
In the study of Spanish grammar, understanding subject pronouns and the verb “ser” is essential. Subject pronouns are used to replace a noun and indicate who is performing the action in a sentence. The verb “ser” is used to indicate essential characteristics such as identity, nationality, profession, and physical attributes.
Subject pronouns are important because they help us avoid repetition in sentences. Instead of saying “the boy is tall,” we can say “he is tall.” The subject pronouns in Spanish are: yo (I), tú (you, informal), él (he), ella (she), usted (you, formal), nosotros/nosotras (we), vosotros/vosotras (you all, informal), ellos/ellas (they), ustedes (you all, formal). It is important to note that subject pronouns are often omitted in Spanish since the verb ending provides enough information about the subject.
The verb “ser” is irregular and does not follow the regular conjugation patterns. Its conjugation depends on the subject pronoun and is as follows: yo soy (I am), tú eres (you are), él/ella/usted es (he/she/you formal are), nosotros/nosotras somos (we are), vosotros/vosotras sois (you all are), ellos/ellas/ustedes son (they/you all are). The verb “ser” is used to identify and describe people, objects, and locations. For example, “Ella es alta” means “She is tall,” while “Nosotros somos estudiantes” means “We are students.”
Understanding subject pronouns and the verb “ser” is essential for anyone learning Spanish. By mastering these grammar concepts, you will be able to form accurate and meaningful sentences, expressing yourself with clarity and precision.
What are Subject Pronouns?
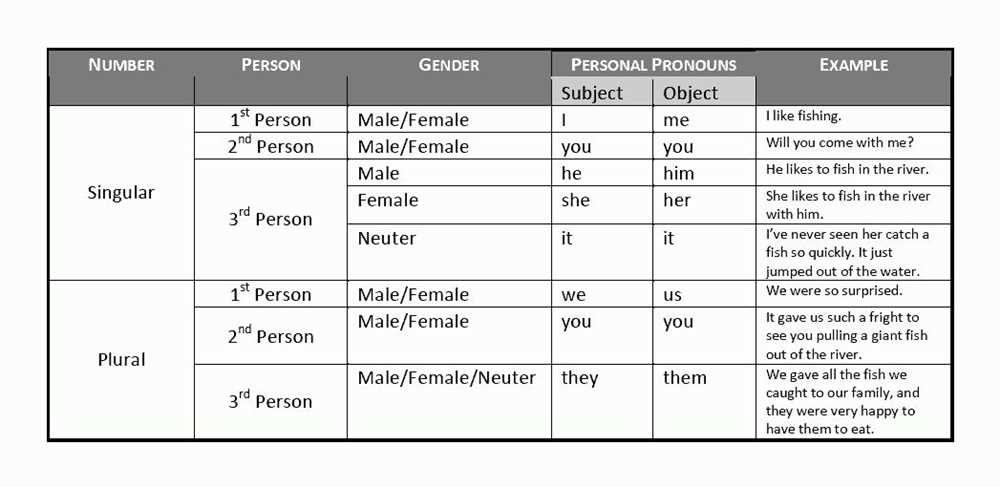
Subject pronouns are words that are used to replace a noun or a noun phrase as the subject of a sentence. They are commonly used to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise and fluent. In English, subject pronouns include words such as “I, you, he, she, it, we, and they”.
Subject pronouns can also indicate the gender and number of the noun they are replacing. For example, “he” is used to replace a male singular noun, while “she” is used for a female singular noun. “They” is used to replace a plural noun, regardless of gender.
Subject pronouns are often used before a verb to indicate who is performing the action. For example, instead of saying “John is running”, we can say “He is running”. Using subject pronouns helps to make sentences more efficient and natural.
Subject pronouns can also be used as the subject of a verb or a subject complement. They are an essential part of sentence construction and are used in almost every sentence to indicate who or what is performing the action.
In conclusion, subject pronouns are words that replace nouns to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise. They indicate the gender and number of the noun they are replacing and are an essential part of sentence construction.
Definition of Subject Pronouns
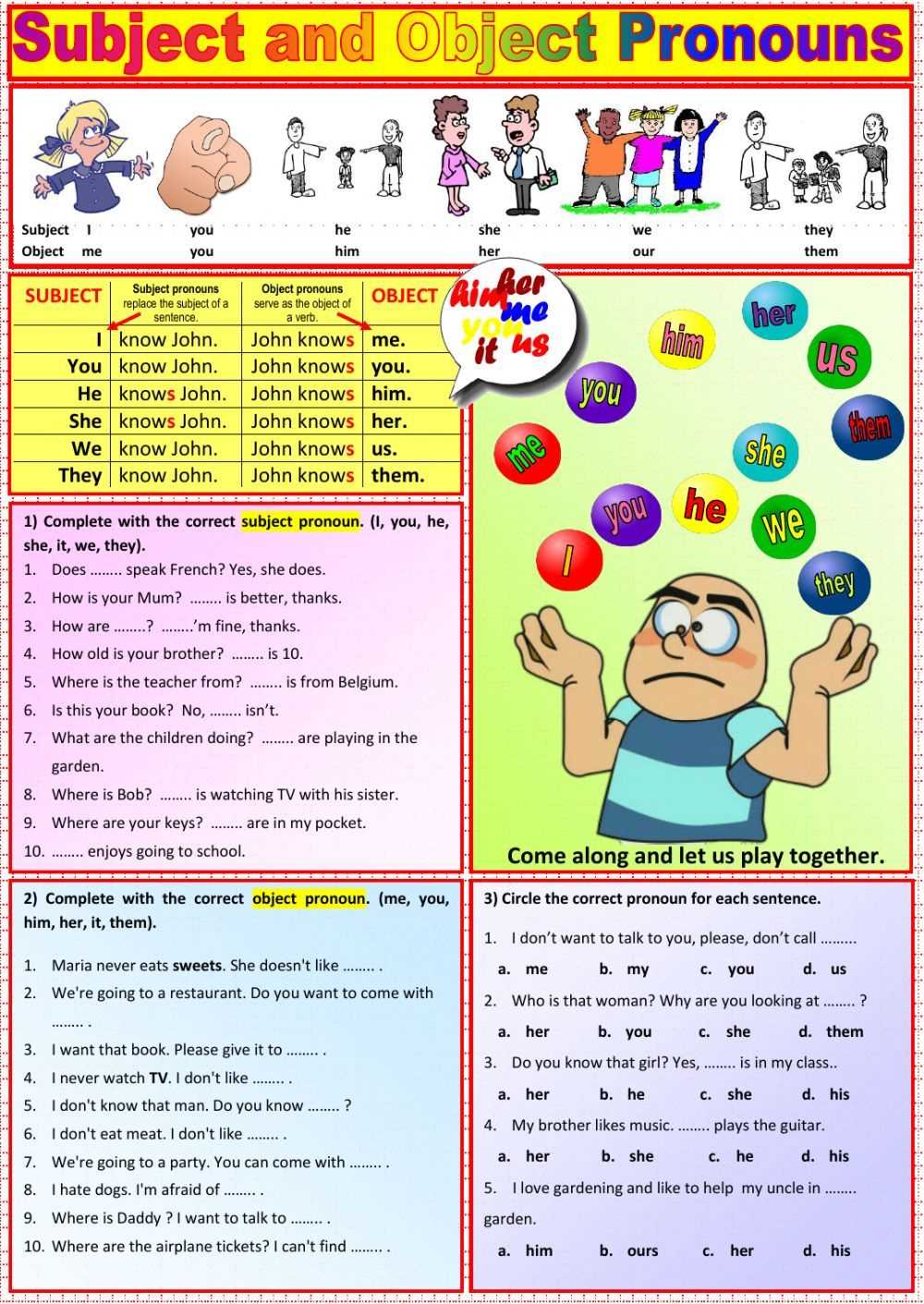
Subject pronouns are words used to replace a noun as the subject of a sentence. They serve the purpose of simplifying the language by avoiding repetitive or unnecessary use of nouns. Subject pronouns typically indicate who or what is performing the action in a sentence.
Subject pronouns in English include: I, you, he, she, it, we, and they. Each pronoun has its own specific usage and refers to different subjects. For example, “I” is used when referring to oneself as the subject of a sentence, while “he” and “she” are used when referring to another person or object as the subject.
The use of subject pronouns can vary based on the verb tense and the relationship between the speaker and the subject. It is important to correctly identify the subject pronoun to ensure clarity and accuracy in communication. Subject pronouns are an essential part of grammar, allowing for concise and efficient communication in English.
Examples of Subject Pronouns:
- I am going to the park.
- She is running late.
- We love to travel.
- They won the game.
Examples of Subject Pronouns
Subject pronouns are used in sentences to replace the subject of the sentence. They help to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise. Here are some examples of subject pronouns:
- I: I love to read.
- You: You are a talented musician.
- He: He is going to the store.
- She: She is studying for her exams.
- It: It is raining outside.
- We: We are going on vacation next week.
- They: They won the championship.
Subject pronouns can also be used to ask questions or give commands:
- Who: Who is coming to the party?
- What: What do you want for dinner?
- Where: Where are you going?
- Let: Let us go to the park.
- Get: Get out of my way!
Subject pronouns are a fundamental part of grammar and are used in everyday conversation. By using subject pronouns, we can communicate more effectively and efficiently.
Importance of Subject Pronouns in Spanish Grammar
In Spanish grammar, subject pronouns play a crucial role in clarifying the subject of a sentence and indicating the verb conjugation. Subject pronouns are used to replace the noun or noun phrase that functions as the subject of a sentence. They help to avoid repetition and make the sentence more concise and clear.
Subject pronouns in Spanish include yo (I), tú (you), él/ella (he/she), nosotros/nosotras (we), vosotros/vosotras (you all), and ellos/ellas (they). These pronouns can change the form of the verb, indicating the person and number of the subject. For example, the verb “hablar” (to speak) conjugates differently depending on the subject pronoun:
| Subject Pronoun | Conjugated Verb |
|---|---|
| Yo | hablo |
| Tú | hablas |
| Él/Ella | habla |
| Nosotros/Nosotras | hablamos |
| Vosotros/Vosotras | habláis |
| Ellos/Ellas | hablan |
Subject pronouns also help to differentiate between formal and informal address. The pronoun “tú” is used in informal situations, while “usted” is used in formal situations. Likewise, “vosotros/vosotras” is used in Spain for addressing a group of people informally, while “ustedes” is used in both formal and informal contexts in Latin America.
Overall, subject pronouns are essential in Spanish grammar as they help to identify the subject of a sentence, indicate verb conjugation, and establish formality or informality in addressing others. They contribute to the clarity and precision of the language, making communication more effective.
Ser: The Verb “To Be”

The verb “ser” is one of the most important verbs in the Spanish language. It is used to indicate identity, characteristics, nationality, profession, and many other attributes. In English, “ser” is usually translated as “to be”.
One key aspect of “ser” is that it is an irregular verb, meaning that its conjugation does not follow regular patterns. The conjugation of “ser” is as follows:
- Yo soy – I am
- Tú eres – You are (informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted es – He/She/You (formal) is
- Nosotros/Nosotras somos – We are
- Vosotros/Vosotras sois – You all are
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes son – They/You all are
Here are some examples of how “ser” is used:
- Yo soy estudiante – I am a student
- Tú eres inteligente – You are intelligent
- Él es médico – He is a doctor
- Nosotros somos hermanos – We are siblings
- Vosotros sois simpáticos – You all are nice
- Ellos son argentinos – They are Argentinian
As you can see, “ser” is a versatile verb that is used to express various aspects of identity and attributes. It is essential to learn and understand how to use “ser” correctly in Spanish.
Overview of Ser
The verb “ser” is one of the most important verbs in the Spanish language. It is used to express identity, characteristics, and origin. In English, the verb “to be” is used to convey the same meanings. However, unlike English, Spanish has different forms of the verb “ser” depending on the subject pronoun.
Subject pronouns, such as “I”, “you”, “he”, “she”, “we”, and “they”, indicate who or what is performing the action of the verb. These subject pronouns have corresponding forms of the verb “ser” in Spanish. For example, the verb “ser” can be conjugated as “soy” for “I am”, “eres” for “you are”, “es” for “he/she is”, “somos” for “we are”, and “son” for “they are”.
The verb “ser” is also used to express physical and personality traits. For example, “Ella es alta” means “She is tall”, and “Él es inteligente” means “He is intelligent”. In these sentences, the verb “es” is used to describe the physical characteristic “tall” and the personality trait “intelligent”.
In addition to describing identity and characteristics, the verb “ser” is used to express origin. For example, “Soy de México” means “I am from Mexico” and “Somos de España” means “We are from Spain”. In these sentences, the verb “ser” is used to indicate the origin or nationality of the subject pronoun.
In summary, the verb “ser” is a crucial verb in Spanish that is used to express identity, characteristics, and origin. Understanding the conjugation of “ser” and its corresponding subject pronouns is essential for building grammatically correct and meaningful sentences in Spanish.
Conjugation of Ser
The verb “ser” is one of the most important verbs in Spanish and it is used to express identity, characteristics, and nationality. It is an irregular verb, which means that it doesn’t follow the regular conjugation patterns of regular verbs.
Here is the conjugation of “ser” in the present tense:
- Yo soy (I am)
- Tú eres (You are)
- Él/ella/usted es (He/she/you formal is)
- Nosotros/nosotras somos (We are)
- Vosotros/vosotras sois (You all are)
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes son (They/you all are)
Here are some examples of how to use “ser” in sentences:
- Yo soy estudiante. (I am a student.)
- Tú eres alto. (You are tall.)
- Él es argentino. (He is Argentinean.)
- Nosotras somos amigas. (We are friends.)
- Vosotros sois inteligentes. (You all are intelligent.)
- Ellos son médicos. (They are doctors.)
It’s important to note that the verb “ser” is also used to talk about professions, nationalities, and characteristics. It is often used with adjectives to describe and identify people, objects, and places.
Overall, conjugating the verb “ser” is essential for anyone learning Spanish as it is used in various situations to express identity and characteristics.
Examples of Ser in Sentences
Ser is the Spanish verb for “to be.” It is a highly irregular verb and is used to express essential characteristics, identities, qualities, or states of being. Here are some examples of ser in sentences:
- Yo soy profesor. – I am a teacher.
- Ellos son hermanos. – They are brothers.
- Ella es inteligente. – She is intelligent.
- Tú eres alto. – You are tall.
- Nosotros somos felices. – We are happy.
In these sentences, ser is used to indicate someone’s profession, relationship, trait, or characteristic. It is important to note that ser is conjugated differently depending on the subject pronoun and the tense of the sentence. For example, “yo soy” is used for “I am” while “tú eres” is used for “you are.”
Additionally, ser is used to describe the hour, day, date, or location of an event. Here are some examples:
- Es la una. – It is one o’clock.
- Hoy es lunes. – Today is Monday.
- Mañana es el veinte de abril. – Tomorrow is April 20th.
- El concierto es en el teatro. – The concert is at the theater.
In these examples, ser is used to express the time, day of the week, date, or location of an event. It helps provide essential information about the event or situation. Remember, ser is an important verb in Spanish, and understanding how to use it correctly is crucial for effective communication in the language.
Answer Key for Subject Pronouns and Ser Exercises
Below is the answer key for the exercises on subject pronouns and the verb “ser”. Make sure to compare your answers to these to check for accuracy.
Exercise 1:
- Yo – soy
- Tú – eres
- Él/ella/usted – es
- Nosotros/nosotras – somos
- Vosotros/vosotras – sois
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes – son
Exercise 2:
- María es mi hermana.
- Tú eres muy inteligente.
- Yo soy de México.
- Él es mi mejor amigo.
- Nosotros somos estudiantes.
- Ellas son profesoras de español.
Exercise 3:

| Subject Pronoun | Ser | Answer |
| Tú | eres | Tú eres de España. |
| Nosotras | son | Nosotras somos estudiantes. |
| Él | somos | Él es mi hermano. |
| Ellos | es | Ellos son médicos. |
Remember, subject pronouns are used before the verb “ser” to indicate who is performing the action. The form of “ser” then changes depending on the subject pronoun used.
Continue practicing these exercises to improve your understanding of subject pronouns and the verb “ser”. With enough practice, you will become more comfortable using them in everyday conversation.