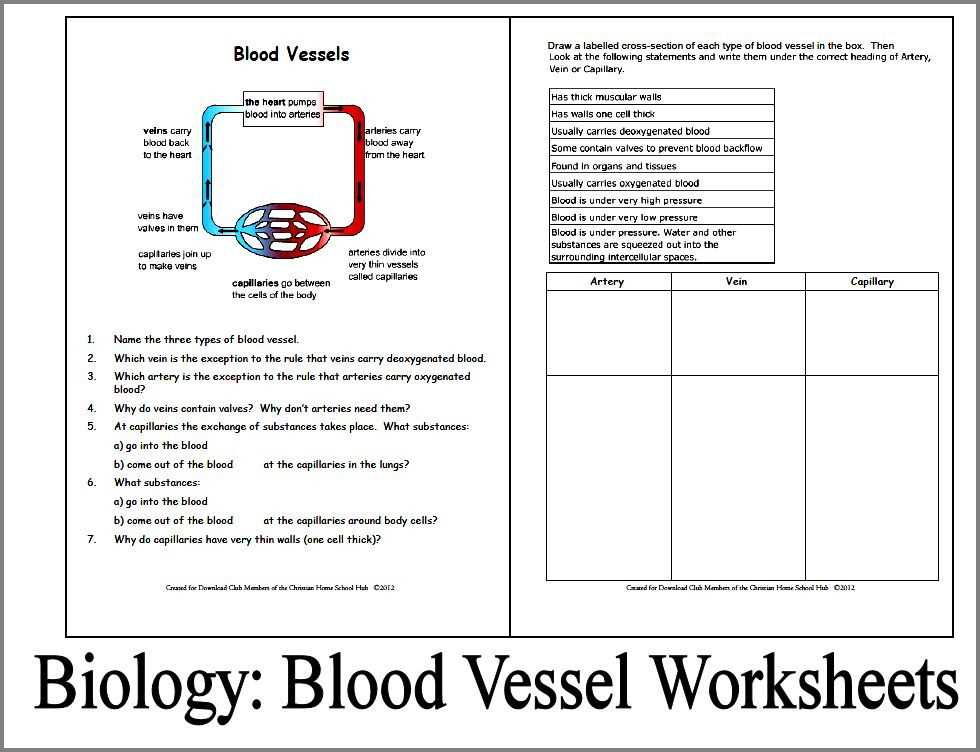
In the study of biology, one of the key concepts is the growth and dynamics of human populations. Understanding how the human population has changed over time is essential for scientists and policymakers who are working to address important issues such as resource management, public health, and social welfare. One tool that has been developed to help track and analyze human population growth is the human population growth worksheet.
A human population growth worksheet is a valuable resource that allows students and researchers to explore the various factors that influence population growth, including birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration. By examining these factors in detail, users can gain a clearer understanding of how and why the human population has changed over time. This worksheet also provides a framework for predicting future population trends and understanding the potential impacts of different scenarios.
By completing a human population growth worksheet, students can sharpen their analytical skills and learn to apply mathematical formulas to real-world data. They may also gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity of population dynamics and the many interconnected factors that shape human population growth. Furthermore, this worksheet can serve as a starting point for discussions and debates on important issues related to population growth, such as the balancing of environmental sustainability with human needs and the importance of access to healthcare and education.
In conclusion, the human population growth worksheet is a valuable tool for understanding and analyzing the dynamics of human populations. It provides a platform for studying past population trends, predicting future growth, and exploring the various factors that influence population dynamics. By using this worksheet, students can develop a deeper understanding of biology and gain insights into important societal issues. The study of human population growth is crucial for addressing the challenges and opportunities that come with a changing world.
What is Human Population Growth?
Human population growth refers to the increase in the number of individuals of the human species over time. It is the result of a combination of factors, including births, deaths, and migration. The growth rate of the human population has been accelerating in recent centuries, leading to concerns about overpopulation and its impact on the environment and resources.
One of the primary drivers of human population growth is the increase in the number of births. As medical advancements and improvements in living conditions have reduced infant mortality rates and increased life expectancy, more individuals are able to reach reproductive age and have children. This has contributed to a significant increase in the global population.
Another factor contributing to human population growth is migration. People often move from one place to another in search of better economic opportunities or to escape conflict and persecution. This movement of people can lead to population growth in certain areas and can also have implications for social and cultural dynamics.
However, the exponential growth of the human population also poses challenges and concerns. It puts pressure on natural resources, such as water, food, and energy, as well as on the environment. Rapid population growth can lead to deforestation, loss of biodiversity, pollution, and climate change, among other environmental problems.
Understanding and managing human population growth is important for sustainable development and ensuring a high quality of life for future generations. It requires implementing strategies that promote access to family planning and reproductive health services, as well as educating individuals about the importance of sustainable lifestyles and conservation of resources.
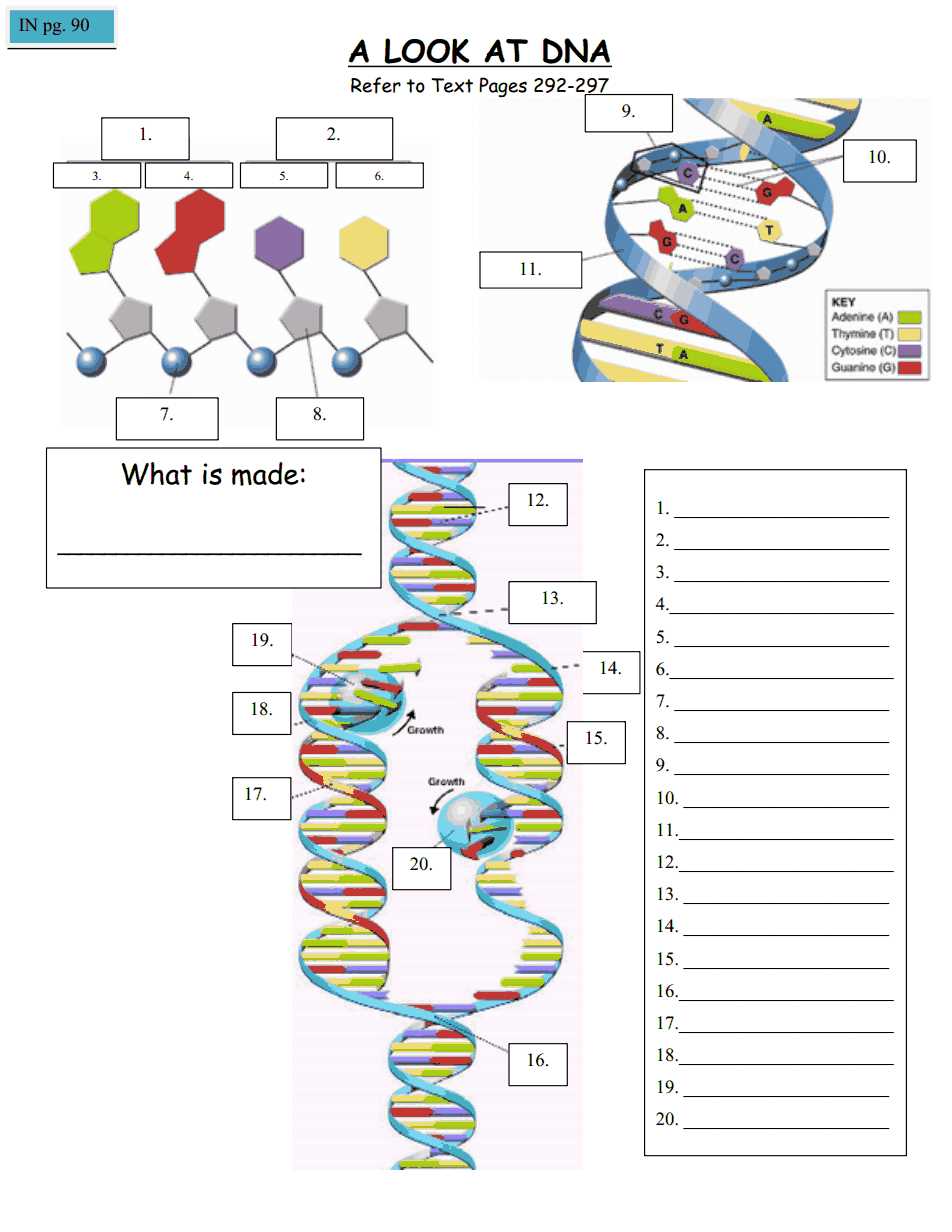
Definition of human population growth
Human population growth refers to the increase in the number of individuals in a human population over time. It is a measure of how fast a population is growing, usually expressed as a percentage or a rate. This growth can be influenced by various factors, including birth rates, death rates, immigration, and emigration.
In biology, population growth is usually studied in the context of population ecology. It is an important concept because it helps us understand the dynamics of populations and their interactions with the environment. By analyzing the rate of population growth, scientists can make predictions about future population sizes and study the factors that influence population dynamics.
The growth of the human population has been a major concern in recent times due to its implications on resources and the environment. Rapid population growth can strain the availability of resources such as food, water, and energy, leading to increased competition and potential environmental degradation. It can also have social and economic implications, particularly in developing countries where resources are already limited.
To manage human population growth, various strategies have been proposed and implemented, including family planning programs, education, and promoting sustainable development. These efforts aim to balance population growth with the available resources and ensure a sustainable future for all individuals.
Factors contributing to human population growth
There are several factors that contribute to the growth of the human population. These factors can be categorized into two main groups: natural factors and anthropogenic factors.
Natural factors
- Birth rate: The natural reproductive capacity of humans is one of the main factors contributing to population growth. The birth rate measures the number of births per 1,000 individuals in a given population. Higher birth rates lead to an increase in population size.
- Death rate: The death rate measures the number of deaths per 1,000 individuals in a given population. Lower death rates result in higher life expectancies, which can also contribute to population growth.
- Fertility rate: The fertility rate measures the average number of children born to a woman over her lifetime. Higher fertility rates can lead to population growth if the number of births exceeds the number of deaths.
Anthropogenic factors
- Medical advancements: Advances in medical technology have significantly reduced mortality rates, especially among infants and children. This has led to longer life expectancies and population growth.
- Improved sanitation: The introduction of sanitation systems, such as clean water supply and proper waste disposal, has led to a decrease in the spread of diseases. This has also contributed to lower death rates and population growth.
- Availability of food: The development of agricultural practices and advancements in food production have increased food availability, reducing the risk of famine and malnutrition. This has allowed populations to grow by providing sustenance to a larger number of individuals.
It is important to note that while these factors contribute to global human population growth, the rate of growth varies significantly across different regions and countries. Various social, economic, and cultural factors also play a role in shaping population growth patterns.
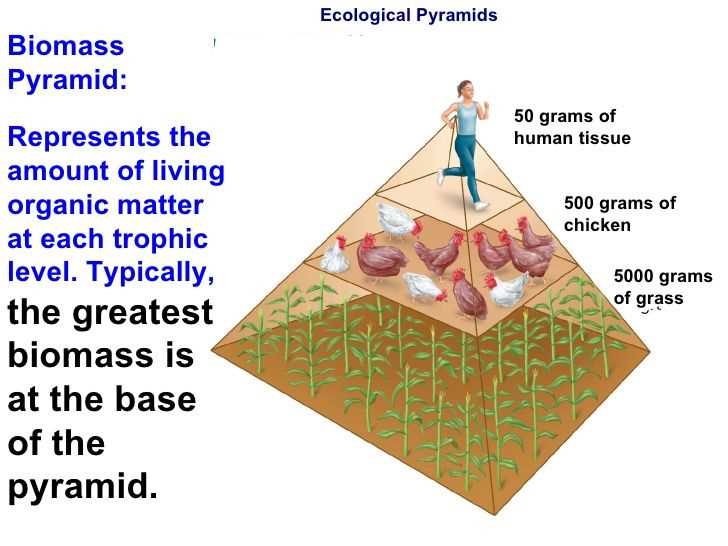
The Impact of Human Population Growth on the Environment
Human population growth has had a significant impact on the environment. As the global population continues to grow at an unprecedented rate, the demand for resources and the resulting environmental consequences have become more pronounced. This rapid increase in population has led to the depletion of natural resources, increased deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and the acceleration of climate change.
One of the main consequences of human population growth is the depletion of natural resources. As the population grows, the demand for resources such as land, water, and energy increases. This has led to the overexploitation of natural resources, leading to soil erosion, desertification, and water scarcity. Additionally, the increased demand for energy has resulted in the burning of fossil fuels, which releases greenhouse gases into the atmosphere and contributes to global warming.
The expanding human population has also resulted in increased deforestation. As more land is needed for agriculture, housing, and infrastructure, forests are being cleared at an alarming rate. Deforestation not only leads to the loss of valuable ecosystems and biodiversity, but it also contributes to climate change. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are cleared, this carbon is released into the atmosphere, further exacerbating the greenhouse effect.
Loss of biodiversity is another consequence of human population growth. As more land is developed and ecosystems are destroyed, countless species of plants and animals are becoming extinct. This loss of biodiversity disrupts ecosystems and can have far-reaching effects on the environment. Biodiversity is essential for maintaining ecosystem balance and providing essential ecosystem services, such as clean water and air.
In conclusion, human population growth has had a profound impact on the environment. The depletion of natural resources, increased deforestation, loss of biodiversity, and climate change are all direct consequences of the expanding human population. It is crucial that we find sustainable solutions to manage population growth and reduce our environmental impact to ensure a sustainable future for generations to come.
Deforestation and habitat loss
Deforestation and habitat loss are two major consequences of human population growth that have significant impacts on biodiversity and ecosystem functioning. Deforestation refers to the conversion of forested areas into non-forested lands, primarily for agriculture, urban development, and logging. This process not only leads to the loss of trees but also destroys the habitats of countless plant and animal species.
As human populations expand, the demand for agricultural land increases, leading to the clearing of vast forested areas. This widespread deforestation disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems and results in the displacement or extinction of numerous species. Forests are home to a diverse array of plants and animals, many of which are endemic and found nowhere else in the world. When their habitats are destroyed, these species lose their homes and struggle to survive.
In addition to the direct loss of habitat, deforestation also contributes to habitat fragmentation. Large forested areas are divided into smaller, isolated patches, which restrict the movement and gene flow of species. This fragmentation can lead to population decline and increased vulnerability to diseases, predators, and other ecological pressures. Furthermore, deforestation disrupts the water cycle, soil erosion, and contributes to climate change by releasing carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
To address the issue of deforestation and habitat loss, it is crucial to promote sustainable land management practices, foster reforestation efforts, and protect existing natural habitats. This includes implementing stricter regulations on land use, promoting responsible logging practices, and supporting conservation initiatives. Additionally, raising awareness about the importance of forests and the impacts of deforestation is essential in encouraging individuals and communities to take action and make choices that prioritize the long-term health of our planet and its biodiversity.
Pollution and Waste Generation
Pollution and waste generation are major concerns associated with human population growth. As the global population continues to increase, so does the amount of pollution and waste we generate. This has significant impacts on the environment and human health.
Air pollution: The increase in industrial activities and transportation associated with a growing population leads to the release of various pollutants into the air. These pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on ecosystems and human respiratory health.
Water pollution: The growing population puts more pressure on water resources, leading to increased pollution of lakes, rivers, and oceans. Industrial and domestic waste, agricultural runoff, and sewage discharge contaminate water bodies, making them unsafe for both humans and wildlife. This can lead to the destruction of aquatic ecosystems and the loss of biodiversity.
Land pollution: As the population grows, the demand for land for housing, agriculture, and industry also increases. However, improper waste disposal and the use of harmful chemicals in agriculture can lead to land degradation and contamination. This affects soil fertility, biodiversity, and can result in the loss of arable land.
Waste generation: With more people comes more waste. The production of consumer goods, packaging materials, and single-use products contributes to the generation of vast amounts of waste. Improper waste management and the disposal of non-biodegradable materials in landfills or oceans further exacerbate the problem, leading to pollution and the depletion of natural resources.
In order to address these issues, it is crucial to implement sustainable practices that reduce pollution and waste generation. This includes promoting renewable energy sources, implementing stricter regulations on industrial emissions, improving waste management systems, and encouraging recycling and composting. Educating the population about the importance of reducing pollution and waste is also key to achieving a more sustainable future.
Climate change
Climate change refers to long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns, and other aspects of the Earth’s climate system. It is primarily caused by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, which release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These greenhouse gases, including carbon dioxide and methane, trap heat from the sun and cause the Earth’s temperature to rise, leading to global warming.
One of the main consequences of climate change is rising sea levels. As the Earth’s temperature increases, glaciers and ice sheets melt, resulting in the expansion of seawater. This poses a threat to coastal communities and ecosystems, as well as increased frequency and intensity of floods and coastal erosion. Additionally, climate change can lead to shifts in precipitation patterns, causing droughts in some areas and increased rainfall in others, which can disrupt ecosystems and agricultural productivity.
Key phrases:
- Climate change
- Long-term changes in temperature, precipitation, wind patterns
- Human activities, such as burning of fossil fuels and deforestation
- Release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere
- Greenhouse gases trap heat from the sun, causing global warming
- Rising sea levels
- Melting of glaciers and ice sheets
- Expansion of seawater
- Threat to coastal communities and ecosystems
- Floods and coastal erosion
- Shifts in precipitation patterns
- Droughts and increased rainfall
- Disruption of ecosystems and agricultural productivity