
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a vital economic indicator that measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country in a specific period. Understanding how to calculate GDP and analyze its components is crucial for evaluating the economic health of a nation. In this article, we will provide answers to a GDP worksheet, helping you grasp the concepts and calculations involved.
One of the main components of GDP is consumer spending. It includes personal expenditures on durable goods, non-durable goods, and services. When calculating GDP, you need to consider the total amount spent by consumers in a specific timeframe. This can be obtained by combining data from various sources, such as consumer surveys and government records.
Investment is another essential component of GDP. It refers to businesses’ spending on capital goods, such as machinery, equipment, and infrastructure. Additionally, it includes changes in inventory levels and the amount spent on research and development. To calculate investment, you need to collect data from business reports and financial statements.
Government spending is also considered when calculating GDP. It includes all public expenditures, such as defense, education, healthcare, and infrastructure. To determine the government’s contribution to GDP, you must gather data from the government budget and expenditure reports.
Net exports, the final component of GDP, represents the difference between a country’s exports and imports. It measures the amount of goods and services that a country sells abroad, minus the value of what it buys from other nations. To calculate net exports, you need data on exports and imports from trade records and customs reports.
In conclusion, calculating GDP involves understanding the components of consumer spending, investment, government spending, and net exports. By accurately gathering and analyzing data from various sources, you can determine the overall economic output of a country and gauge its economic performance. These answers to the GDP worksheet will help you navigate the intricacies of GDP calculations and interpretation.
Gross Domestic Product Worksheet Answers
The Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the total value of goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. It is an important indicator of a country’s economic health and is often used to compare the economic performance of different nations.
Calculating GDP involves adding up the values of different components, including personal consumption, government spending, private investment, and net exports. Each component contributes to the overall GDP figure, and understanding their individual contributions helps us analyze the factors that drive economic growth.
Worksheet Answers
1. Calculate the GDP using the expenditure approach.
To calculate GDP using the expenditure approach, we sum up the spending on consumption, investment, government expenditure, and net exports. This formula can be represented as:
| GDP = C + I + G + (X – M) |
Where:
- C represents personal consumption expenditures
- I represents gross private domestic investment
- G represents government consumption and gross investment
- X represents exports of goods and services
- M represents imports of goods and services
2. Identify the components of GDP and explain their importance.
The components of GDP include personal consumption expenditures, gross private domestic investment, government consumption and gross investment, and net exports. Each component plays a vital role in determining the overall economic activity and growth of a country.
– Personal consumption expenditures (C): This represents the spending by individuals on goods and services. It is a key driver of economic growth as higher consumer spending indicates higher demand, which stimulates production and job creation.
– Gross private domestic investment (I): This includes all spending by businesses on capital goods, such as machinery and equipment, and changes in inventory. Investment is important for expanding production capacity, driving innovation, and increasing productivity.
– Government consumption and gross investment (G): This includes all spending by the government on goods and services, as well as investments in infrastructure and public projects. Government spending can influence economic activity and stability, especially during times of economic downturn or recession.
– Net exports (X – M): This component represents the difference between a country’s exports and imports. Positive net exports indicate that a country is exporting more than it is importing, which contributes to economic growth and generates income.
Understanding the components of GDP helps policymakers, economists, and investors assess the overall health and performance of an economy, identify areas of strength or weakness, and make informed decisions to promote economic growth and stability.
What is Gross Domestic Product?
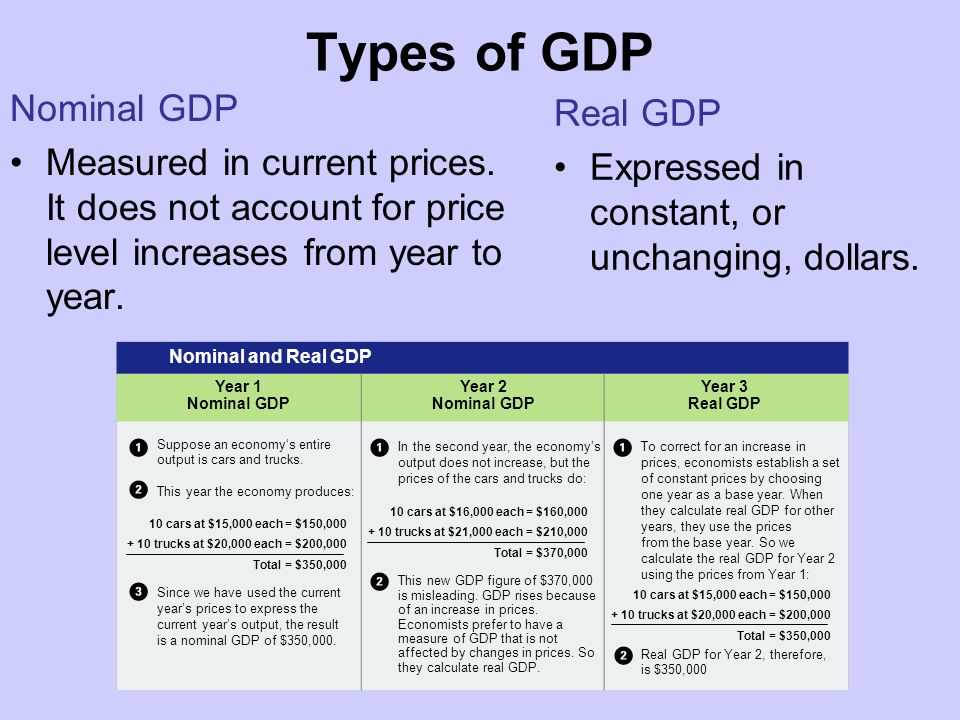
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the total value of all final goods and services produced within a country during a specific period of time. It is often used as an indicator of the economic health and size of a country’s economy. GDP is calculated by adding up the value of goods and services produced by all sectors of the economy, including agriculture, manufacturing, and services.
GDP provides a snapshot of the overall economic activity within a country. It includes the value of both goods and services because both contribute to the overall economic output. Goods refer to tangible products that are produced, such as cars and furniture, while services include intangible activities such as healthcare and financial services.
There are two main approaches to calculating GDP: the expenditure approach and the income approach. The expenditure approach adds up the value of all final goods and services consumed by households, businesses, and the government, as well as the value of exports and imports. The income approach calculates GDP based on the income generated by the production and sale of goods and services.
GDP is typically measured over a specific time period, such as a quarter or a year. It is often used as a key measure of economic growth and is an important factor for policymakers, investors, and businesses to assess the health and direction of an economy. However, GDP alone does not provide a complete picture of an economy’s well-being, as it does not take into account factors such as income distribution, quality of life, or environmental impact.
How is Gross Domestic Product calculated?
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure used to assess the economic performance of a country. It represents the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders over a specific period of time. Calculating GDP involves the use of various methods and indicators.
One common approach used to calculate GDP is the expenditure method. According to this method, GDP is calculated by summing up the four major components of expenditure: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports. Consumption refers to the total spending by individuals and households on goods and services, investment includes business spending on capital goods and housing, government spending includes all government expenditures on goods and services, and net exports represent the difference between a country’s exports and imports.
To calculate GDP using the expenditure method, data on spending in each of these categories is collected and added up. This data is often obtained from surveys, tax records, and financial reports. By adding up the total spending in these categories, the overall GDP for a particular period can be determined.
Another approach used to calculate GDP is the income method. This method focuses on the total income generated by the production of goods and services within a country. It looks at the income earned by individuals, businesses, and the government, including wages, profits, and taxes. By summing up all these income components, the GDP can be calculated.
In addition to the expenditure and income methods, there is also the production or output method. This method calculates GDP by summing up the value added at each stage of production. It considers the value of intermediate goods and services used in the production process and avoids counting the same value multiple times.
In summary, Gross Domestic Product (GDP) can be calculated using different methods, including the expenditure, income, and production methods. Each method provides a different perspective on the economy and allows for a comprehensive assessment of a country’s economic performance.
Components of Gross Domestic Product
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is a measure of the total economic output of a country. It represents the value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. The components that make up GDP can be classified into four main categories: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports.
1. Consumption
Consumption refers to the spending by individuals and households on goods and services. It includes purchases of durable goods (such as cars and appliances), non-durable goods (such as food and clothing), and services (such as healthcare and education). Consumption is the largest component of GDP in most countries and is a key indicator of the overall health of the economy.
2. Investment
Investment includes spending on business capital goods, such as machinery and equipment, as well as residential and non-residential structures. It also includes changes in inventories, which are goods produced but not yet sold. Business investment is an important driver of economic growth, as it increases production capacity and productivity over time.
3. Government Spending
Government spending represents expenditures by federal, state, and local governments on goods and services. It includes spending on public infrastructure, education, defense, healthcare, and social welfare programs. Government spending can have a significant impact on GDP, as it directly contributes to economic activity and job creation.
4. Net Exports

Net exports are the difference between a country’s exports and imports. Exports represent the value of goods and services produced domestically and sold abroad, while imports represent the value of foreign goods and services purchased domestically. A positive net export value indicates that a country is exporting more than it is importing, contributing to GDP growth. Conversely, a negative net export value indicates that a country is importing more than it is exporting, which can have a negative impact on GDP.
In conclusion, understanding the components of GDP is crucial for analyzing the overall performance of an economy. By examining the levels of consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports, policymakers and economists can gain insights into the strengths and weaknesses of an economy and make informed decisions to promote sustainable economic growth.
The role of Consumption in Gross Domestic Product
In the calculation of Gross Domestic Product (GDP), consumption plays a crucial role. Consumption refers to the total spending by individuals and households on goods and services within a country during a specified period of time. It is one of the main components of GDP and reflects the overall level of economic activity within an economy.
Consumption is an important indicator of the health and vitality of an economy. It reflects the purchasing power and spending patterns of consumers, which in turn drives production and business investment. When consumers have more disposable income and are confident about the future, they are more likely to spend money on goods and services, which boosts economic growth. On the other hand, when consumer spending decreases, it can indicate economic downturn and contraction.
The components of consumption that are included in the calculation of GDP are personal consumption expenditures, which include durable goods (such as cars and appliances), nondurable goods (such as food and clothing), and services (such as healthcare and education). These expenditures are measured at market prices and reflect the final consumption of goods and services by individuals and households.
Consumption also influences other components of GDP, such as investment, government spending, and net exports. High levels of consumption can stimulate investment as businesses expand production to meet the increased demand. Similarly, government spending can be influenced by consumer behavior, as increased consumption may lead to higher tax revenues and government expenditure. Additionally, consumption patterns can affect the balance of trade and net exports, as increased consumption of imported goods can lead to a trade deficit.
In conclusion, consumption plays a critical role in determining the level of economic activity and is an important component of Gross Domestic Product. It reflects consumer spending patterns and indicates the overall health of the economy. Understanding the role of consumption in GDP is essential for policymakers and economists to make informed decisions and assess the state of the economy.
The Role of Investment in Gross Domestic Product
Investment plays a crucial role in the calculation and determination of a country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP is the total value of all goods and services produced within a country’s borders during a specific time period.
Investment is classified as one of the components of GDP and represents the spending on physical assets such as machinery, equipment, buildings, and infrastructure, as well as intellectual property rights and research and development activities. It is an important driver of economic growth as it contributes to the expansion of productive capacity and the creation of employment opportunities.
The investment component of GDP can be further divided into two categories: fixed investment and inventory investment. Fixed investment refers to the expenditure on durable goods that are used for production, such as machinery and equipment, while inventory investment represents the changes in the stock of goods held by businesses. Both types of investment contribute to GDP by increasing the overall level of economic activity.
Investment also has a multiplier effect on GDP. When businesses invest in new capital goods, it stimulates additional spending in the economy. For example, an increase in investment may lead to an increase in employment, which in turn leads to higher consumer spending. This creates a positive feedback loop that boosts GDP growth.
- In conclusion, investment is a vital component of Gross Domestic Product and plays a significant role in driving economic growth. It contributes to the expansion of productive capacity, job creation, and stimulates additional spending in the economy. Governments and policymakers often focus on promoting investment to foster economic development and support overall GDP growth.