Graphing and data analysis are essential skills in many scientific and mathematical fields. Whether you are a student studying physics, biology, or economics, or a professional researcher analyzing trends and patterns in data, understanding how to graph and analyze data is crucial.
This article provides the answers key for a graphing and data analysis worksheet. The worksheet includes a variety of questions and exercises that cover different aspects of graphing and data analysis, such as interpreting graphs, calculating averages, and identifying trends.
By providing the answers key, this article aims to help students and researchers check their work and verify their understanding of graphing and data analysis concepts. It also serves as a resource for teachers and instructors to assess their students’ progress and guide them in the right direction.
Overall, the graphing and data analysis worksheet answers key presented in this article can be a valuable tool for anyone looking to improve their skills in interpreting and analyzing data. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced data analyst, practicing these exercises and checking your answers can contribute to your overall competence in graphing and data analysis.
Understanding the Importance of Graphing and Data Analysis

Graphing and data analysis are essential tools in today’s data-driven world. They allow us to visually represent and understand complex information, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. By organizing data into graphs, charts, and tables, we can effectively communicate information and draw meaningful conclusions.
One of the primary benefits of graphing and data analysis is that they provide a clear and concise way to present information. Instead of overwhelming readers with a long list of numbers and statistics, a visual representation can convey the same information in a more digestible format. This is particularly important when dealing with large datasets or when trying to highlight important trends or outliers.
Graphs also enable us to compare and contrast different data points and identify correlations between variables. For example, a scatter plot can show us if there is a relationship between two variables, such as temperature and ice cream sales, by plotting data points on a graph. This visual representation allows us to see if there is a pattern or if the variables are independent of each other.
Furthermore, graphing and data analysis can help researchers and decision-makers make informed and evidence-based decisions. By analyzing data, we can identify problems, evaluate potential solutions, and monitor the effectiveness of interventions. This is particularly valuable in fields such as healthcare, economics, and environmental sciences, where data-driven decision-making can have a significant impact.
In conclusion, graphing and data analysis play a crucial role in understanding and interpreting data. They allow us to simplify complex information, identify patterns, and make informed decisions based on evidence. Therefore, acquiring skills in graphing and data analysis is essential for success in today’s data-driven world.
Types of Graphs Used in Data Analysis
Data analysis involves the collection, organization, and interpretation of data to draw meaningful conclusions and make informed decisions. Graphs are an essential tool in data analysis as they provide a visual representation of the data, making it easier to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. There are several types of graphs commonly used in data analysis, each with its own purpose and benefits.
Bar graphs: Bar graphs are used to compare discrete categories or groups. They consist of rectangular bars that represent different categories, with the height of each bar corresponding to the quantity or frequency being measured. Bar graphs are particularly useful for displaying categorical data and making comparisons between different groups.
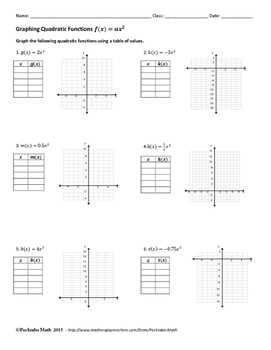
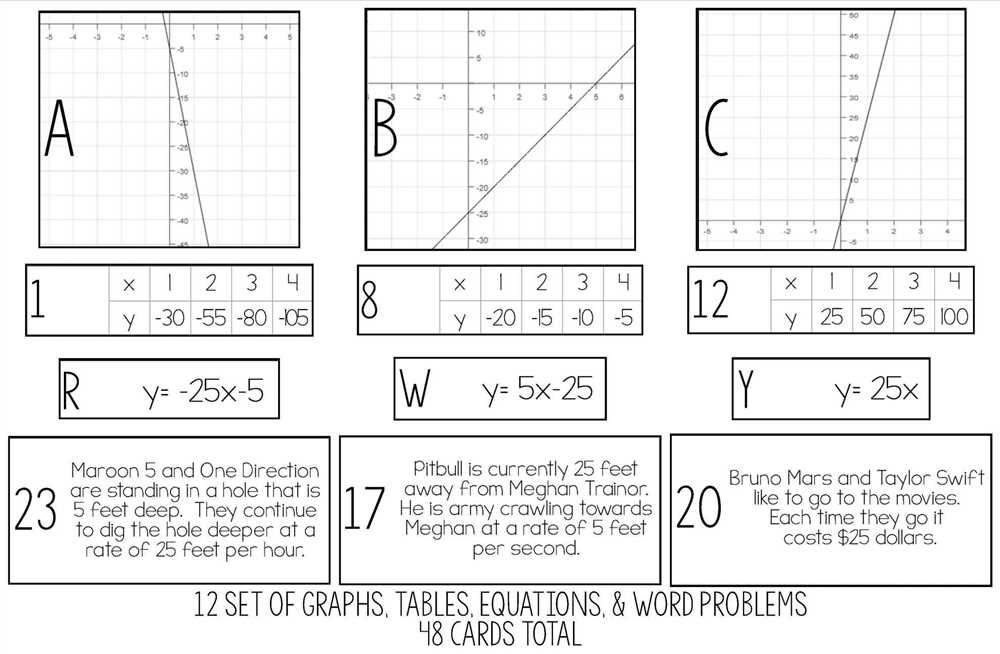
Line graphs: Line graphs are used to show the relationship between two variables over time or another continuous interval. They consist of points connected by lines, with the x-axis representing the independent variable and the y-axis representing the dependent variable. Line graphs are commonly used for tracking trends and changes over time, such as measuring temperature fluctuations or population growth.
Pie charts: Pie charts are used to represent parts of a whole. They consist of a circle divided into sectors, with each sector representing a different category or group. The size of each sector corresponds to the proportion or percentage of the whole it represents. Pie charts are commonly used for displaying proportions and percentages, such as market shares or demographic distributions.
Scatter plots: Scatter plots are used to show the relationship between two continuous variables. They consist of individual points plotted on a graph, with one variable represented on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Scatter plots are particularly useful for identifying correlations and trends between variables, such as examining the relationship between age and income.
Histograms: Histograms are used to display the distribution of continuous data. They consist of bars that represent different ranges or intervals of data, with the height of each bar indicating the frequency or count of data points falling within that range. Histograms are commonly used for analyzing data distributions, such as measuring test scores or household incomes.
By selecting the appropriate type of graph for the given data, analysts can effectively visualize and analyze the information, leading to meaningful insights and informed decision-making. These various types of graphs provide different perspectives and representations of the data, allowing analysts to explore patterns, trends, and relationships in a clear and concise manner.
Bar Graphs: Analyzing Categorical Data
A bar graph is a useful tool for analyzing categorical data, which is data that can be divided into distinct categories or groups. It provides a visual representation of the frequency or count of each category, making it easier to interpret and draw conclusions from the data.
When analyzing categorical data using a bar graph, there are a few key steps to follow. First, you need to identify the categories or groups you want to analyze. This could be anything from different types of fruits to the results of a survey question.
Next, you will need to collect the data and organize it into a frequency table. This table should list the categories and the corresponding number of occurrences or counts for each category. Once you have your frequency table, you can start creating the bar graph.
To create a bar graph, you will need to plot the categories along the x-axis and the counts or frequencies along the y-axis. Each category will be represented by a separate bar, with the height of the bar corresponding to the count or frequency. You can choose to either use horizontal or vertical bars, depending on personal preference or the nature of the data.
A key benefit of bar graphs is that they allow for easy comparison between different categories. You can quickly see which category has the highest count or frequency, as well as identify any patterns or trends in the data. Additionally, bar graphs can be used to present data over time, by creating multiple bars for each category representing different time periods.
Overall, bar graphs are a powerful tool for analyzing and communicating categorical data. They provide a clear visual representation of the distribution of data, making it easier to understand and draw insights. By following the steps outlined above, you can effectively analyze and interpret data using bar graphs.
Line Graphs: Representing Trends and Changes Over Time
Line graphs are a powerful tool for representing and analyzing trends and changes over time. They provide a visual representation of data, allowing us to easily identify patterns and relationships. By plotting data points on a graph and connecting them with lines, we can see how variables change in relation to each other and how they evolve over time.
One key feature of line graphs is that they show the relationship between two variables on a Cartesian coordinate system. They have an x-axis, which represents time, and a y-axis, which represents the values of the variables being measured. The data points are plotted on the graph, with the x-coordinate corresponding to the time and the y-coordinate corresponding to the value of the variable. Connecting these data points with lines creates a visual representation of how the variable changes over time.
Line graphs are particularly useful for tracking trends and changes over time. They allow us to easily identify if a variable is increasing, decreasing, or staying constant. By analyzing the slope of the line, we can determine the rate at which the variable is changing. If the slope is steep, it indicates a rapid change, while a gentler slope suggests a slower change. Additionally, line graphs can help us identify any patterns or cycles in the data, such as seasonal fluctuations or recurring patterns.
Line graphs are commonly used in various fields, including economics, finance, public health, and environmental science. They are used to analyze trends in stock prices, track changes in disease prevalence, monitor environmental indicators, and much more. By representing data visually, line graphs enable us to gain a better understanding of how variables evolve and interact over time, making them an essential tool for data analysis and decision-making.
Pie Charts: Examining Proportions and Percentages
Pie charts are a visual representation of data that showcase proportions and percentages. They are particularly useful when analyzing data with categorical variables, as they provide a clear and easy-to-interpret depiction of the distribution of each category.
Proportions: Pie charts display proportions by dividing a circle into slices, where each slice represents a category. The size of each slice is proportional to the corresponding category’s proportion in the data. In other words, the larger the slice, the larger the proportion of that category.
Percentages: Pie charts also show percentages by adding labels to each slice that indicate the percentage it represents. These labels help viewers understand the relative importance of each category and make comparisons between different categories.
When examining a pie chart, it’s important to consider the following aspects:
- Number of categories: The number of categories represented in the pie chart affects its readability. Too many categories can make the chart cluttered and difficult to interpret. It’s best to limit the number of categories to ensure clarity.
- Color choices: Selecting appropriate colors for each category can enhance the pie chart’s overall visual impact. It’s essential to choose colors that are distinguishable and visually appealing.
- Label placement: Labels should be strategically placed to avoid overlapping and ensure readability. They should be positioned near the corresponding slice and aligned in a way that does not obscure the data.
Overall, pie charts are a valuable tool for analyzing and presenting data with categorical variables. They allow viewers to grasp proportions and percentages quickly, making them an effective choice for visualizing data distributions.
Interpreting Graphs and Analyzing Data
Graphs are visual representations of data that allow us to understand patterns, trends, and relationships between variables. Interpreting graphs is an essential skill in data analysis as it helps us make sense of complex information and draw meaningful conclusions.
When analyzing data, it is important to pay attention to the axes of the graph. The x-axis represents the independent variable, which is typically the one we have control over or that is changing systematically. The y-axis represents the dependent variable, which is the variable we are measuring or observing. By examining the position of data points in relation to the axes, we can determine how the independent variable affects the dependent variable.
Another key aspect of graph interpretation is identifying the type of graph used. There are several common types of graphs, such as line graphs, bar graphs, pie charts, and scatter plots. Each type of graph serves a specific purpose and provides different insights into the data. For example, line graphs are useful for showing trends and changes over time, while bar graphs are effective for comparing different categories or groups.
In addition to interpreting graphs, data analysis also involves looking for patterns and trends in the data. This can be done by examining the shape of the graph, the direction of the line or bar, and the distribution of data points. Trends can be positive (increasing), negative (decreasing), or stable (consistent). By analyzing these patterns, we can make predictions, draw conclusions, and make informed decisions based on the data.
To effectively interpret graphs and analyze data, it is important to have good critical thinking skills and the ability to ask questions. By asking questions such as “What does this data tell us?”, “Why is there a difference between the groups?”, or “What might explain this trend?”, we can dig deeper into the meaning behind the data and uncover valuable insights.
Key Points:
- Graphs help us understand patterns, trends, and relationships between variables.
- The x-axis represents the independent variable, while the y-axis represents the dependent variable.
- Different types of graphs provide different insights into the data.
- Data analysis involves identifying patterns, trends, and making informed decisions based on the data.
- Asking questions is essential for effective interpretation and analysis of graphs and data.
Identifying Patterns and Relationships in Graphs
When analyzing graphs, one of the key tasks is to identify patterns and relationships between the variables being represented. By examining the shape and direction of the graph, as well as the values of the coordinates, we can gain valuable insights into the data.
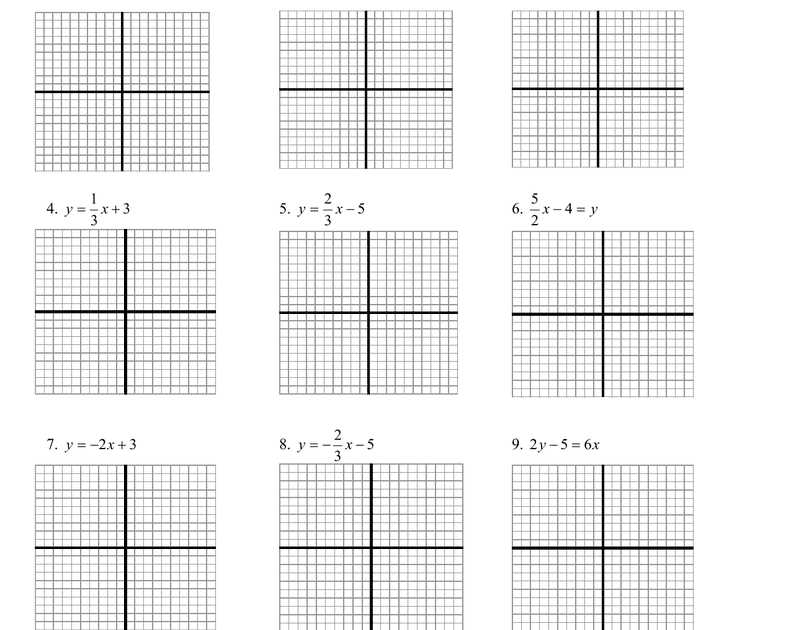
Linear Relationships: A linear relationship can be identified when the data points on a graph form a straight line. This indicates a constant rate of change between the variables. In a linear graph, the slope of the line represents the rate of change, and the y-intercept represents the initial value.
- Positive Linear Relationship: When the line slopes upwards from left to right, it indicates a positive linear relationship. This means that as one variable increases, so does the other.
- Negative Linear Relationship: When the line slopes downwards from left to right, it indicates a negative linear relationship. This means that as one variable increases, the other decreases.
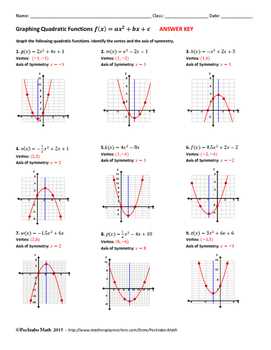
Nonlinear Relationships: In some cases, the relationship between variables may not be linear. Nonlinear relationships can take various forms, such as exponential, logarithmic, or quadratic. The key is to observe the shape of the graph and determine the best fit curve.
- Exponential Relationship: In an exponential relationship, the graph will show a rapid increase or decrease, often in the form of a curve that gets steeper or shallower.
- Logarithmic Relationship: In a logarithmic relationship, the graph will show a curve that starts steeply but gradually levels off.
- Quadratic Relationship: In a quadratic relationship, the graph will show a parabolic shape, with the vertex indicating the maximum or minimum point.
By accurately identifying these patterns and relationships in graphs, we can better understand the data and make informed decisions or predictions based on the trends observed.