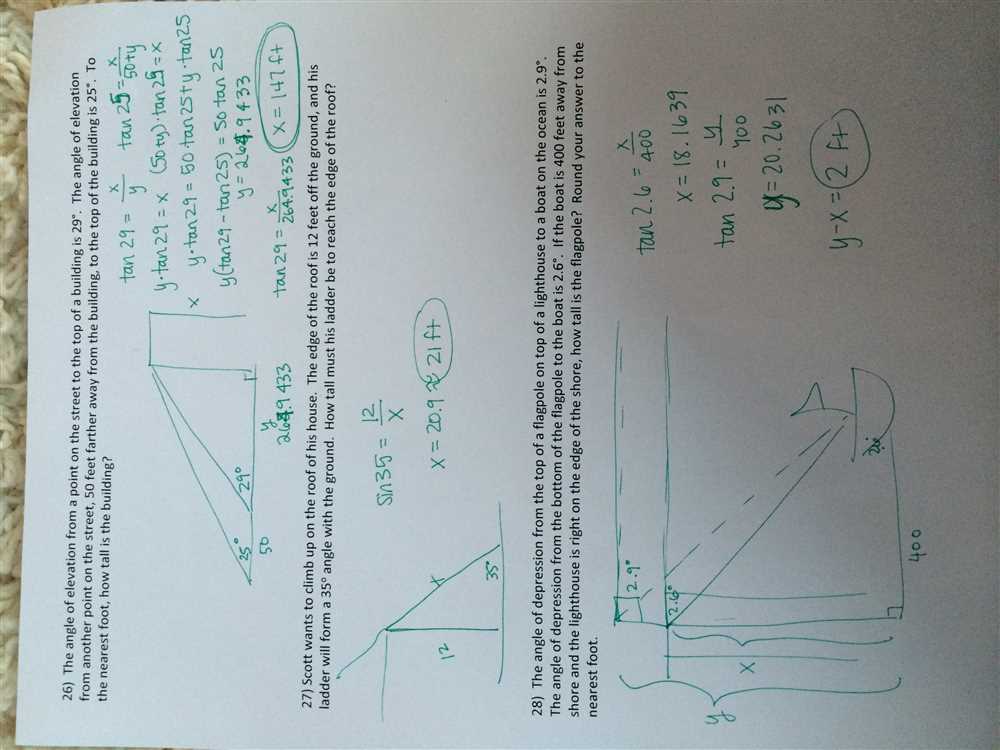
If you’ve recently completed a chapter on geometry, chances are you’re facing a test on the subject. Geometry can be a challenging topic, with its focus on shapes, angles, and proofs. However, with the right preparation and understanding of the concepts, you can confidently tackle the test and earn a great score.
In this article, we will provide you with the answers to the Chapter 8 Test in geometry. In this particular chapter, you likely covered topics such as right triangles, Pythagorean Theorem, special right triangles, and trigonometric ratios. By understanding these concepts and practicing with various problems, you can ensure success on your test.
Mastering the concepts in Chapter 8 is crucial for building a strong foundation in geometry. Right triangles are fundamental shapes that appear in various applications, from architecture to engineering. Understanding their properties and relationships is essential for solving problems in real-life scenarios.
With the answers to the Chapter 8 Test, you’ll be able to check your understanding of the material before the actual exam. Make sure to thoroughly review and understand each answer, and if you encounter any difficulties, don’t hesitate to seek additional help from your teacher or classmates. By mastering these geometric concepts, you’ll not only excel in your test but also lay a solid foundation for future math courses.
Geometry Chapter 8 Test Answers: A Comprehensive Overview
Geometry Chapter 8 encompasses various topics related to circles and their properties. In this test, students are expected to demonstrate their understanding of concepts such as tangents, chords, secants, arcs, and angles within circles. The test aims to assess students’ ability to apply these geometric principles to solve problems and make deductions.
The test consists of several sections, each focusing on different aspects of circle geometry. One section may require students to identify the relationships between tangents and chords, while another may involve calculating the measures of angles formed by intersecting chords. Additionally, the test may also include questions on the properties of inscribed angles and their intercepted arcs.
Key answers and concepts covered in this chapter:
- Definition and properties of a circle
- Tangents and their relationship with radii and chords
- Chords and their relationship with arcs and central angles
- Secants and their properties in relation to circles
- Inscribed angles and their intercepted arcs
- Measures of angles formed by intersecting chords
By studying and practicing the concepts covered in this chapter, students will be able to approach the Geometry Chapter 8 Test with confidence, as they will have a solid understanding of the principles and properties of circles. It is essential for students to review and reinforce their knowledge to ensure success on this assessment.
Overall, the Geometry Chapter 8 Test serves as a comprehensive evaluation of students’ grasp of circle geometry concepts. By thoroughly understanding the topics covered and practicing problem-solving techniques, students can expect to perform well on this test and demonstrate their proficiency in this area of geometry.
Understanding the Importance of Chapter 8 in Geometry
The study of geometry is crucial for understanding the patterns and relationships of the physical world around us. Chapter 8 is an important part of this study, as it focuses on the concept of similarity and congruence. This chapter explores the ways in which shapes can be compared and classified based on their attributes and properties. Understanding these concepts is fundamental in various fields, including engineering, architecture, and graphic design.
One of the key concepts introduced in Chapter 8 is similarity. Similar shapes have the same shape, but can be different in size. This concept is essential for understanding proportionality and scaling. Whether it’s resizing images, designing blueprints, or calculating dimensions, an understanding of similarity allows us to accurately represent real-world objects and structures.
In addition to similarity, Chapter 8 also covers the concept of congruence. Congruent shapes have the same shape and size. This concept is fundamental for understanding symmetry and transformations. It allows us to determine if two shapes are identical or can be transformed into one another through translation, rotation, or reflection.
By studying Chapter 8 in geometry, students gain a solid foundation in these essential geometric concepts. They learn how to identify and classify shapes, determine similarity and congruence, and apply these concepts to real-world problems. This knowledge is not only useful for future careers in STEM fields, but also for developing critical thinking, problem-solving, and analytical skills that are applicable in various areas of life.
Overall, Chapter 8 in geometry plays a crucial role in laying the groundwork for future mathematical and scientific studies. By understanding the importance of similarity and congruence, students can develop a deeper understanding of the world around them and apply these concepts to solve complex problems.
Preparing for the Geometry Chapter 8 Test

As you prepare for the Geometry Chapter 8 Test, it’s important to review the key concepts and skills that you have learned throughout this chapter. This test will focus on coordinate geometry and transformations, so make sure you have a solid understanding of these topics.
Coordinate Geometry: Be sure to review how to plot points on a coordinate plane and find the coordinates of a given point. Familiarize yourself with the different quadrants of the coordinate plane and understand how to identify the location of a point based on its coordinates.
Transformations: This chapter covers various types of transformations, including translations, reflections, rotations, and dilations. Practice identifying the rules for each type of transformation and understand how they affect the position and shape of a figure.
When reviewing for the test, create a study guide that includes examples and practice problems for each concept. Consider using flashcards to help you memorize important definitions and formulas.
Additionally, don’t forget to review any notes or handouts from class, as well as the chapter review questions at the end of the textbook chapter. Take the time to work through any challenging problems and seek help from your teacher or classmates if needed.
Good luck on your Geometry Chapter 8 Test!
Exploring Key Concepts Covered in Geometry Chapter 8
In Geometry Chapter 8, students are introduced to several key concepts that build upon their previous knowledge of shapes and angles. This chapter focuses on the properties and relationships of polygons, as well as the applications of these properties in real-world scenarios.
One of the main topics covered in Chapter 8 is the classification of polygons based on their sides and angles. Students learn about the different types of polygons, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons, and how to identify them based on their characteristics. They also explore the properties of regular polygons, which have equal side lengths and angles.
Another important concept covered in this chapter is the calculation of the interior and exterior angles of polygons. Students learn how to find the sum of the interior angles in a polygon, as well as how to calculate the measure of each interior angle in regular polygons. They also explore the relationship between the interior and exterior angles of a polygon, and how to find the measure of each exterior angle.
The chapter also delves into the application of polygon properties in real-world scenarios. Students are given the opportunity to solve problems involving the perimeter and area of polygons, as well as their use in construction and design. They explore how to find the perimeter of irregular polygons by adding the lengths of their sides, and how to calculate the area of regular polygons using formulas such as the apothem and side length.
Overall, Geometry Chapter 8 provides students with a solid foundation in the properties and relationships of polygons. It equips them with the necessary knowledge and skills to analyze and solve problems involving polygons in both mathematical and real-world contexts.
Evaluating Angles and Triangles
Angles and triangles are fundamental concepts in geometry. By understanding how to evaluate angles and triangles, we can solve various geometric problems and analyze the properties of different shapes.
One way to evaluate angles is by using the properties of parallel lines and transversals. When a transversal intersects two parallel lines, the corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, and alternate exterior angles can be determined. These angles have specific relationships, such as being congruent or supplementary, which can help us find their measures and solve for unknown angles.
Another method for evaluating angles is through the use of trigonometry. Trigonometric ratios, such as sine, cosine, and tangent, can be used to find the measures of angles in right triangles. By knowing the lengths of certain sides of the triangle, we can determine the angles using the appropriate trigonometric function.
Triangles can also be evaluated in terms of their properties and characteristics. For example, the interior angles of a triangle always add up to 180 degrees, and the exterior angles always add up to 360 degrees. These properties can be used to solve for missing angles in a triangle.
Additionally, triangles can be classified based on their side lengths and angle measures. The classification includes equilateral triangles, isosceles triangles, scalene triangles, acute triangles, obtuse triangles, and right triangles. Each classification has its own unique properties and relationships that can be used to evaluate and solve problems involving triangles.
Overall, evaluating angles and triangles is an essential skill in geometry. It allows us to understand the relationships between angles, solve geometric problems, and analyze the properties of various shapes. Whether through the use of parallel lines, trigonometry, or triangle properties, being able to evaluate angles and triangles is crucial for success in geometry.
Applying Properties of Polygons
Polygons are geometric shapes that have straight sides and angles. They can be categorized based on the number of sides they have, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and so on. Understanding the properties of polygons is essential in solving geometry problems and analyzing different shapes.
One important property of polygons is the sum of their interior angles. The sum of the interior angles in any polygon can be found using the formula 180(n-2), where n represents the number of sides in the polygon. For example, a triangle has three sides, so the sum of its interior angles is 180 degrees (180(3-2) = 180). A quadrilateral has four sides, so the sum of its interior angles is 360 degrees (180(4-2) = 360).
Another property of polygons is their exterior angles. The exterior angle of a polygon is the angle formed by extending one of its sides. The sum of the exterior angles in any polygon is always 360 degrees. This property can be useful when determining the measure of a missing exterior angle or finding the number of sides in a polygon.
In addition, polygons can have special properties based on their shape and symmetry. For example, a regular polygon has equal side lengths and equal interior angles. Examples of regular polygons include equilateral triangles, squares, and hexagons. These special properties allow for easier calculations and identification of shapes when solving geometry problems.
Overall, applying the properties of polygons is essential in geometry. By understanding the formulas and rules associated with polygons, students can successfully analyze shapes, solve problems, and navigate through the various concepts and applications of geometry.
How to Solve Problems Related to Triangles for the Geometry Chapter 8 Test

Solving problems related to triangles is an essential skill for mastering the Geometry Chapter 8 Test. By understanding the properties and relationships of angles and sides in triangles, you can confidently approach any problem. Here are some steps to help you tackle triangle problems effectively:
1. Identify the type of triangle: Determine if the triangle is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. This will give you insight into the properties and relationships of its angles and sides.
2. Find the missing angle: Use the fact that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees to find any missing angle. If you have two angles, subtract their sum from 180 degrees to find the third angle.
3. Use the triangle inequality theorem: This theorem states that the sum of the lengths of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the length of the third side. Use this theorem to determine if a given set of side lengths can form a triangle.
4. Apply the Pythagorean theorem: If you’re dealing with a right triangle, you can use the Pythagorean theorem (a^2 + b^2 = c^2) to find the length of the missing side.
5. Apply the properties of special triangles: Equilateral triangles have all sides and angles equal, while isosceles triangles have two sides and angles equal. Use these properties to solve problems involving these types of triangles.
6. Use the properties of triangle congruence: If you can prove that two triangles are congruent, you can apply their corresponding parts to solve for unknown lengths or angles.
By following these steps and practicing with various triangle problems, you will become more confident in your ability to solve problems related to triangles for the Geometry Chapter 8 Test.
Identifying Different Triangle Types
Triangles are one of the most basic and fundamental shapes in geometry. They are formed by connecting three line segments to form three angles. Triangles can be classified into different types based on their side lengths and angle measurements. Understanding the different types of triangles can help in solving various geometric problems and applications.
Equilateral Triangle: An equilateral triangle is a type of triangle that has three equal side lengths and three equal angles, each measuring 60 degrees. It is the most symmetrical and regular type of triangle. In an equilateral triangle, the altitude, median, and angle bisectors all coincide.
Isosceles Triangle: An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two equal side lengths and two equal angles. The angle opposite the unequal side is known as the base angle, while the angle at the apex is called the vertex angle.
Scalene Triangle: A scalene triangle is a type of triangle that has three different side lengths and three different angles. None of the angles or sides in a scalene triangle are equal. It is the most irregular type of triangle.
Right Triangle: A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one right angle, measuring 90 degrees. The side opposite the right angle is called the hypotenuse, while the other two sides are known as the legs. The Pythagorean theorem is commonly used to solve problems involving right triangles.
Obtuse Triangle: An obtuse triangle is a type of triangle that has one obtuse angle, measuring more than 90 degrees. The other two angles in an obtuse triangle are acute angles, measuring less than 90 degrees.