
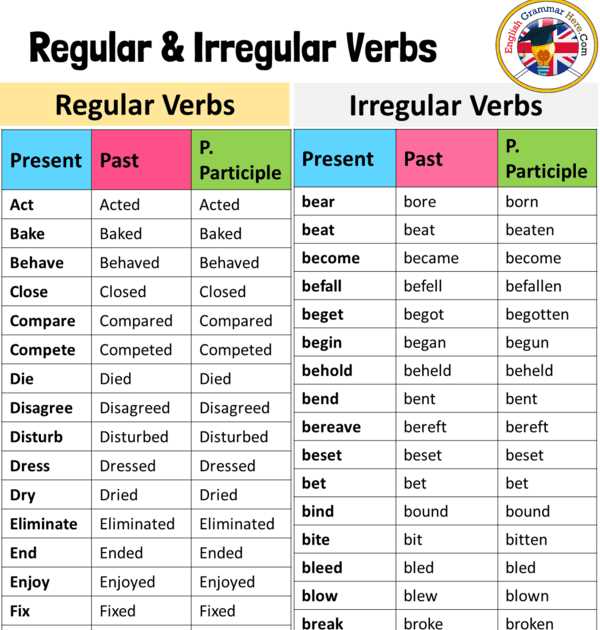
Verbs play a crucial role in any language, and mastering their various forms and tenses is key to becoming fluent. In English, one aspect of verb conjugation that can be challenging is the preterite tense, especially for irregular verbs. One group of irregular verbs that falls into this category is the B verbs.
B verbs are a subset of irregular verbs that deviate from the regular pattern of verb conjugation in the preterite tense. These verbs undergo unique changes in their stem when conjugated in the preterite tense, leading to different endings for each person.
Examples of B verbs in the preterite tense include “be, was/were,” and “been.” These verbs, unlike regular verbs, do not follow a consistent pattern of adding -ed to form the past tense. Instead, they have their own specific conjugation rules that need to be memorized.
Learning the conjugation of B verbs in the preterite tense is essential for effective communication and comprehension in English. By understanding and practicing these irregular forms, learners can enhance their language skills and express past actions accurately. So, let’s dive into the grammar of B irregular verbs in the preterite and unravel the mysteries behind their conjugation!
What are irregular verbs in the preterite?
The preterite tense in Spanish is used to describe actions that were completed in the past. While most verbs follow a regular pattern in the preterite, there are a number of verbs that are considered irregular. These irregular verbs have their own conjugation patterns and do not follow the regular rules.
Some commonly used irregular verbs in the preterite include:
- Ser (to be) – Fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, fueron
- Ir (to go) – Fui, fuiste, fue, fuimos, fuisteis, fueron
- Hacer (to do/make) – Hice, hiciste, hizo, hicimos, hicisteis, hicieron
- Tener (to have) – Tuve, tuviste, tuvo, tuvimos, tuvisteis, tuvieron
- Estudiar (to study) – Estudié, estudiaste, estudió, estudiamos, estudiasteis, estudiaron
These verbs have unique endings or stem changes in the preterite tense. It is important to memorize these irregular verb conjugations in order to accurately convey past actions. Practice and repetition are key in mastering the conjugation of irregular verbs in the preterite.
It is worth noting that while irregular verbs may seem challenging at first, they are quite common in everyday conversation. Becoming familiar with these irregular verbs will greatly improve your Spanish speaking and writing skills.
Definition of irregular verbs in the preterite
In Spanish, regular verbs in the preterite tense follow a predictable pattern of conjugation. However, there are also a group of verbs that are considered irregular in this tense. Irregular verbs in the preterite have different conjugations than regular verbs, making them a bit trickier to learn and use correctly.
Irregular verbs in the preterite tense can have various changes in their stem, which affects the way they are conjugated. These changes can include vowel changes, consonant changes, or a combination of both. Some common irregular verbs in the preterite include “ser” (to be), “ir” (to go), “hacer” (to do/make), “tener” (to have), and “decir” (to say/tell).
For example, the verb “ser” is irregular in the preterite because its conjugation does not follow the typical -ar, -er, or -ir verb endings. In the preterite tense, “ser” is conjugated as follows:
- yo fui (I was)
- tú fuiste (you were)
- él/ella/usted fue (he/she/you were)
- nosotros/nosotras fuimos (we were)
- vosotros/vosotras fuisteis (you all were)
- ellos/ellas/ustedes fueron (they/you all were)
It is important to study and memorize the irregular verb conjugations in the preterite tense, as they do not follow the regular patterns. Practice and repetition are key to mastering the irregular verbs in the preterite and using them correctly in Spanish conversation and writing.
Benefits of learning irregular verbs in the preterite
Learning irregular verbs in the preterite can be challenging, but it comes with several benefits. Firstly, knowing the irregular forms of these verbs allows for more accurate and natural communication in the past tense. Instead of always relying on regular verb conjugations, learners can express past actions more precisely, adding depth and fluency to their speech.
Another benefit is that learning irregular verbs in the preterite enhances vocabulary knowledge. By studying the irregular forms of verbs like “ser” (to be) or “ir” (to go), learners not only expand their proficiency with these specific verbs but also learn new vocabulary associated with past actions. This can greatly enrich their overall vocabulary and improve their ability to understand and express themselves in a variety of contexts.
Improved comprehension in reading and listening
The ability to recognize and understand irregular verbs in the preterite can greatly improve reading and listening comprehension. Texts and conversations frequently contain irregular verbs, and being able to identify and understand them allows learners to grasp the meaning of the text or conversation more effectively. This skill is particularly important when consuming authentic materials, such as books, movies, or real-life conversations.
- Increased confidence in speaking
- Expanded range of expression
- Improved accuracy in writing
- Enhanced understanding of grammar
- Preparation for higher levels of language learning
In conclusion, the benefits of learning irregular verbs in the preterite are numerous. From improved communication skills to enhanced comprehension, learners who take the time to study and practice these verbs can expect to see significant improvements in their overall proficiency in the Spanish language.
Improving your Spanish language skills with irregular verbs
Learning a new language can be a challenging and rewarding experience, and Spanish is no exception. One aspect of Spanish grammar that often poses difficulties for learners is the use of irregular verbs, especially in the preterite tense. However, with concerted effort and practice, it is possible to improve your Spanish language skills and become more confident in using these verbs.
1. Regular exposure to irregular verbs
To improve your knowledge and understanding of irregular verbs, it is crucial to expose yourself to them regularly. This can be done through reading Spanish texts, listening to Spanish music or podcasts, or watching Spanish movies or TV shows. By immersing yourself in Spanish-language content, you will become more familiar with how irregular verbs are used in context.
2. Memorization techniques
Memorizing irregular verb conjugations can be daunting, but there are several techniques that can make the process easier. One method is to create flashcards with the verb infinitive on one side and the corresponding preterite conjugation on the other. By regularly reviewing these flashcards, you will gradually internalize the correct forms.
3. Practice with targeted exercises
In order to reinforce your understanding and application of irregular verbs, it is important to practice with targeted exercises. This can involve completing worksheets, participating in online quizzes, or engaging in conversation exercises with a language partner or tutor. Through these activities, you will gain confidence and fluency in using irregular verbs in the preterite tense.
4. Seek feedback and correction
Another effective way to improve your Spanish language skills with irregular verbs is to seek feedback and correction from native speakers or experienced language learners. They can help identify any mistakes or areas of improvement, allowing you to make necessary adjustments in your language use.
5. Use irregular verbs in context
Finally, the best way to solidify your understanding of irregular verbs is to use them in real-life situations. Whether it’s writing essays, engaging in conversations, or participating in language exchange programs, actively incorporating irregular verbs in your communication will help you become more comfortable and proficient.
In conclusion, improving your Spanish language skills with irregular verbs requires dedication and practice. By exposing yourself to the verbs, employing memorization techniques, practicing with exercises, seeking feedback, and using the verbs in context, you can enhance your language abilities and confidently navigate the world of Spanish grammar.
Enhancing your communication abilities with native Spanish speakers
Improving your communication skills with native Spanish speakers can be a valuable asset in today’s globalized world. Whether you have an interest in traveling, conducting business, or simply connecting with people from different backgrounds, learning how to effectively communicate in Spanish opens up a myriad of opportunities.
1. Practice authentic conversations
One of the best ways to enhance your communication abilities with native Spanish speakers is by engaging in authentic conversations. Seek out opportunities to practice speaking with native speakers, whether it be through language exchange programs, online forums, or local meetups. Immersing yourself in real-life conversations will not only improve your fluency but also help you gain confidence in using the language.
2. Learn idiomatic expressions
Another key aspect of effective communication is understanding and using idiomatic expressions. Spanish is rich in idioms and colloquial expressions that may not have a direct translation in English. By familiarizing yourself with these idiomatic expressions, you will be better equipped to communicate naturally with native speakers and understand the nuances of the language.
3. Embrace cultural differences
Communication is not only about language but also about understanding cultural differences. When interacting with native Spanish speakers, make an effort to learn about their customs, traditions, and etiquette. This cultural understanding will not only enhance your communication skills but also help you build stronger relationships with Spanish speakers.
4. Use technology to your advantage
In today’s digital age, there are numerous technological tools that can help you enhance your communication abilities with native Spanish speakers. Language learning apps, online courses, and video conferencing platforms can make it easier to practice your language skills and connect with native speakers from anywhere in the world. Take advantage of these resources to continue improving your Spanish proficiency.
By actively seeking out opportunities to engage with native Spanish speakers and continually practicing your communication skills, you will gradually become more confident and proficient in your ability to connect with Spanish speakers on a deeper level. Remember that learning a language is an ongoing process, so embrace every opportunity to expand your knowledge and understanding of the Spanish language and culture.
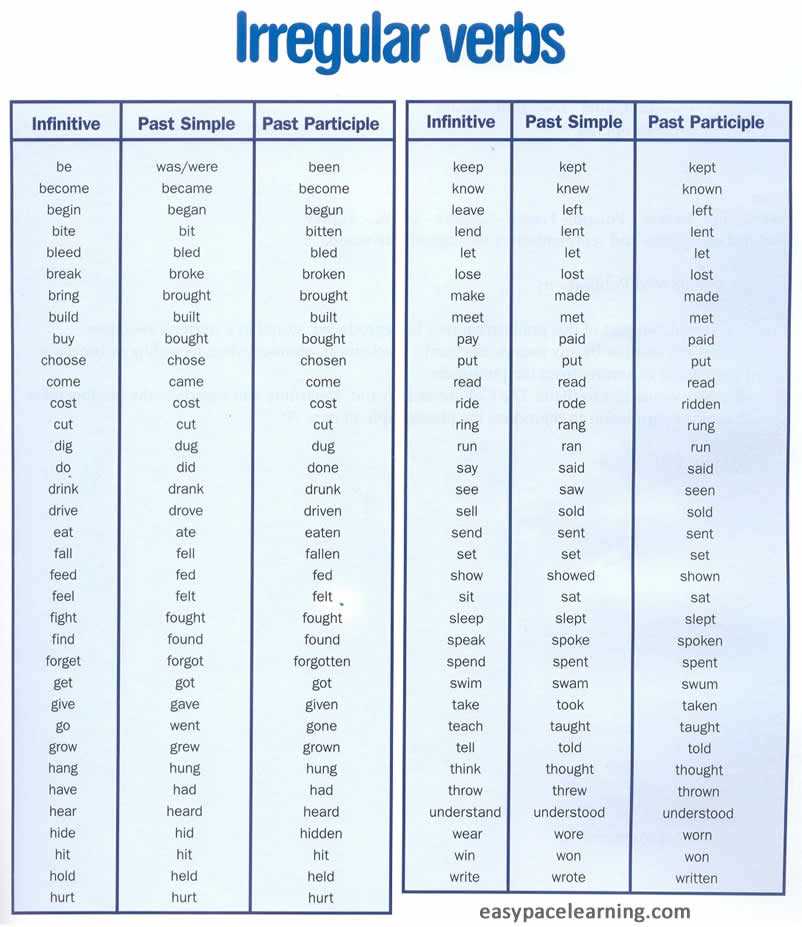
Examples of irregular verbs in the preterite
In the Spanish language, there are several irregular verbs that undergo changes in the preterite tense. These verbs do not follow the regular conjugation patterns, and their stems change to form the past tense. Here are some examples:
1. Ser (to be)
The verb “ser” is irregular in the preterite tense. Its conjugation in the past tense is as follows:
- Yo fui (I was)
- Tú fuiste (You were)
- Él/ella/usted fue (He/she/you were)
- Nosotros fuimos (We were)
- Vosotros fuisteis (You all were)
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes fueron (They/you all were)
2. Ir (to go)
The verb “ir” is also irregular in the preterite tense. Its conjugation in the past tense is as follows:
- Yo fui (I went)
- Tú fuiste (You went)
- Él/ella/usted fue (He/she/you went)
- Nosotros fuimos (We went)
- Vosotros fuisteis (You all went)
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes fueron (They/you all went)
3. Hacer (to do/make)
The verb “hacer” is irregular in the preterite tense. Its conjugation in the past tense is as follows:
- Yo hice (I did/made)
- Tú hiciste (You did/made)
- Él/ella/usted hizo (He/she/you did/made)
- Nosotros hicimos (We did/made)
- Vosotros hicisteis (You all did/made)
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes hicieron (They/you all did/made)
4. Ver (to see)
The verb “ver” is irregular in the preterite tense. Its conjugation in the past tense is as follows:
- Yo vi (I saw)
- Tú viste (You saw)
- Él/ella/usted vio (He/she/you saw)
- Nosotros vimos (We saw)
- Vosotros visteis (You all saw)
- Ellos/ellas/ustedes vieron (They/you all saw)
These are just a few examples of irregular verbs in the preterite tense. It’s important to study and practice these irregular conjugations to become proficient in Spanish.
Common irregular verbs in the preterite
The preterite tense is used to express completed actions in the past. While regular verbs in Spanish follow a predictable pattern in the preterite, there are some verbs that are irregular and do not follow these rules. Here are some common irregular verbs in the preterite.
1. Ser (to be)
The verb “ser” is irregular in the preterite tense. In the yo form, it changes to “fui” instead of the expected “fué”. Here is the conjugation of “ser” in the preterite:
- Yo fui (I was)
- Tú fuiste (You were)
- Él/Ella/Usted fue (He/She/You was)
- Nosotros/Nosotras fuimos (We were)
- Vosotros/Vosotras fuisteis (You all were)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes fueron (They/You all were)
2. Ir (to go)
The verb “ir” is also irregular in the preterite tense. It does not follow the regular -ar verb ending pattern. Here is the conjugation of “ir” in the preterite:
- Yo fui (I went)
- Tú fuiste (You went)
- Él/Ella/Usted fue (He/She/You went)
- Nosotros/Nosotras fuimos (We went)
- Vosotros/Vosotras fuisteis (You all went)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes fueron (They/You all went)
3. Hacer (to do/make)
The verb “hacer” is irregular in the preterite tense as well. The “hac-” stem changes to “hic-” in the preterite. Here is the conjugation of “hacer” in the preterite:
- Yo hice (I did/made)
- Tú hiciste (You did/made)
- Él/Ella/Usted hizo (He/She/You did/made)
- Nosotros/Nosotras hicimos (We did/made)
- Vosotros/Vosotras hicisteis (You all did/made)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes hicieron (They/You all did/made)
These are just a few examples of irregular verbs in the preterite tense. It is important to memorize their conjugations to express past actions correctly in Spanish.