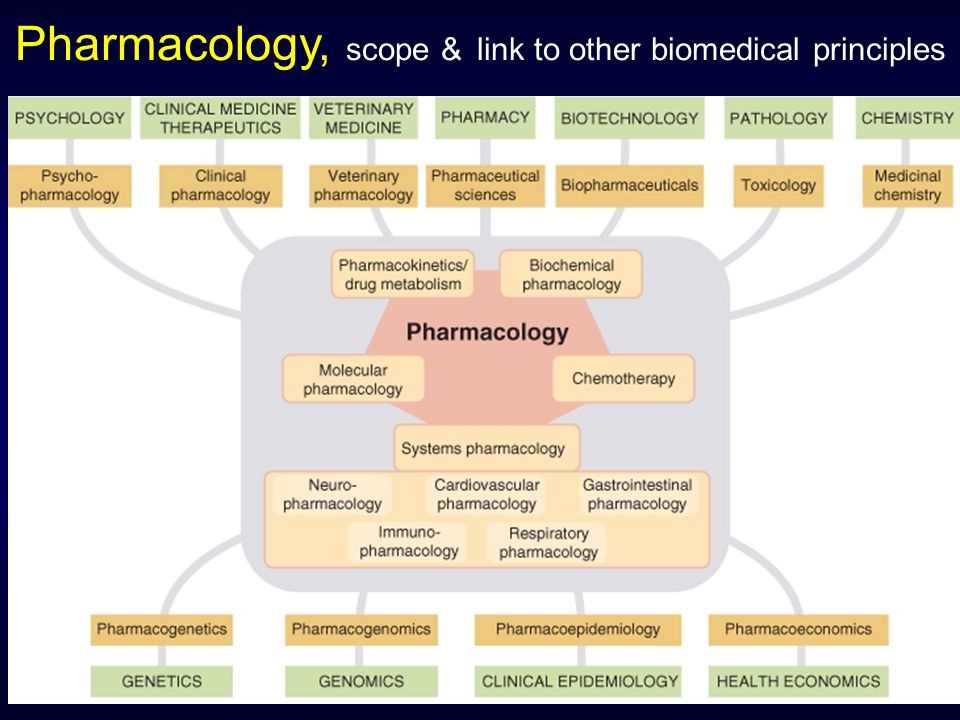
In the field of healthcare, clinical pharmacology plays a vital role in ensuring the safe and effective use of medications. This branch of pharmacology focuses on studying the effects of drugs on humans and aims to enhance patient care by providing evidence-based recommendations for drug therapy. To navigate through the complexities of clinical pharmacology, study guides can be immensely helpful. In this article, we will provide answers to some common questions found in study guides, offering a comprehensive introduction to the world of clinical pharmacology.
One key concept in clinical pharmacology is pharmacokinetics, which refers to how drugs are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated by the body. Understanding pharmacokinetics is crucial in determining the appropriate dosage and dosing interval for a specific drug. Study guides often include questions about drug absorption, such as the factors that affect it and the different routes of administration. By grasping these concepts, healthcare professionals can ensure optimal drug delivery to achieve the desired therapeutic effect.
Another essential aspect covered in clinical pharmacology study guides is pharmacodynamics. This term describes how drugs exert their effects on the body through interactions with specific receptors or enzymatic pathways. By studying pharmacodynamics, healthcare professionals can comprehend how drugs produce therapeutic and adverse effects, which helps in selecting the right medication for a patient and anticipating potential side effects. Frequently included in study guides are questions about the mechanisms of drug action and the factors that influence drug-receptor interactions, providing a comprehensive understanding of pharmacodynamics.
What is Clinical Pharmacology?
Clinical pharmacology is a branch of pharmacology that focuses on the study of the effects of drugs on humans. It involves the understanding of how drugs interact with the body, including their absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, as well as their therapeutic effects and potential adverse reactions.
Clinical pharmacologists play a crucial role in the development and evaluation of new drugs. They conduct clinical trials to assess the safety and efficacy of drugs in humans, analyze and interpret the data obtained from these trials, and make recommendations for the optimal use of drugs in patients. Their expertise helps in determining the appropriate dosage, monitoring for drug interactions or side effects, and individualizing treatment regimens based on factors such as age, sex, and coexisting medical conditions.
In addition to their role in drug development and evaluation, clinical pharmacologists also contribute to the field of personalized medicine. By understanding the genetic variations that influence drug response, they can help tailor treatments to individual patients and minimize the risk of adverse reactions. They also collaborate with other healthcare professionals to provide evidence-based recommendations on the use of drugs in specific patient populations, such as pregnant women or the elderly.
Overall, clinical pharmacology plays a critical role in ensuring safe and effective drug therapy for patients. By studying the interactions between drugs and the human body, clinical pharmacologists provide valuable insights that guide healthcare professionals in making informed decisions about the use of medications.
Why is Clinical Pharmacology important?
Clinical Pharmacology is a crucial field of study in healthcare because it plays a vital role in the safe and effective use of medications. It encompasses the study of how drugs interact with the human body, how they are absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and eliminated, and how they affect different individuals based on factors such as age, gender, genetics, and other medical conditions.
One of the main reasons Clinical Pharmacology is important is because it helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions when prescribing medications. By understanding how drugs work and their potential side effects, healthcare providers can choose the most appropriate medication for a specific patient, taking into account their medical history and individual characteristics. This helps minimize the risk of adverse drug reactions and optimize therapeutic outcomes.
In addition, Clinical Pharmacology is essential in advancing medical research and drug development. It provides valuable insights into the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs, which are necessary for designing and conducting clinical trials. By studying the pharmacological properties of medications, researchers can explore new treatment options, identify potential drug-drug interactions, and better understand the mechanisms of action of existing drugs.
Moreover, Clinical Pharmacology plays a critical role in patient safety by promoting rational prescribing practices and preventing medication errors. It helps healthcare professionals assess the benefits and risks of different treatment options, including potential drug interactions and contraindications. This knowledge allows them to adjust medication dosages, monitor therapeutic responses, and identify any issues that may arise during drug therapy.
In conclusion, Clinical Pharmacology is essential in healthcare as it provides the necessary knowledge and tools for safe and effective medication use, supports medical research and drug development, and ensures patient safety by optimizing prescribing practices. By studying the pharmacological aspects of drugs, we can improve patient outcomes, enhance drug therapy, and make significant advancements in healthcare.
Key Principles of Clinical Pharmacology
Clinical pharmacology is a branch of pharmacology that focuses on the application of drugs in the clinical setting. It is an essential field in healthcare as it involves the safe and effective use of medications to treat patients. There are several key principles that guide clinical pharmacology practice.
Individualization of Drug Therapy
A fundamental principle in clinical pharmacology is the individualization of drug therapy. Every patient is unique, and factors such as age, weight, gender, genetics, and underlying health conditions can affect the way medications are metabolized and the response to treatment. Therefore, clinical pharmacologists aim to tailor drug therapy to each patient’s specific needs and characteristics to achieve optimal therapeutic outcomes while minimizing adverse effects.
Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics
Understanding the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs is another key principle in clinical pharmacology. Pharmacokinetics refers to how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and eliminates drugs, while pharmacodynamics focuses on how drugs interact with their target receptors or molecules to produce therapeutic effects. By studying these aspects, clinical pharmacologists can determine the appropriate dosage, dosing interval, and route of administration for a particular drug, ensuring its efficacy and safety.
Evidence-based Medicine
The practice of clinical pharmacology is rooted in evidence-based medicine. This means that treatment decisions are based on the best available evidence from clinical trials, systematic reviews, and other scientific studies. Clinical pharmacologists critically appraise the evidence to determine the effectiveness and safety of drugs, considering factors such as study design, sample size, outcome measures, and statistical analysis. By adopting an evidence-based approach, clinical pharmacologists can make informed decisions about drug therapy, promoting the use of effective and safe medications.
Monitoring and Adverse Drug Reaction Reporting
Monitoring patients for the therapeutic response and potential adverse drug reactions is another important principle in clinical pharmacology. Clinical pharmacologists closely monitor patients’ clinical outcomes, laboratory values, and other relevant parameters to assess the effectiveness and safety of drug therapy. Additionally, they encourage healthcare providers and patients to report any adverse drug reactions to regulatory authorities, contributing to the ongoing surveillance of medication safety and enabling the identification of potential drug-related problems.
In summary, the key principles of clinical pharmacology involve the individualization of drug therapy, understanding pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, practicing evidence-based medicine, and monitoring patients for therapeutic response and adverse drug reactions. These principles ensure the safe and effective use of medications in the clinical setting, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
How are drugs classified and what does it mean?

Drugs are classified based on various criteria, including their chemical structure, therapeutic use, and mechanism of action. The classification of drugs helps to organize and categorize them, which aids in understanding their properties and guiding their appropriate use.
One common classification of drugs is based on their chemical structure. This classification groups drugs that have similar chemical characteristics together. For example, drugs that belong to the class of opioids have a similar chemical structure and share common properties, such as pain relief and potential for addiction.
Another important classification is based on the therapeutic use of drugs. This classification categorizes drugs based on the diseases or conditions they are used to treat. For example, drugs that are used to lower blood pressure are classified as antihypertensives, while drugs that are used to treat bacterial infections are classified as antibiotics.
Drugs can also be classified based on their mechanism of action. This classification categorizes drugs based on the specific biological target they interact with in the body. For example, drugs that inhibit the action of an enzyme involved in blood clotting are classified as anticoagulants. Understanding the mechanism of action of drugs allows healthcare professionals to predict their effects on the body and select the most appropriate drug for a specific condition.
In conclusion, drug classification is an important tool in clinical pharmacology as it helps to organize drugs based on their chemical structure, therapeutic use, and mechanism of action. This classification system aids in understanding the properties of drugs and guides their appropriate use in healthcare settings.
What is Pharmacokinetics and why is it important?
Pharmacokinetics refers to the study of how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted by the body. It involves understanding the processes by which drugs are absorbed into the bloodstream, how they are distributed to various tissues and organs, how they are metabolized or broken down, and how they are eliminated from the body. Pharmacokinetics helps us understand how drugs interact with the body and how their concentration changes over time.
Pharmacokinetics is crucial in clinical pharmacology as it helps determine the appropriate dosage and dosing regimens for drugs. By understanding how drugs are processed and eliminated by the body, healthcare professionals can optimize drug therapy to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects and toxicity. Pharmacokinetics also plays a role in determining drug interactions, as drugs that affect the same metabolic pathways or compete for transporters may have altered pharmacokinetics when used together.
The knowledge of pharmacokinetics is essential in predicting drug behavior and optimizing drug therapy. By understanding how a drug is absorbed, distributed, metabolized, and excreted, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about drug dosing, frequency, and route of administration. This knowledge also helps in the development of new drugs as pharmacokinetic data plays a crucial role in drug discovery and development, including dose optimization, drug-drug interaction studies, and predicting drug behavior in different patient populations.
In summary, pharmacokinetics is a fundamental aspect of clinical pharmacology that helps us understand how drugs interact with the body and how their concentration changes over time. It is essential for determining appropriate drug dosing, optimizing drug therapy, predicting drug behavior, and ensuring drug safety and efficacy.
What is Pharmacodynamics and why is it important?
Pharmacodynamics is the study of how drugs exert their effects on the body and the mechanisms by which these effects are produced. It involves the study of drug receptors, drug-receptor interactions, and the downstream cellular and molecular events that occur after drug binding. Understanding pharmacodynamics is crucial for healthcare practitioners as it helps in predicting and understanding the therapeutic and adverse effects of drugs.
Pharmacodynamics is important in clinical pharmacology as it provides valuable information about the potency, efficacy, and safety of drugs. By studying the pharmacodynamics of a drug, healthcare professionals can determine the optimal dose, frequency, and duration of drug administration to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Pharmacodynamics also plays a key role in personalized medicine and individualized drug therapy. Different patients may have variations in their drug receptors or other cellular components that can affect drug response. By understanding the pharmacodynamics of a drug and considering individual patient characteristics, healthcare practitioners can tailor drug therapy to maximize its effectiveness and minimize potential harm.
Overall, pharmacodynamics is a fundamental aspect of clinical pharmacology that provides insight into how drugs interact with the body and helps guide the safe and effective use of medications. By understanding the pharmacodynamics of a drug, healthcare professionals can make informed decisions about drug therapy and optimize patient outcomes.
Common Pharmacology Terminologies
In the field of pharmacology, there are numerous terminologies that are commonly used to describe various aspects of drugs and their effects. Understanding these terms is essential for healthcare professionals, researchers, and students studying clinical pharmacology. Here are some of the common pharmacology terminologies:
- Pharmacokinetics: This term refers to the study of how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes drugs. It involves understanding the processes that occur in the body after drug administration and how they affect drug concentration levels.
- Pharmacodynamics: Pharmacodynamics is the study of how drugs interact with their target receptors and produce biological effects. It involves understanding the mechanisms of action, potency, and efficacy of drugs, as well as their side effects and toxicity.
- Half-life: The half-life of a drug is the time it takes for the concentration of the drug in the body to decrease by half. It is an important pharmacokinetic parameter that determines the duration of action and dosing frequency of a drug.
- Bioavailability: Bioavailability refers to the proportion of an administered dose of a drug that reaches the systemic circulation unchanged. It is affected by factors such as absorption, metabolism, and excretion and is an important consideration for determining the appropriate dosage form and route of administration.
- Drug-drug interactions: Drug-drug interactions occur when the presence of one drug affects the pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics of another drug, leading to altered drug effects or increased toxicity.
- Adverse drug reaction: An adverse drug reaction is any unwanted or harmful reaction that occurs following the administration of a drug. It can range from mild side effects to severe allergic reactions or organ damage.
These are just a few examples of the many pharmacology terminologies that are commonly used in the field. Familiarizing oneself with these terms can greatly enhance understanding and communication in clinical pharmacology practice and research.