The verb “tener” is one of the most important verbs in the Spanish language. It is used to express possession and is also commonly used in idiomatic expressions. Understanding its conjugation and usage is essential for any student of Spanish.
Conjugating “tener” can be a bit tricky at first, but with practice, it becomes easier. In this article, we will provide an answer key to help you understand how to conjugate “tener” in different tenses and moods.
One of the key features of “tener” is its irregular conjugations in some forms. For example, in the first and second-person singular forms of the present tense, “tengo” and “tienes” are used instead of the regular forms “tengo” and “tienes”. It is important to memorize these irregular forms to use “tener” correctly.
In addition to its regular conjugations, “tener” is also used in various idiomatic expressions. For example, “tener ganas de” is used to express a desire or willingness to do something, like “tengo ganas de comer” (I feel like eating). These expressions can be a bit confusing at first, but with practice, you will become more comfortable using them.
Overall, mastering the grammar of the verb “tener” is crucial for becoming fluent in Spanish. By understanding its conjugations and idiomatic expressions, you will be able to express possession and communicate effectively in various situations. With this answer key, you are one step closer to mastering the verb “tener”!
Understanding the basics of the verb “tener”
The verb “tener” is one of the most important verbs in the Spanish language. It is translated as “to have” in English and is used to express possession. Understanding the different conjugations and uses of “tener” is essential for building basic sentences in Spanish.
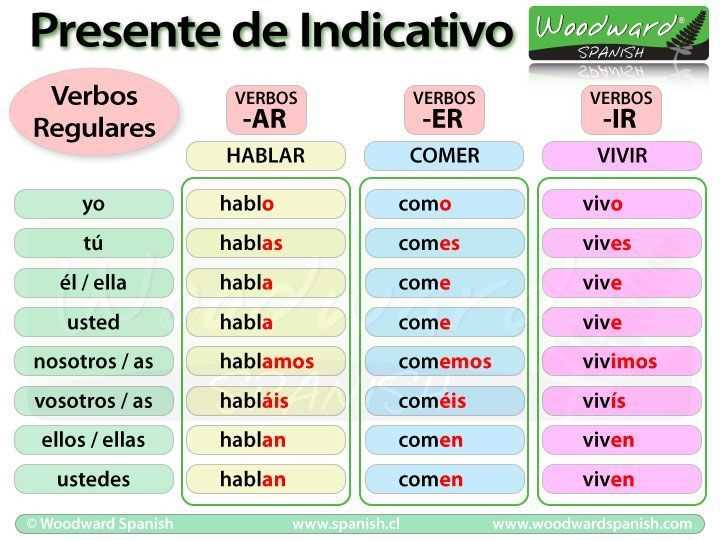
In its present tense, “tener” is conjugated as follows:
- Yo tengo (I have)
- Tú tienes (You have)
- Él/Ella tiene (He/She has)
- Nosotros/Nosotras tenemos (We have)
- Vosotros/Vosotras tenéis (You all have)
- Ellos/Ellas tienen (They have)
The verb “tener” can also be used to express age. In this case, it is conjugated with the verb “tener” + “number” + “años” (years old). For example:
- Tengo veinticinco años (I am twenty-five years old)
- Él tiene treinta años (He is thirty years old)
- Nosotros tenemos dieciséis años (We are sixteen years old)
Furthermore, “tener” is often used in idiomatic expressions such as “tener hambre” (to be hungry), “tener sed” (to be thirsty), and “tener frío” (to be cold). These expressions indicate a certain state or feeling rather than possession.
Exploring the different forms of the verb “tener”

The verb “tener” is an essential verb in Spanish, as it is used to express possession, age, and various other meanings. In this article, we will explore the different forms of the verb “tener” and how they are used in different contexts.
Firstly, let’s look at the basic forms of “tener” in the present tense. The conjugations are as follows:
- Yo tengo – I have
- Tú tienes – You have (informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted tiene – He/She/You (formal) has
- Nosotros tenemos – We have
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes tienen – They/You all have
These forms can be used to express possession of physical objects, such as “Tengo un coche” (I have a car). They can also be used to indicate age, for example, “Tienes veinte años” (You are twenty years old).
In addition to the present tense, “tener” can also be conjugated in other tenses, such as the preterite and the future. In the preterite tense, the conjugations are as follows:
- Yo tuve – I had
- Tú tuviste – You had (informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted tuvo – He/She/You (formal) had
- Nosotros tuvimos – We had
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes tuvieron – They/You all had
These forms can be used to talk about past possession or past events, such as “Tuve un perro cuando era niño” (I had a dog when I was a child). In the future tense, the conjugations of “tener” are as follows:
- Yo tendré – I will have
- Tú tendrás – You will have (informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted tendrá – He/She/You (formal) will have
- Nosotros tendremos – We will have
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes tendrán – They/You all will have
These forms are used to talk about future possession or future events, for example, “Tendré una reunión mañana” (I will have a meeting tomorrow).
In conclusion, “tener” is a versatile verb that is used to express possession, age, and various other meanings. By mastering its different forms, you can enhance your Spanish communication skills and express yourself more effectively.
Learning how to conjugate “tener” in the present tense
In Spanish, “tener” means “to have”. It is a very important verb and is used frequently in everyday conversations. Learning how to conjugate “tener” in the present tense is essential for building basic sentences and expressing possession or obligation.
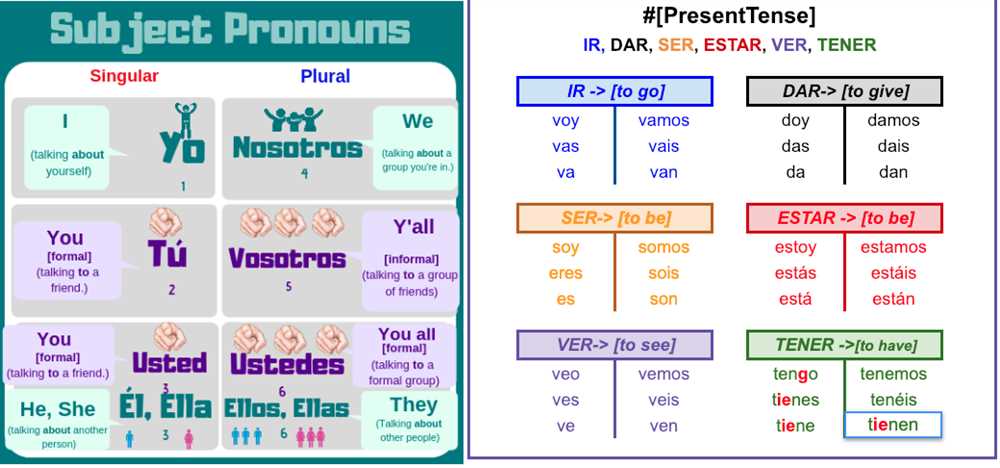
To conjugate “tener” in the present tense, you need to know the different forms it takes depending on the subject pronoun. Here is the conjugation of “tener” in the present tense:
- Yo tengo – I have
- Tú tienes – You have (informal)
- Él/Ella/Usted tiene – He/She/You have (formal)
- Nosotros/Nosotras tenemos – We have
- Vosotros/Vosotras tenéis – You all have (informal, Spain)
- Ellos/Ellas/Ustedes tienen – They/You all have
It is important to note that the verb form and the subject pronoun have to agree in gender and number. For example, “Yo tengo” means “I have” while “Ellos tienen” means “They have”.
Here are some examples of sentences using the verb “tener” in the present tense:
- Tengo tres hermanos. – I have three brothers.
- ¿Tienes hambre? – Are you hungry?
- Él tiene una casa muy grande. – He has a very big house.
- Nosotros tenemos una reunión importante mañana. – We have an important meeting tomorrow.
- ¿Tenéis tiempo para ir al cine? – Do you all have time to go to the movies?
- Ellos tienen muchos libros en su biblioteca. – They have many books in their library.
By practicing the conjugation of “tener” in the present tense and using it in different contexts, you will become more comfortable with expressing possession and obligations in Spanish.
Mastering the use of “tener” in expressions of age
One of the most common uses of the verb “tener” in Spanish is to express someone’s age. In these expressions, “tener” is used to indicate someone’s age in a straightforward way. To talk about someone’s age, we simply use the formula “tener + age.”
For example, if we want to say “I am 25 years old” in Spanish, we would say “Tengo 25 años”. The verb “tener” is conjugated according to the subject of the sentence, in this case, the first person singular pronoun “yo” (I). So, “tengo” is the conjugated form of “tener” for “yo”.
It’s important to note that in Spanish, we don’t use the verb “to be” to express age like in English. Instead, we use “tener”. This is a common mistake made by English speakers learning Spanish, but with practice, it can be easily mastered. Here are a few more examples of using “tener” to express age:
- Tienes 30 años – You are 30 years old
- Tenemos 15 años – We are 15 years old
- Tiene 50 años – He/She is 50 years old
Remember to always use the corresponding form of “tener” based on the subject of the sentence. Practicing these expressions will help you become more confident in using “tener” to talk about age.
Using “tener” to express possession

The verb “tener” in Spanish is widely used to express possession. It is equivalent to the English verb “to have”. Tener is a regular verb, which means that its conjugation follows a predictable pattern. Understanding how to use “tener” correctly is essential for communicating possession in Spanish.
To express possession, “tener” is used in conjunction with a noun. For example, to say “I have a book”, you would say “Yo tengo un libro” in Spanish. Here, “yo” means “I”, “tengo” means “I have”, and “un libro” means “a book”. It is important to note that in Spanish, the subject pronoun is often omitted because the verb conjugation already indicates the subject.
Tener can also be used to express age. For example, to say “I am 25 years old” in Spanish, you would say “Tengo 25 años”. Here, “tengo” means “I have” and “25 años” means “25 years”. So, in this context, “tener” is used to indicate possession of a certain age.
Additionally, tener is used in idiomatic expressions. For example, the phrase “tener hambre” means “to be hungry” and “tener sed” means “to be thirsty”. These expressions use “tener” to express a certain state or condition.
Overall, understanding how to use “tener” to express possession is essential for mastering Spanish grammar. By learning the different contexts in which “tener” is used, you will be able to effectively communicate possession and express various states or conditions in Spanish.
Discovering idiomatic expressions with “tener”
Idiomatic expressions are phrases or expressions that cannot be understood literally based on the individual meanings of the words used. One such set of idiomatic expressions in Spanish includes those that use the verb “tener” which means “to have”. These expressions provide a way to convey various emotions, states, or characteristics.
Let’s explore some commonly used idiomatic expressions with “tener” and their English equivalents:
- Tener hambre: This expression means “to be hungry”. Literal translation: “to have hunger”.
- Tener sed: This expression means “to be thirsty”. Literal translation: “to have thirst”.
- Tener sueño: This expression means “to be sleepy”. Literal translation: “to have sleep”.
- Tener miedo: This expression means “to be afraid”. Literal translation: “to have fear”.
- Tener prisa: This expression means “to be in a hurry”. Literal translation: “to have hurry”.
- Tener cuidado: This expression means “to be careful”. Literal translation: “to have care”.
These idiomatic expressions are essential to know in order to effectively communicate in Spanish. They add depth and nuance to the language, allowing speakers to convey their emotions and describe situations more accurately.
By familiarizing yourself with idiomatic expressions with “tener”, you can expand your vocabulary and sound more like a native speaker. Practice using these expressions in context to improve your fluency and understanding of the Spanish language.
Practicing with exercises and activities on “tener”
The verb tener is an essential verb to learn in Spanish as it is used to express possession and to indicate how old someone is. To become proficient in using this verb, it is crucial to practice with exercises and activities that reinforce its usage in different contexts.
Exercise 1:
Create a list of five possessions you have using the verb tener. For example, “Tengo un teléfono” (I have a phone). Share your list with a partner and ask them about their possessions using the verb tener. This exercise will help you become more comfortable using the verb in conversations.
Exercise 2:
Write five sentences describing different ages using the verb tener. For instance, “Tengo veinte años” (I am twenty years old). Then, read your sentences aloud and try to remember the different forms of tener for each age. This activity will improve your understanding of how the verb is used to express age.
Exercise 3:
Create a dialogue with a partner where you both discuss your possessions and ages using the verb tener. Take turns asking and answering questions, making sure to use the appropriate forms of tener. This conversational exercise will help you practice using the verb in an interactive and natural way.
Activity 1:
Create a crossword puzzle using words related to possessions and ages. Use clues such as “I have a car” or “She is twenty years old” to fill in the crossword. Share your puzzle with a partner or a group and see who can complete it first. This activity will test your knowledge of the verb tener and reinforce vocabulary related to possessions and ages.
Activity 2:
Role-play different scenarios where you have to talk about possessions and ages using the verb tener. For example, pretend you are a salesperson and have to describe the products you have in stock, or pretend you are a teacher and have to ask your students how old they are. This activity will help you practice using the verb in specific situations and develop your conversational skills.
By incorporating these exercises and activities into your language learning routine, you will strengthen your knowledge and usage of the verb tener. Remember to practice regularly and seek opportunities to use the verb in real-life conversations to solidify your understanding.