Understanding interior angles is an essential skill in geometry, and worksheets can be a valuable tool for practicing and reinforcing this knowledge. These worksheets provide students with a variety of problems to solve, helping them develop their understanding of angles and polygons. In this article, we will provide answers to some common interior angles worksheets, offering explanations and insights into the concepts involved.
One of the most basic types of interior angle problems is finding the sum of the interior angles in a polygon. These worksheets often present students with a polygon and ask them to calculate the sum of the interior angles. By examining the number of sides in the polygon, students can use the formula (n-2) * 180, where n is the number of sides, to find the answer. These worksheets help students develop a deeper understanding of the relationship between the number of sides and the sum of the interior angles.
In addition to finding the sum of interior angles, worksheets may also focus on finding individual interior angles in a polygon. These problems often involve using the sum of interior angles formula and then solving for a specific angle. Students are then asked to find the measure of a given angle by using the information provided. These types of problems help students develop their problem-solving skills and apply the concepts they have learned about interior angles.
Interior angles worksheet answers provide students with the opportunity to check their work and ensure they have mastered the concepts. By reviewing the answers and explanations provided, students can identify any areas where they may need extra practice or help. These worksheets are an excellent resource for both individual practice and classroom instruction, allowing students to develop their geometry skills and build a strong foundation in the topic of interior angles.
Understanding Interior Angles
In geometry, interior angles are the angles formed inside a polygon. They are crucial in understanding the properties and relationships of figures. To grasp the concept of interior angles, it is important to understand their definition and how they can be calculated.
Definition: Interior angles are the angles formed between two adjacent sides of a polygon, inside the figure. They can be labeled using the vertices of the polygon (e.g., angle ABC or angle BCD).
One property of interior angles is that the sum of all interior angles in a polygon equals (n-2) * 180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon. This formula can be used to find the measure of each interior angle in a regular polygon, where all sides and angles are congruent.
Additionally, interior angles can be classified based on their measures. An acute angle measures less than 90 degrees, a right angle measures exactly 90 degrees, and an obtuse angle measures more than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees. In a regular polygon, all interior angles are congruent.
To calculate the measure of an interior angle:
- For a regular polygon, divide the sum of all interior angles (n-2) * 180 degrees by the number of sides (n).
- For an irregular polygon, subtract the measures of the known interior angles from the sum of all interior angles (n-2) * 180 degrees to find the measure of the unknown angle.
Understanding interior angles is essential in solving geometry problems involving polygons. By knowing their properties and how to calculate their measures, one can determine the angles of various polygons and analyze their characteristics.
Definition of Interior Angles
Interior angles are angles that are formed inside a polygon. They are the angles formed by two sides of the polygon that meet at a vertex or corner of the shape. These angles are important in geometry as they help us understand the properties and characteristics of polygons.
To find the measure of an interior angle of a polygon, we can use the formula (n-2) × 180° / n, where n represents the number of sides of the polygon. This formula allows us to calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon, which is always a multiple of 180 degrees. By dividing the sum by the number of sides, we can find the measure of each individual interior angle.
For example, in a triangle, which has three sides, the sum of the interior angles is 180 degrees, so each angle measures 60 degrees. In a square, which has four sides, the sum of the interior angles is 360 degrees, so each angle measures 90 degrees. The formula works for any polygon, regardless of the number of sides.
Understanding the concept of interior angles is essential in geometry as it helps us analyze and solve various problems related to polygons. By knowing the measure of interior angles, we can determine the type of polygons, identify congruent or supplementary angles, and solve equations involving angles and sides of polygons.
Properties of Interior Angles
The interior angles of a polygon are the angles formed inside the polygon. These angles can be classified based on their properties and relationships. Understanding the properties of interior angles is essential in solving problems and finding missing angles in geometrical figures.
1. Sum of Interior Angles: The sum of the interior angles in any polygon can be found using the formula (n-2) * 180, where n represents the number of sides of the polygon. This formula allows us to determine the total measure of the interior angles in a polygon without measuring each individual angle.
2. Regular vs. Irregular Polygons: Regular polygons are polygons with equal sides and equal interior angles, while irregular polygons have sides and angles of different lengths and measures. In a regular polygon, each interior angle is equal to the sum of the interior angles divided by the number of sides.
3. Relationship with Exterior Angles: The measure of an interior angle and its corresponding exterior angle is always 180 degrees. The exterior angle is the angle formed by extending one of the sides of the polygon outside the figure. The sum of an interior angle and its corresponding exterior angle always equals 180 degrees.
4. Triangles and Quadrilaterals: In a triangle, the sum of the interior angles is always 180 degrees. In a quadrilateral, the sum of the interior angles is always 360 degrees.
By understanding the properties of interior angles, we can solve problems involving angles in polygons, identify regular and irregular polygons, and determine the measures of missing angles in various geometric figures.
Worksheet Questions
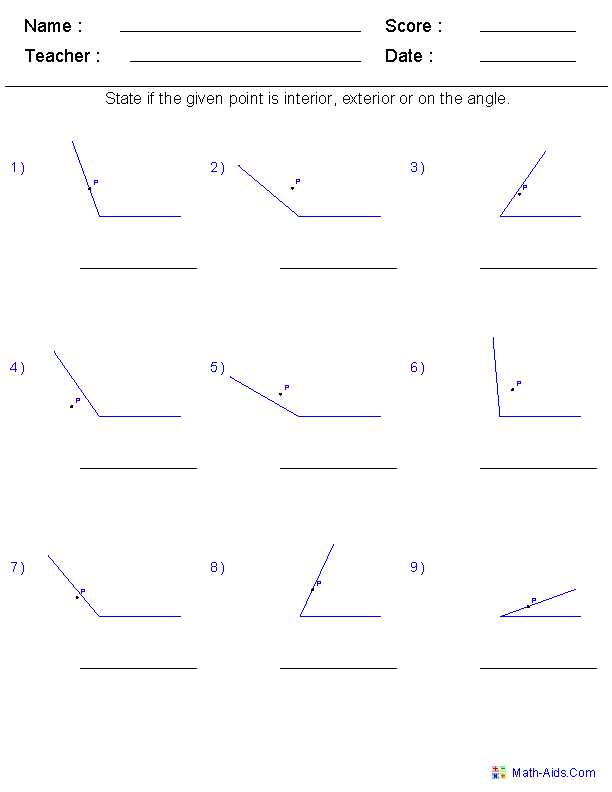
When studying interior angles, it can be helpful to have practice questions to test your understanding. Worksheet questions provide an opportunity to apply the concepts learned and reinforce your knowledge.
1. Calculate the measure of the interior angles:
- Triangle ABC with angle A = 45° and angle B = 60°
- Quadrilateral PQRS with angle P = 90°, angle Q = 75°, angle R = 110°
- Pentagon LMNOP with angle L = 120°, angle M = 90°, angle N = 45°, angle O = 135°
2. Determine the type of polygon based on its interior angles:
- A polygon has interior angles measuring 150°, 150°, 150°, 150°, and 150°. What type of polygon is it?
- A polygon has interior angles measuring 80°, 110°, 100°, 140°, and 120°. What type of polygon is it?
- A polygon has interior angles measuring 90°, 110°, 135°, 125°, and 100°. What type of polygon is it?
3. Solve for x in the following polygons:
- A triangle has angles measuring (2x + 10)°, (3x – 20)°, and (4x + 10)°. Find the value of x.
- A quadrilateral has angles measuring (5x – 30)°, (3x + 20)°, (2x + 40)°, and (4x – 10)°. Find the value of x.
- A pentagon has angles measuring (x + 30)°, (2x – 40)°, (3x – 20)°, (2x + 60)°, and (4x – 10)°. Find the value of x.
By answering these worksheet questions, you can strengthen your knowledge of interior angles and improve your problem-solving skills. Remember to show your work and check your answers to ensure accuracy. Happy calculating!
Question 1
Find the measure of the interior angles of the given polygon:
Polygon: Triangle
Solution:
To find the measure of the interior angles of a triangle, we can use the formula:
Interior Angle = (n-2) * 180° / n
where n is the number of sides in the polygon.
In the case of a triangle, we have n = 3.
Substituting the values into the formula:
Interior Angle = (3-2) * 180° / 3 = 1 * 180° / 3 = 60°
Therefore, the measure of each interior angle of the triangle is 60°.
Question 2
The second question on the worksheet asks students to find the measure of the interior angles of a pentagon. This is a great opportunity for students to apply their knowledge of the sum of interior angles of polygons.
To find the measure of the interior angles of a pentagon, students need to remember that the sum of the interior angles of any polygon is given by the formula (n-2) × 180 degrees, where n is the number of sides of the polygon. In this case, since we are dealing with a pentagon (which has 5 sides), we can substitute n=5 into the formula.
(n-2) × 180 degrees = (5-2) × 180 degrees = 3 × 180 degrees = 540 degrees
Therefore, the measure of each interior angle of the pentagon is 540 degrees divided by the number of angles, which gives us 540 degrees ÷ 5 = 108 degrees.
In conclusion, the measure of each interior angle of a pentagon is 108 degrees.
Question 3:
To find the measure of angle $x$, we need to set up an equation using the properties of polygons. A polygon is a closed figure with straight sides, and the sum of its interior angles is always equal to $(n-2) times 180$, where $n$ is the number of sides of the polygon.
In this case, the polygon has $n$ sides, and we know the sum of its interior angles is equal to $180$ degrees. We can set up the equation:
$$(3x – 10) + 120 + 95 + 87 = 180$$
By combining like terms and solving for $x$, we can find the value of angle $x$.
Question 4
In question 4, we are given a triangle with two interior angles measuring 45° and 85°. The task is to find the measure of the third interior angle.
To solve this problem, we can use the fact that the sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180°. Therefore, to find the measure of the third angle, we can subtract the sum of the given angles from 180°.
Given that one angle measures 45° and the other measures 85°, we can calculate the measure of the third angle as follows:
- Sum of the given angles: 45° + 85° = 130°
- Measure of the third angle: 180° – 130° = 50°
Therefore, the measure of the third interior angle in question 4 is 50°.
Question 5
This question asks students to find the value of an unknown angle in a given triangle. The given triangle is a right triangle, meaning one of its angles measures 90 degrees. The question provides measurements for two of the angles in the triangle: 60 degrees and 30 degrees.
Using the fact that the sum of all angles in a triangle is 180 degrees, students can find the measure of the third angle. In this case, the known angles add up to 90 degrees, leaving 90 degrees for the unknown angle.
To find the value of the unknown angle, students can subtract the sum of the known angles from 180. In this case, subtracting 90 from 180 gives a value of 90 degrees for the unknown angle. Therefore, the measure of the unknown angle in this triangle is 90 degrees.
Solutions and Explanations
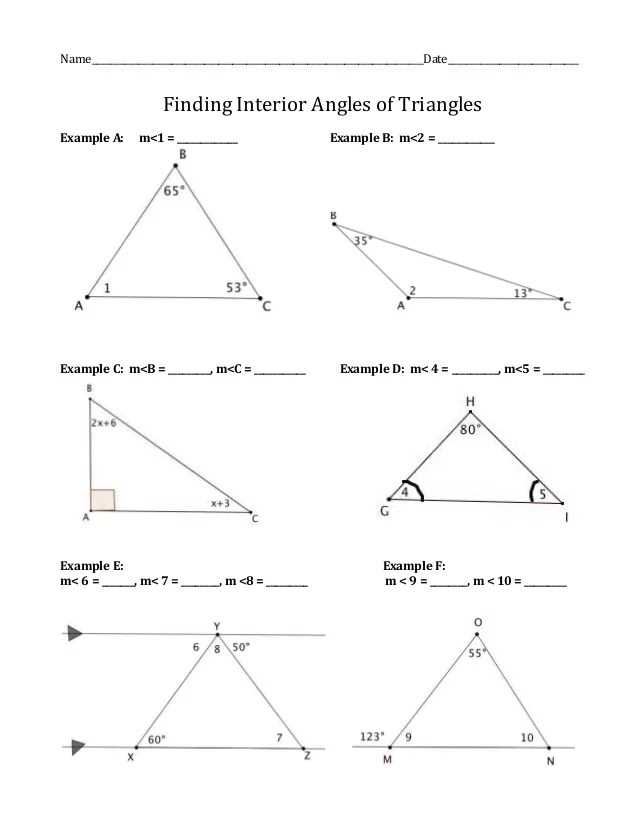
Here are the solutions and explanations for the interior angles worksheet:
Question 1:
Calculate the measure of the angle marked x in the diagram below:
| Diagram: |  |
| Solution: | The diagram shows a straight line, so the sum of the interior angles is 180 degrees. Therefore, we can set up the equation: x + 50 + 40 = 180. Simplifying the equation, we get x + 90 = 180. Subtracting 90 from both sides, we find that x = 90 degrees. |
Question 2:
Find the missing angle marked y in the diagram below:
| Diagram: |  |
| Solution: | In the given diagram, we have two parallel lines being intersected by a transversal. This means that the alternate interior angles are equal. Therefore, we can set up the equation: y = 3x. We also know that the sum of the interior angles in a triangle is 180 degrees. Hence, 2x + 2y = 180. Substituting the value of y from the first equation into the second equation, we have 2x + 2(3x) = 180. Simplifying the equation, we get 8x = 180. Dividing both sides by 8, we find that x = 22.5 degrees. Substituting this value of x back into the first equation, we get y = 3(22.5) = 67.5 degrees. Therefore, the missing angle y is 67.5 degrees. |
Note: The solutions and explanations provided here are for illustrative purposes only. There may be alternative methods or different approaches to solve these problems. It is important to understand the concepts and principles involved in finding interior angles in order to solve similar problems successfully.