
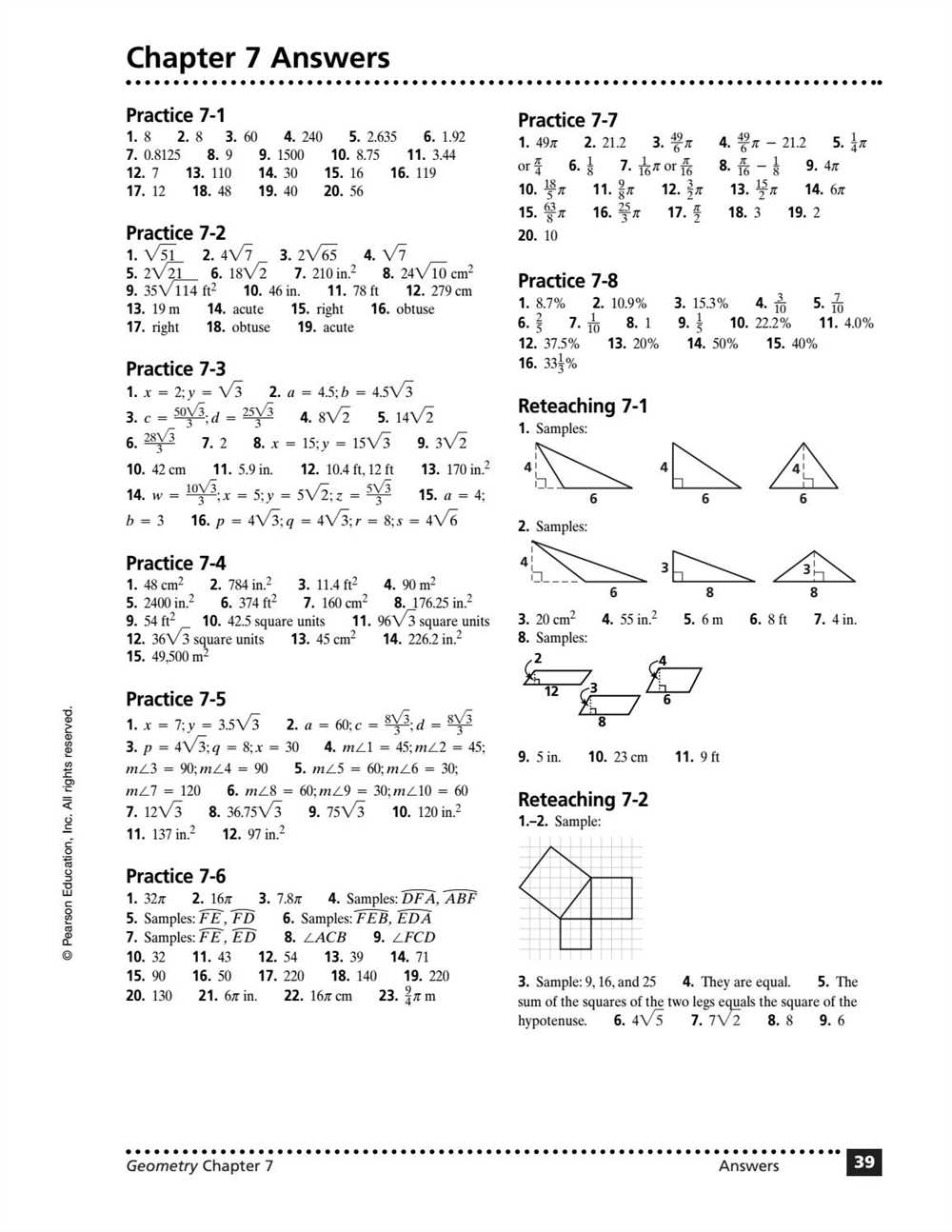
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, their properties, and the relationships between them. It is a fundamental subject that lays the foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts. As students progress in their geometry studies, they are often required to take tests to assess their understanding of the material covered in each chapter.
Chapter 1 of a geometry textbook typically introduces basic concepts such as points, lines, planes, and angles. It is crucial for students to master these concepts as they form the basis for further exploration of geometry. To aid students in their preparation for Chapter 1 tests, many textbooks provide sample tests in PDF format for practice.
A Geometry Chapter 1 test PDF usually includes a variety of questions that assess a student’s knowledge of the basic concepts introduced in the chapter. These questions may involve identifying and classifying different types of angles, drawing and labeling geometric figures, solving problems using the properties of lines and angles, and understanding the relationship between points, lines, and planes.
By practicing with a Geometry Chapter 1 test PDF, students can familiarize themselves with the types of questions they may encounter on the actual test. This allows them to identify areas where they may need additional study and review, helping them to improve their understanding of the material and achieve better results on the test.
What is Geometry?

Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with the study of shapes, sizes, and properties of figures and spaces. It is derived from the Greek words “geo” meaning Earth and “metron” meaning measurement. Geometry can be described as the study of space and its properties, including points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids.
Geometry has been studied for thousands of years and has played a vital role in various fields such as architecture, engineering, art, and astronomy. The Greek mathematician Euclid is considered the father of geometry, as he wrote the influential book “Elements” around 300 BCE, which laid the foundation for the subject.
In geometry, points are considered as the basic building blocks, and they are represented by dots. Lines are straight paths that extend in both directions without an end. Angles are formed when two lines meet at a point. Surfaces refer to flat, two-dimensional figures, while solids are three-dimensional objects.
Geometry helps us understand the relationships between shapes and objects in the physical world. It allows us to calculate areas, volumes, and distances and provides a framework for understanding patterns and symmetry. Geometry also helps develop logical reasoning and problem-solving skills, as it requires careful observation and logical deduction.
Overall, geometry is a fundamental branch of mathematics that helps us make sense of the spatial world around us and provides a foundation for many other disciplines.
Importance of Geometry
Geometry is a fundamental branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of shapes, sizes, figures, and spaces. It plays a crucial role in various fields and aspects of our daily lives. Understanding geometry is important for several reasons.
Firstly, geometry helps us make sense of our physical world. It allows us to understand and describe the shape, size, and position of objects around us. Whether it’s determining the area of a room, calculating the volume of a container, or measuring distances using angles, geometry provides us with the tools to analyze and comprehend the physical dimensions of objects and spaces.
Moreover, geometry is essential in many practical applications and professions. Architects, engineers, and designers use geometry to create and construct buildings, bridges, and structures with precision. Without a solid understanding of geometric principles, the construction industry would not be able to function effectively.
Geometry also plays a significant role in fields such as computer graphics, computer-aided design (CAD), and video game development. These industries rely on geometric algorithms and models to create realistic 3D simulations and graphics. An understanding of geometry is essential for professionals working in these fields to create visually appealing and accurate virtual spaces.
Furthermore, geometry fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It requires logical reasoning and the ability to visualize and manipulate figures and shapes mentally. By engaging in geometric problem-solving, students develop analytical thinking, spatial reasoning, and mathematical inference skills that are transferable to other areas of life.
In summary, geometry is a crucial branch of mathematics that has both practical and theoretical applications. It helps us understand and navigate the physical world, is essential in various professions and industries, and enhances critical thinking skills. Whether you’re an architect, engineer, artist, or simply a student, a solid understanding of geometry is invaluable.
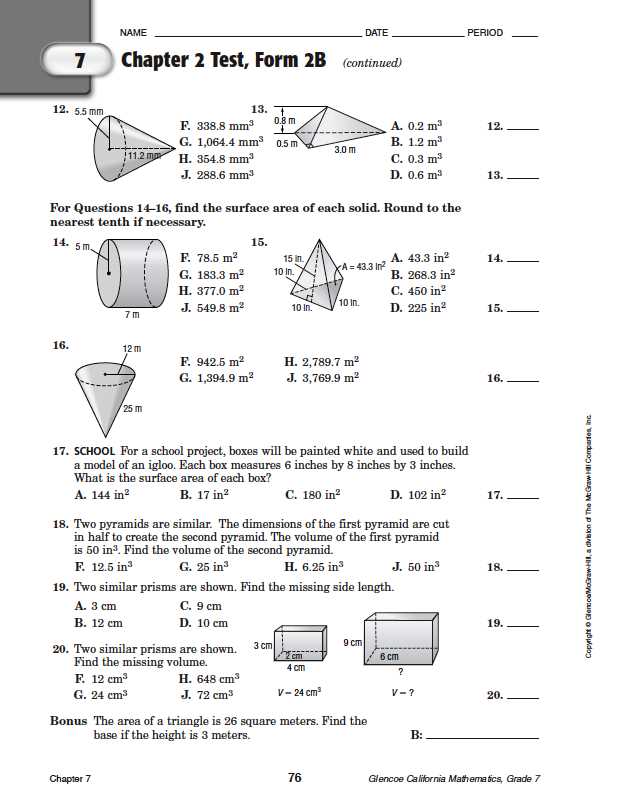
Chapter 1 Test PDF
In geometry, Chapter 1 often covers fundamental concepts such as points, lines, and planes, as well as angles, segments, and polygons. To assess students’ understanding of these concepts, a Chapter 1 test is usually given. This test is often provided in a PDF format, which allows for easy distribution and printing.
The Chapter 1 test PDF typically contains a variety of questions that require students to apply their knowledge of the basic geometry concepts. These questions may include identifying different types of angles or polygons, solving problems involving the measurement of angles or lengths, and determining the relationships between different geometric figures.
One common format for the Chapter 1 test PDF is a multiple-choice style, where students are given a question and several possible answer choices. This format allows for quick grading and provides immediate feedback to students. It also helps to reinforce the key concepts covered in Chapter 1.
Another possible format for the Chapter 1 test PDF is a short answer or problem-solving style. In this format, students may be required to show their work and provide a detailed explanation for their answers. This format encourages critical thinking and allows students to demonstrate a deeper understanding of the geometry concepts.
Overall, the Chapter 1 test PDF serves as an essential assessment tool for both teachers and students in the study of geometry. It helps to gauge students’ comprehension of the foundational concepts and allows for targeted instruction and remediation as needed. By completing the Chapter 1 test PDF, students can solidify their understanding of geometry and prepare for more advanced topics in the subject.
Overview of the Chapter 1 Test

As we wrap up our first chapter on geometry, it is time to put our knowledge to the test. The Chapter 1 test will assess your understanding of the fundamental concepts and principles we have covered so far.
The test will consist of multiple-choice, true/false, and short answer questions, testing your ability to identify geometric shapes, understand their properties, and apply geometric formulas. It is important to review your notes and study materials to ensure you are prepared for the test.
Key Topics Covered:
- Basic geometric shapes and their properties
- Angles and their measurements
- Lines and line segments
- Parallel and perpendicular lines
- Triangles and their classifications
- Quadrilaterals and their classifications
- Circles and their properties
Remember to bring a scientific calculator and any necessary formulas or notes. Be sure to answer each question fully and show your work when applicable. Good luck!
Below is a table of the test breakdown:
| Question Type | Number of Questions | Total Points |
|---|---|---|
| Multiple-Choice | 15 | 30 |
| True/False | 10 | 20 |
| Short Answer | 5 | 50 |
| Total | 100 | |
Test Format and Structure
When preparing for a geometry test, it is important to understand the format and structure of the test in order to effectively study and review the material. Knowing what to expect can help to alleviate test anxiety and ensure that you are well-prepared for the assessment.
The test format typically consists of a combination of different question types, including multiple choice, true or false, fill in the blank, and problem-solving questions. These different question types assess your understanding of concepts, ability to apply formulas and principles, and critical thinking skills. It is important to review the material thoroughly and practice solving different types of questions in order to become familiar with the format and build confidence in your abilities.
Multiple choice: In multiple choice questions, you are presented with a question and several answer choices. Your task is to select the correct answer from the given options. It is important to carefully read the question and all the answer choices before making your selection, as sometimes there may be distractors that can mislead you.
True or false: True or false questions require you to determine whether a statement is true or false based on your knowledge of the subject matter. It is crucial to pay attention to the wording of the statement and consider any exceptions or special cases that may affect its accuracy.
Fill in the blank: Fill in the blank questions involve completing a sentence or phrase by filling in the missing word or words. These questions require you to have a solid understanding of key terms and definitions related to geometry.
Problem-solving: Problem-solving questions are designed to assess your ability to apply geometric principles and formulas to solve real-world or theoretical problems. These questions may require you to draw diagrams, calculate measurements, or determine the relationships between different geometric elements.
By familiarizing yourself with the different question types and practicing solving various types of questions, you can improve your test-taking skills and increase your chances of success on the geometry test.
Topics Covered in the Test:
The Geometry chapter 1 test covers a range of topics related to basic geometric principles and concepts. Students will be evaluated on their understanding and application of these key areas:
-
Lines and Angles: Students will be required to identify and classify different types of lines and angles, such as parallel lines, perpendicular lines, acute angles, obtuse angles, and right angles. They will also need to solve problems involving the properties of angles formed by transversals.
-
Triangles: Knowledge of the properties of triangles will be assessed in this test. Students should be able to classify triangles based on the length of their sides (scalene, isosceles, or equilateral) and the measure of their angles (acute, obtuse, or right). They should also be able to apply the triangle inequality theorem to determine whether or not a set of side lengths could form a triangle.
-
Polygons: Understanding the properties of polygons is crucial in geometry. Students will need to identify and classify different types of polygons based on the number of sides and angles they have. They should also be able to calculate the sum of the interior angles of a polygon using the formula (n – 2) * 180, where n is the number of sides.
-
Geometric Transformations: Students will be tested on their knowledge of geometric transformations, such as translations, rotations, reflections, and dilations. They should be able to identify the transformation performed on a figure based on its image and describe the effects of various transformations on the properties of shapes.
-
Coordinate Geometry: This test will assess students’ ability to plot and locate points on a coordinate plane, as well as their understanding of the distance formula and midpoint formula. They should also be familiar with the concept of slope and its application in determining parallel and perpendicular lines.
In order to perform well on the Geometry chapter 1 test, students should review these topics thoroughly and practice solving related problems. It is important to understand the definitions, properties, and formulas associated with each concept in order to confidently apply them in different situations.
Sample Questions and Answers
In this section, you will find a comprehensive list of sample questions and their corresponding answers to help you practice for your geometry chapter 1 test. These questions cover various topics such as points, lines, angles, and triangles.
1. What is the starting point of a line segment called?
The starting point of a line segment is called the endpoint. It is the point where the line segment begins.
2. Define an acute angle.
An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90 degrees. It is smaller than a right angle.
3. Identify the type of triangle based on its sides: a = 3 cm, b = 3 cm, c = 3 cm.
The triangle with sides a = 3 cm, b = 3 cm, and c = 3 cm is an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all sides are equal.
4. What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always equal to 180 degrees.
5. Determine the type of angle based on its measure: 180 degrees.
An angle measuring 180 degrees is called a straight angle. It forms a straight line.
6. Calculate the area of a rectangle with length 8 cm and width 5 cm.
The area of a rectangle can be calculated by multiplying its length and width. In this case, the area is 8 cm x 5 cm = 40 cm2.
7. Describe a line that intersects two parallel lines.
A line that intersects two parallel lines is called a transversal. It forms eight different angles, including corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles.
8. Identify the type of quadrilateral with four sides of equal length.
A quadrilateral with four sides of equal length is called a rhombus. It is also known as a diamond shape.
9. Determine the missing angle in a right triangle with angles measuring 30 degrees and 60 degrees.
In a right triangle, the sum of the two acute angles is always equal to 90 degrees. Therefore, the missing angle is 90 degrees – (30 degrees + 60 degrees) = 90 degrees – 90 degrees = 0 degrees.
10. Calculate the perimeter of a square with side length 10 cm.
The perimeter of a square can be calculated by multiplying its side length by 4. In this case, the perimeter is 10 cm x 4 = 40 cm.
These sample questions and answers should give you a solid foundation for understanding and solving geometry problems. Make sure to practice and review the concepts covered in your chapter 1 test to ensure your success.