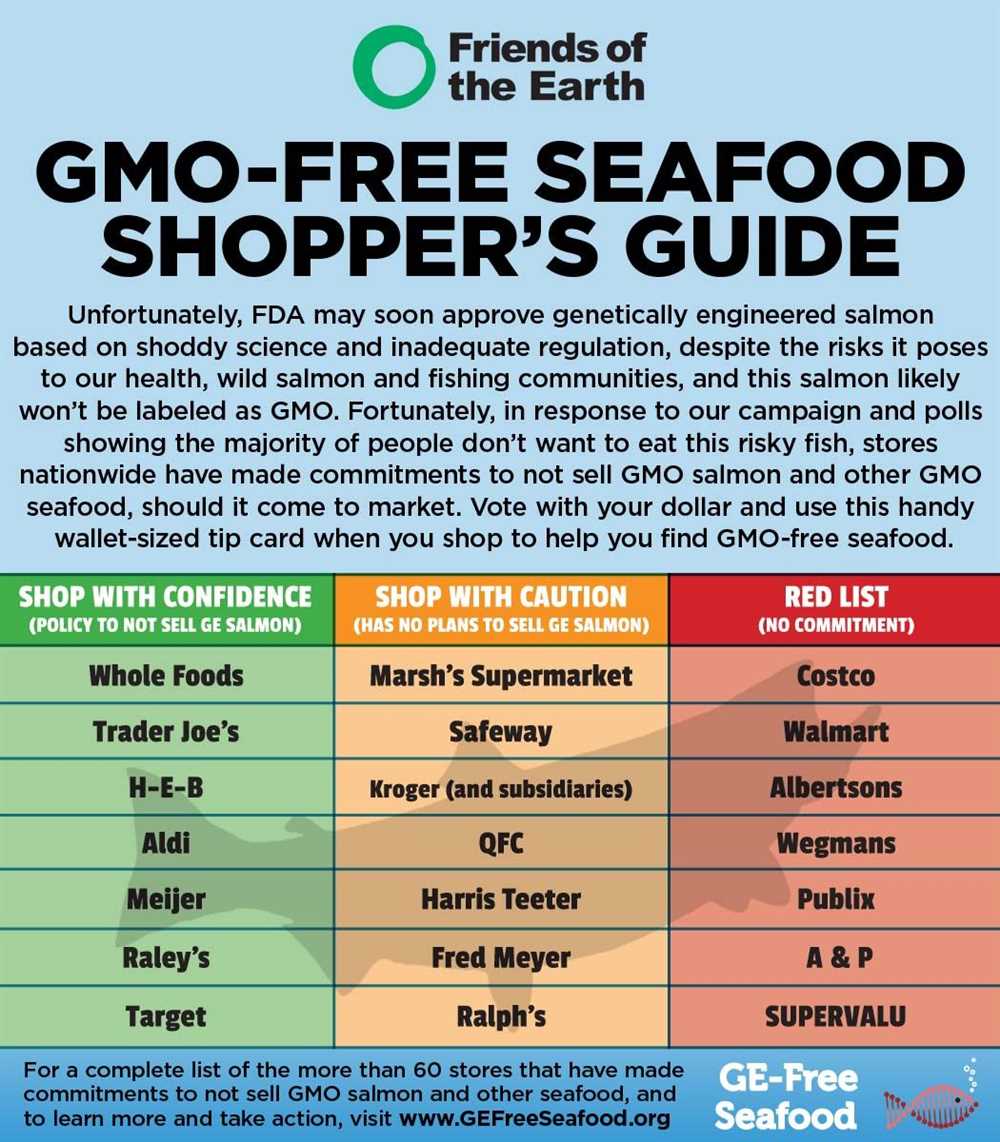
Genetically modified salmon, also known as “frankenfish,” has been a topic of heated debate in recent years. While some argue that GM salmon can help address the growing demand for seafood and reduce pressure on wild fish populations, others have concerns about the potential risks to human health and the environment.
Proponents of genetically modified salmon argue that it has several advantages over traditional wild-caught or farm-raised salmon. They claim that GM salmon can grow faster, allowing for more efficient production and potentially reducing the need for overfishing. Additionally, they argue that GM salmon can be engineered to be more resistant to diseases, reducing the need for antibiotics and improving overall fish health.
However, critics of genetically modified salmon have raised several concerns. One major issue is the potential for GM salmon to escape from fish farms and interbreed with wild salmon populations, potentially reducing genetic diversity and disrupting ecosystems. There are also concerns about the long-term effects of consuming GM salmon on human health, as well as the potential for allergenic reactions to the altered genes.
In conclusion, the debate over genetically modified salmon is complex and multifaceted. While there are potential benefits to GM salmon in terms of increasing seafood production and reducing pressure on wild fish populations, there are also valid concerns about the potential risks to human health and the environment. Ultimately, it is important to carefully consider the scientific evidence and engage in informed discussions to make informed decisions about the future of genetically modified salmon.
Understanding Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
Genetically modified organisms (GMOs) are living organisms whose genetic material has been altered in a laboratory using genetic engineering techniques. This process involves the manipulation of an organism’s DNA, genetic material responsible for its characteristics and traits, in order to introduce or remove specific traits.
GMOs are created through the use of modern biotechnology tools and techniques that enable scientists to directly modify an organism’s genetic code. This is done by transferring genes from one organism to another, or by altering the existing genes within an organism. These genetic modifications can result in a wide range of desired traits, such as increased resistance to pests or diseases, enhanced nutritional value, or improved crop yield.
Genetically modified salmon, also known as “frankenfish,” is one such example of a GMO. These salmon are engineered to grow faster and larger than their non-modified counterparts by incorporating a growth hormone gene from another fish species. However, the creation and consumption of genetically modified salmon have raised concerns and controversy due to potential environmental impacts and food safety issues.
- Some argue that GMOs offer significant benefits, such as increased crop productivity and improved nutritional content, which can help address global food security and malnutrition.
- Others express concerns about the potential long-term effects of GMOs on human health and the environment, such as the development of antibiotic resistance or the transfer of modified genes to non-target organisms.
- Regulations and labeling requirements for GMOs vary across countries, with some implementing strict regulations and mandatory labeling, while others have more relaxed policies.
Understanding the science, benefits, and risks associated with GMOs is crucial in order to make informed decisions about their use and consumption. Ongoing research and public debates continue to shape the future of GMOs, as scientists, policymakers, and consumers navigate the complexities of this controversial topic.
The Debate Surrounding Genetically Modified Salmon

The topic of genetically modified salmon has sparked a heated debate among scientists, environmentalists, and consumers. On one hand, proponents argue that genetically modified salmon can help address the growing demand for seafood and provide a more sustainable and efficient way to feed the world’s population. They believe that genetically modifying salmon can make them grow faster, bigger, and more resistant to diseases, thus increasing their availability and reducing the pressure on wild fish stocks.
However, opponents of genetically modified salmon raise concerns about the potential risks and unknown long-term effects of consuming such fish. They worry that the genetic modifications could have unintended consequences, such as allergic reactions or harmful effects on human health. Furthermore, critics argue that genetically modified salmon could escape into the wild and interbreed with wild salmon populations, potentially causing irreversible damage to delicate ecosystems and threatening the biodiversity of native fish species.
These differing viewpoints have led to a complex and contentious regulatory landscape surrounding genetically modified salmon. In the United States, for example, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the commercial production and sale of genetically modified salmon in 2015. However, the decision faced significant opposition, with environmental organizations and consumer advocacy groups filing lawsuits to block its introduction into the market. While genetically modified salmon is currently available for consumption in the US, it continues to be a highly controversial and polarizing issue.
As the debate around genetically modified salmon continues, it is clear that both sides have valid concerns and arguments. The key lies in striking a balance between innovation and precautionary measures to ensure the safety and sustainability of our food supply. It is essential for regulators, scientists, and consumers to engage in open and transparent discussions, considering the potential benefits as well as the potential risks associated with genetically modified salmon, in order to make informed decisions about its future.
Benefits of Genetically Modified Salmon
Genetically modified salmon, also known as frankenfish, has been a topic of debate and controversy. However, there are several potential benefits that come with genetically modifying these fish.
1. Increased food production: Genetically modified salmon can grow faster and larger than conventional salmon. This means that farmers can produce more salmon in a shorter period of time, which can help meet the growing demand for seafood. With the world’s population constantly increasing, genetically modified salmon can be a valuable tool in increasing food production and addressing global food security.
2. Enhanced nutritional value: Genetic modification can also be used to enhance the nutritional value of salmon. For example, scientists have successfully developed genetically modified salmon that are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart health. By increasing the omega-3 content in salmon, consumers can benefit from a healthier diet and potentially reduce the risk of heart disease.
- Genetically modified salmon has the potential to increase food production and address global food security.
- Genetic modification can enhance the nutritional value of salmon, making it a healthier choice for consumers.
- By modifying the genes of salmon, scientists can make them more resistant to diseases and parasites, reducing the need for antibiotics and pesticides.
- The introduction of genetically modified salmon can also have positive environmental impacts, as it can reduce the pressure on wild fish populations.
3. Disease resistance: By modifying the genes of salmon, scientists can make them more resistant to diseases and parasites. This can help reduce the need for antibiotics and pesticides in fish farming, promoting sustainable and environmentally-friendly practices.
4. Environmental impact: The introduction of genetically modified salmon can also have positive environmental impacts. By increasing the production of farmed salmon, the pressure on wild fish populations can be reduced. This can help protect vulnerable species and maintain the balance of ecosystems.
In conclusion, while the debate around genetically modified salmon continues, it is important to consider the potential benefits that come with genetic modification. Increased food production, enhanced nutritional value, disease resistance, and positive environmental impacts are just some of the advantages that genetically modified salmon can offer. It is crucial to conduct further research and engage in informed discussions to fully understand and evaluate the implications of genetically modified salmon.
Potential Risks of Genetically Modified Salmon
Genetically modified salmon, also known as “frankenfish,” has been a topic of controversy and concern for many consumers and activists. While proponents argue that genetically modifying salmon can help meet the increasing demand for seafood and provide potential benefits such as faster growth rates and disease resistance, there are several potential risks associated with this technology.
1. Environmental impact
One of the major concerns regarding genetically modified salmon is the potential environmental impact. If these genetically modified fish were to escape into the wild, they could pose a threat to native salmon populations. There is a risk that these genetically modified fish could outcompete native species for resources or interbreed with wild populations, causing genetic contamination and irreversible damage to the ecosystem.
2. Unknown health effects
Another significant concern is the unknown health effects of consuming genetically modified salmon. While proponents argue that these fish are safe to eat, there is limited research on the long-term impact of consuming genetically modified organisms (GMOs) on human health. Some studies have suggested potential allergenic reactions or other adverse effects, raising questions about the safety of genetically modified salmon.
3. Ethical and animal welfare concerns
There are also ethical and animal welfare concerns associated with genetically modified salmon. The process of genetic modification often involves techniques such as gene editing or inserting genes from other species into the fish. This raises ethical questions about manipulating the genetic makeup of animals for human consumption and the potential suffering or harm caused to the salmon during the modification process.
4. Regulatory challenges
Regulating genetically modified salmon also poses a challenge. Currently, there is no specific regulation in place for genetically modified animals intended for food consumption. This lack of regulation raises concerns about the potential for inadequate safety assessments and monitoring of the effects of genetically modified salmon on human health and the environment.
In conclusion, while genetically modified salmon may offer potential benefits, such as increased food production, it is essential to consider the potential risks associated with this technology. The environmental impact, unknown health effects, ethical concerns, and regulatory challenges all contribute to the debate surrounding genetically modified salmon and highlight the need for thorough research and assessment before widespread adoption.
Regulatory Efforts and Labeling Requirements

Regulatory efforts and labeling requirements play a crucial role in addressing concerns over genetically modified salmon or “frankenfish”. Various regulatory bodies, such as the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, have been involved in evaluating and approving the safety of genetically modified organisms (GMOs) for commercial use. These efforts aim to ensure that GMOs, including genetically modified salmon, are safe for consumption and do not pose significant risks to human health or the environment.
The FDA has established a rigorous process for evaluating genetically modified salmon before it can be marketed. This process involves assessing the potential risks and benefits of the GMO, as well as conducting detailed scientific reviews and consultations with experts. If the FDA determines that the genetically modified salmon is safe and substantially equivalent to non-modified counterparts, it may grant approval for commercialization.
To address concerns regarding consumer choice and transparency, labeling requirements have also been implemented in some countries. These requirements mandate that genetically modified salmon and other GMOs must be labeled as such, allowing consumers to make informed decisions about the products they purchase and consume. Labeling can provide transparency, facilitate product traceability, and empower consumers to choose whether they want to support or avoid GMOs.
However, the issue of labeling requirements for genetically modified salmon remains a contentious topic. Some argue that labeling is necessary to protect consumer rights and provide clear information, while others believe that labeling may create unnecessary fears and stigmatize genetically modified products. Balancing the interests of consumers and industry stakeholders is a complex task, and regulatory bodies continue to reassess and adapt labeling policies based on scientific advancements, public opinion, and international standards.