
Geometry is a fascinating branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of shapes and figures. In Unit 7, we delve into the world of polygons and quadrilaterals, exploring their unique characteristics and mathematical properties. A quiz is a common method used by teachers to assess students’ understanding of the material covered in class. This article serves as an answer key to Quiz 7-2, providing students with the correct solutions and explanations to help them improve their geometry skills.
In this quiz, students will encounter a variety of questions that challenge their knowledge of polygons and quadrilaterals. They will be asked to identify different types of polygons, such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and hexagons. Understanding the properties and attributes of these shapes is crucial in differentiating them and determining their characteristics. The quiz also covers topics like finding the measures of interior angles and the sum of exterior angles for various types of polygons.
By providing students with this answer key, they are given the opportunity to review their quiz and identify any mistakes or areas of misunderstanding. This not only enables them to correct their answers but also allows them to gain a deeper understanding of the concepts covered in the quiz. It serves as a valuable learning tool to reinforce the material and improve their geometry skills.
Understanding polygons and quadrilaterals
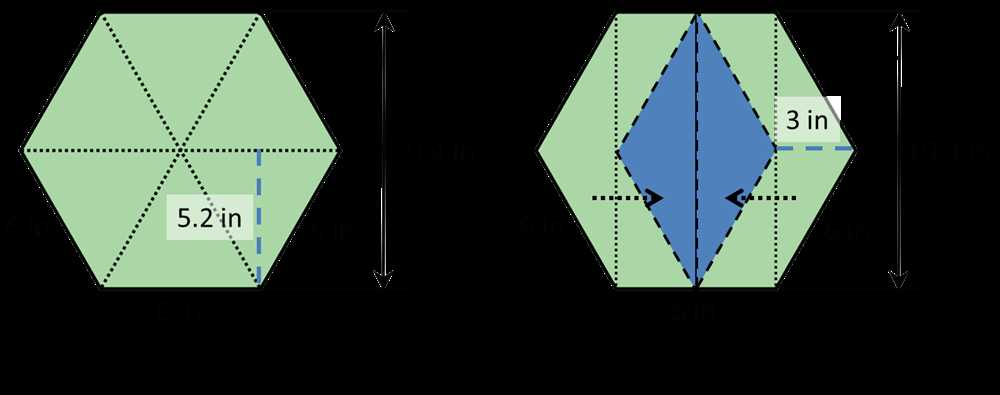
Geometry unit 7 focuses on the study of polygons and quadrilaterals. Understanding these concepts is crucial for building a strong foundation in geometry.
A polygon is a closed figure formed by straight sides. It can have three or more sides. Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have. For example, a triangle is a polygon with three sides, while a quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides.
Each side of a polygon is called an edge, and each vertex is a point where two or more edges meet. The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with n sides can be found using the formula (n-2) × 180 degrees. This formula allows us to calculate the total measure of the interior angles of any polygon.
A quadrilateral is a special type of polygon with four sides. There are different types of quadrilaterals, including parallelograms, rectangles, squares, and trapezoids. Each type has its own unique properties and characteristics.
Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with opposite sides that are parallel. They have equal opposite angles and equal opposite sides. Rectangles are quadrilaterals with four right angles. Squares are a special type of rectangle with all sides equal in length.
Trapezoids are quadrilaterals with one pair of parallel sides. The other two sides are not parallel. Trapezoids can be isosceles or scalene, depending on the lengths of their sides. Understanding the properties of these quadrilaterals is essential for solving geometry problems and identifying their unique characteristics in real-world applications.
In conclusion, studying polygons and quadrilaterals helps us understand the fundamental principles of geometry and provides a basis for solving more complex geometric problems. By familiarizing ourselves with the properties and formulas associated with these shapes, we can better analyze and manipulate geometric figures.
Overview of Unit 7 Quiz 7 2
In unit 7 of the geometry course, students will be tested on their knowledge of polygons and quadrilaterals. The main focus of this unit is to understand the properties and characteristics of these geometric shapes.
The quiz for this unit, quiz 7 2, will assess students’ understanding of various topics related to polygons and quadrilaterals. It will include questions on the properties of polygons, different types of quadrilaterals, and their properties, as well as the relationships between polygons and quadrilaterals.
Some specific topics that may be covered in the quiz include identifying the number of sides and angles in a given polygon, identifying and classifying different types of quadrilaterals such as squares, rectangles, parallelograms, and trapezoids, and determining the properties and relationships of angles and sides within these shapes.
Students will also need to demonstrate their ability to apply their knowledge to solve practical problems involving polygons and quadrilaterals. This may include finding the perimeter or area of a given shape, identifying congruent or similar shapes, or determining missing angles or sides based on the given information.
Overall, the quiz will assess students’ understanding and application of the concepts and properties related to polygons and quadrilaterals. It is important for students to review and practice these concepts in order to prepare for the quiz and demonstrate their mastery of the material.
Key concepts for polygons and quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals are two important concepts in geometry. Understanding them is crucial in various mathematical calculations and practical applications. Here are some key concepts to keep in mind when dealing with polygons and quadrilaterals.
Polygons:
- A polygon is a closed figure made up of straight line segments.
- All the line segments in a polygon are called sides.
- Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have.
- A polygon with three sides is called a triangle, four sides is called a quadrilateral, five sides is called a pentagon, and so on.
- Polygons can be further classified as regular polygons or irregular polygons.
- In a regular polygon, all the sides and angles are equal, whereas in an irregular polygon, they are not.
Quadrilaterals:
- A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides.
- The sum of interior angles in a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees.
- Quadrilaterals can be further classified into various types:
- A square is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length and all four angles equal to 90 degrees.
- A rectangle is a quadrilateral with opposite sides equal in length and all four angles equal to 90 degrees.
- A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel to each other.
- A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length.
Understanding these key concepts is essential for solving problems related to polygons and quadrilaterals, as well as for exploring their properties and relationships in geometry.
Common types of polygons
A polygon is a closed figure with straight sides formed by connecting multiple line segments. There are several common types of polygons, each characterized by the number of sides it has:
- Triangle: A triangle is a polygon with three sides. It is the simplest polygon and can be classified into three types based on the length of its sides: equilateral (all sides are equal), isosceles (two sides are equal), and scalene (no sides are equal).
- Quadrilateral: A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides. Some common types of quadrilaterals include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and rhombuses. Each type has its own unique characteristics, such as equal angles in squares and rectangles, opposite sides parallel in parallelograms, and opposite sides equal in rhombuses.
- Pentagon: A pentagon is a polygon with five sides. It can be classified into regular and irregular pentagons, with regular pentagons having all sides and angles equal in length.
- Hexagon: A hexagon is a polygon with six sides. It can also be classified into regular and irregular hexagons, with regular hexagons having all sides and angles equal in length.
- Octagon: An octagon is a polygon with eight sides. It can also be classified into regular and irregular octagons, with regular octagons having all sides and angles equal in length.
These are just a few examples of the many types of polygons that exist. Each type has its own properties and characteristics, making them interesting objects of study in the field of geometry.
Properties of quadrilaterals
A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides and four angles. Quadrilaterals have various properties and classifications based on their angles and side lengths. Understanding these properties is crucial when working with quadrilaterals in geometry.
1. Parallelogram: A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides that are parallel. This means that the opposite sides are always equal in length. Additionally, opposite angles of a parallelogram are congruent.
2. Rectangle: A rectangle is a parallelogram with all angles measuring 90 degrees. This means that all four angles of a rectangle are right angles. In a rectangle, opposite sides are also congruent.
3. Rhombus: A rhombus is a parallelogram with all sides of equal length. This means that all four sides of a rhombus are congruent. Additionally, opposite angles of a rhombus are congruent.
4. Square: A square is a rectangle and a rhombus. This means that a square has all the properties of both a rectangle and a rhombus. In a square, all four angles measure 90 degrees and all sides are congruent.
5. Trapezoid: A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of opposite sides that are parallel. The other two sides of a trapezoid are not parallel. Trapezoids can have different side lengths and angles.
These are just a few of the many properties and classifications of quadrilaterals. By understanding these properties, you can easily identify and analyze different types of quadrilaterals in geometry problems.
Solved examples for unit 7 quiz 7 2

1. Triangle ABC is an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 8 cm. Find the perimeter and area of the triangle.
To find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle, we need to multiply the length of one side by 3. Therefore, the perimeter of triangle ABC is 8 cm x 3 = 24 cm.
To find the area of an equilateral triangle, we can use the formula: Area = (√3/4) x (side length)^2. Substituting the values into the formula, we get: Area = (√3/4) x (8 cm)^2 = √3 x 16 = 16√3 cm^2.
2. Quadrilateral PQRS is a rectangle with PQ = 6 cm and QR = 4 cm. Find the perimeter and area of the rectangle.
The perimeter of a rectangle can be found by adding the lengths of all four sides. In this case, we have two pairs of equal sides, so we can calculate the perimeter as: (PQ + QR) x 2 = (6 cm + 4 cm) x 2 = 10 cm x 2 = 20 cm.
The area of a rectangle can be found by multiplying the length and width. In this case, the length is PQ = 6 cm and the width is QR = 4 cm. Therefore, the area of the rectangle is: 6 cm x 4 cm = 24 cm^2.
Tips and strategies for solving the quiz
When tackling the Geometry Unit 7 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Quiz, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of the concepts and properties related to polygons and quadrilaterals. Here are a few tips and strategies to help you navigate through the quiz successfully.
1. Review key definitions and properties
Before diving into the quiz, make sure to review the key definitions and properties of polygons and quadrilaterals. Familiarize yourself with terms like angles, sides, diagonals, and symmetry. Understand the relationships between different types of polygons and the properties unique to each quadrilateral.
2. Read the questions carefully
Take your time to read each question carefully and understand what it’s asking for. Pay attention to any specifics mentioned, such as a particular polygon or quadrilateral being referred to. Be mindful of the language used in the question to avoid misinterpretation.
3. Break down complex problems
If a question seems complex, break it down into smaller, manageable parts. Analyze the given information and identify any patterns or relationships that can help solve the problem step by step. Don’t rush and take your time to ensure accuracy.
4. Use diagrams and visuals
Visualize the given shapes and problems by drawing diagrams or sketches whenever possible. Visual representation can often provide insights and help you see connections between different elements. Label the important angles, sides, and diagonals to aid in your analysis.
5. Check your answers
Once you’ve completed the quiz, go back and double-check your answers. Make sure you haven’t overlooked any details or made any calculation errors. Verify that your solutions align with the given problem and the properties of polygons and quadrilaterals.
By following these tips and strategies, you’ll be better prepared to approach the Geometry Unit 7 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Quiz with confidence and accuracy. Remember to practice regularly and seek help if needed to strengthen your understanding of the subject matter.
Answer Key for Unit 7 Quiz 7.2
In geometry, unit 7 focuses on polygons and quadrilaterals. The quiz 7.2 is a assessment that tests students’ understanding of these geometric concepts. Below is the answer key for this particular quiz:
- Question 1: What is the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon?
- Answer: The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon is 720 degrees.
- Question 2: What is the measure of each interior angle of a regular heptagon?
- Answer: Each interior angle of a regular heptagon measures 128.57 degrees (approximately).
- Question 3: What is the name of a quadrilateral with all sides congruent and opposite angles congruent?
- Answer: The name of a quadrilateral with all sides congruent and opposite angles congruent is a parallelogram.
- Question 4: What is the name of a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides?
- Answer: The name of a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides is a trapezoid.
These are just a few examples of the questions and answers that can be found in the answer key for the unit 7 quiz 7.2 on polygons and quadrilaterals. It is important for students to practice and understand these concepts in order to succeed in geometry.