
Karyotyping is a vital tool in genetic testing and analysis. It allows scientists and researchers to examine and evaluate the genetic composition of an individual by studying the patterns and structure of chromosomes. With the help of karyotyping, scientists can identify chromosomal abnormalities and disorders, such as Down syndrome or Turner syndrome, which can have a significant impact on an individual’s health and development.
The Karyotyping Gizmo is an interactive online tool that simulates the process of analyzing chromosomes and determining their abnormalities. It provides a hands-on learning experience for students and enables them to practice their skills in karyotyping. This gizmo comes with an answer key that serves as a guide, giving students the opportunity to check their work and understand any mistakes they may have made.
The Karyotyping Gizmo answer key offers a step-by-step solution to the various activities and questions presented in the Gizmo. It provides an in-depth explanation of how to analyze and interpret karyotypes, helping students grasp the fundamental concepts of chromosome analysis. By using the answer key, students can verify their answers, reinforce their understanding, and develop their skills in karyotyping.
Overall, the Karyotyping Gizmo answer key is an invaluable resource for educators and students alike. It serves as a tool for self-assessment, allowing students to gauge their progress and identify areas that may require further study. By using this answer key, students can enhance their knowledge and proficiency in karyotyping, ultimately leading to a better understanding of genetics and its applications in the field of medicine.
Karyotyping Gizmo Answer Key
Karyotyping is a laboratory technique used to analyze an individual’s chromosomes. By examining the chromosomes in a sample of cells, scientists can identify any abnormalities or genetic disorders. The Karyotyping Gizmo is an online simulation that allows students to practice analyzing karyotypes and determine the chromosome abnormalities associated with various genetic disorders. In order to fully utilize the Gizmo, students can refer to the Karyotyping Gizmo Answer Key which provides the correct answers and explanations for each step of the analysis.
The Karyotyping Gizmo Answer Key includes a comprehensive list of chromosome abnormalities and their corresponding genetic disorders. This allows students to identify and classify different types of abnormalities, such as deletions, duplications, inversions, and translocations. With the help of the answer key, students can understand the specific genetic disorders associated with each abnormality and the potential health implications for individuals with these disorders.
The Karyotyping Gizmo Answer Key also provides a step-by-step explanation of how to analyze a karyotype using the Gizmo. It guides students through the process of identifying and counting chromosomes, determining the sex of the individual, and identifying any abnormalities. The answer key includes visuals and diagrams to help students visualize the different types of abnormalities and understand their impact on the overall karyotype.
By using the Karyotyping Gizmo Answer Key, students can gain a better understanding of karyotyping and the analysis of chromosome abnormalities. It provides a valuable tool for learning and practicing the skills necessary for genetic analysis. With this knowledge, students can develop a deeper understanding of genetic disorders and contribute to advancements in the field of genetics.
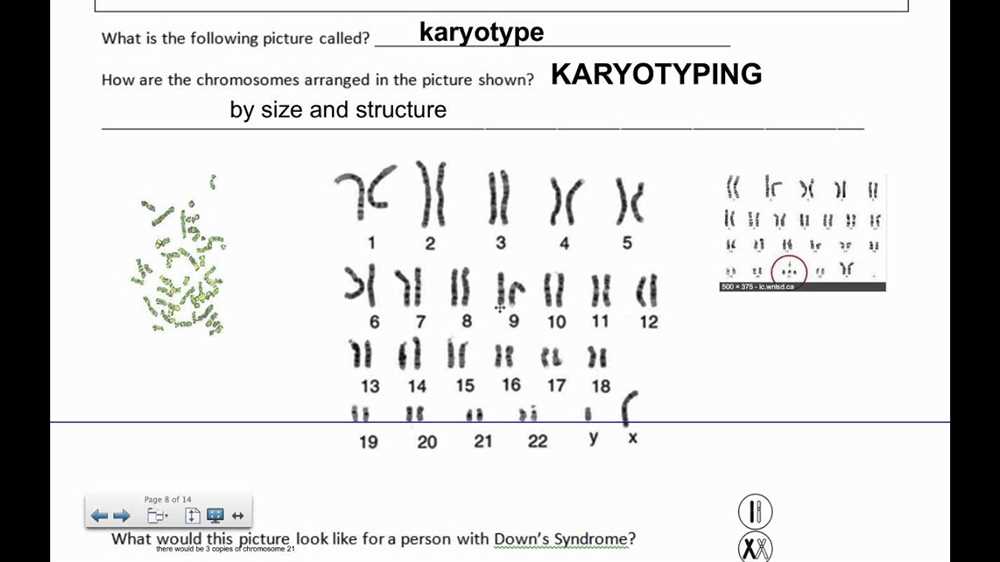
Karyotyping is a technique used in genetics to analyze the chromosomes of an individual. It involves arranging and grouping the chromosomes according to their size, shape, and other characteristics. The resulting pattern of chromosomes is called a karyotype.
What is a karyotype?
A karyotype is a visual representation of an individual’s chromosomes. It shows the chromosomes arranged in pairs, with the longest pair labeled as number 1, the second longest as number 2, and so on. In humans, there are 23 pairs of chromosomes, for a total of 46 chromosomes. The first 22 pairs, known as autosomes, are numbered 1-22, while the 23rd pair is the sex chromosomes, labeled as X and Y.
In a karyotype, the chromosomes are typically stained to make them more visible under a microscope. They are then photographed and the images are arranged in a specific order. This allows geneticists to observe any abnormalities or differences in the number or structure of the chromosomes.
Karyotyping is used in various fields of genetics, including prenatal diagnosis, genetic counseling, and research. It can help identify genetic disorders, such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome. It can also provide information about an individual’s sex, determine the sex of a fetus, and identify chromosomal rearrangements that may be associated with certain diseases.
Understanding the Gizmo
The Karyotyping Gizmo is a powerful and interactive tool designed to help students understand the process of karyotyping and the principles behind it. With this Gizmo, students can gain hands-on experience in analyzing and interpreting karyotypes, which are diagrams of chromosomes arranged in pairs. By manipulating the chromosomes and making observations, students can learn about genetic disorders, chromosomal abnormalities, and the role of chromosomes in determining an individual’s traits and characteristics.
One key feature of the Karyotyping Gizmo is its ability to simulate real-world scenarios. Students can explore different scenarios, such as identifying the gender of an individual or diagnosing genetic disorders, and observe how different genetic variations and abnormalities manifest in the chromosome arrangement. They can also investigate how certain genetic mutations or rearrangements can result in specific traits or conditions, providing them with a deeper understanding of genetics and its impact on human health.
The Karyotyping Gizmo also offers several tools that aid in analysis and interpretation. Students can magnify the chromosomes to examine them in detail, zoom in on specific regions to identify abnormalities, and compare different karyotypes side by side. They can also access a variety of information, such as the size, banding pattern, and gene content of each chromosome, to make informed observations and conclusions. Additionally, the Gizmo provides built-in quizzes and activities that reinforce learning and allow students to apply their knowledge in a practical manner.
In summary, the Karyotyping Gizmo is an invaluable educational tool that facilitates student understanding of karyotyping and its applications. By simulating real-world scenarios, providing interactive tools, and offering valuable information, this Gizmo enables students to explore and analyze karyotypes effectively. Through hands-on experience, students develop critical thinking and analytical skills, as well as a deeper understanding of genetics and its role in human health.
How to Use the Karyotyping Gizmo
The Karyotyping Gizmo is an interactive online tool that allows users to study and analyze different karyotypes. Karyotyping is a laboratory technique used to examine an individual’s chromosomes, which can help identify genetic disorders and abnormalities. This Gizmo provides a virtual simulation of this process and allows users to manipulate and analyze karyotypes.
To use the Karyotyping Gizmo, you first need to open the online tool on your computer or mobile device. Once the Gizmo is loaded, you will see a virtual microscope view with chromosomes displayed. On the right side of the screen, there is a control panel that contains various tools and options for analyzing the karyotype.
To begin the analysis, you can drag and drop the chromosomes into different positions and arrange them in pairs. You can also zoom in and out using the microscope controls to get a closer look at the chromosomes. The Gizmo also provides the option to view the chromosomes in different staining patterns, such as Giemsa or Quinacrine.
One of the key features of the Karyotyping Gizmo is the ability to analyze and identify genetic disorders. You can select specific chromosomes or pairs of chromosomes and view their genetic information, including the length, banding pattern, and any abnormalities or mutations. The Gizmo also provides a detailed explanation of each chromosome’s characteristics and functions.
In addition to analyzing individual chromosomes, you can also compare different karyotypes side by side. This allows you to identify similarities or differences between different individuals or species. You can also cross-reference the information with a reference karyotype to determine if any abnormalities are present.
Overall, the Karyotyping Gizmo is a powerful tool for studying and analyzing karyotypes. It provides a hands-on and interactive approach to understanding chromosomes and genetic abnormalities. Whether you are a student learning about genetics or a researcher studying genetic disorders, the Karyotyping Gizmo is a valuable resource.
Interpreting Chromosome Patterns
When analyzing karyotypes, it is important to understand how to interpret chromosome patterns. A karyotype is a visual representation of an individual’s chromosomes, arranged in pairs according to size and shape. Each chromosome pair is labeled numerically from 1 to 23, with the first 22 pairs known as autosomes, and the last pair representing the sex chromosomes.
In order to interpret a karyotype, it is essential to recognize abnormalities or variations in chromosome structure and number. One common abnormality is a chromosomal rearrangement, where parts of the chromosome are deleted, duplicated, or translocated. These rearrangements can lead to genetic disorders and may be identified through distinct patterns in the karyotype.
Structural abnormalities: Structural abnormalities can be observed in a karyotype by identifying altered banding patterns, missing or extra chromosomes, and other irregularities. For example, a deletion may be indicated by a missing segment, while a duplication may be represented by an extra segment of a particular chromosome.
Numerical abnormalities: Numerical abnormalities involve changes in the number of chromosomes. Down syndrome, for instance, is characterized by an extra copy of chromosome 21. This can be detected by the presence of three copies of chromosome 21 in the karyotype.
By carefully analyzing the chromosome patterns and identifying any abnormalities, geneticists can gain valuable insight into an individual’s genetic makeup and potential genetic disorders. Karyotyping is an essential tool in the field of cytogenetics and can assist in the diagnosis and understanding of various genetic conditions.
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting

When using the Karyotyping Gizmo, there are a few common mistakes that users may encounter. It’s important to be aware of these issues and how to troubleshoot them in order to get accurate results and meaningful data.
Mistake: Incorrect selection of chromosomes
One common mistake is selecting the wrong chromosomes during the karyotyping process. It’s crucial to carefully identify and select the correct chromosomes based on their size, banding patterns, and other characteristics. If the wrong chromosomes are selected, the karyotype analysis will not be accurate and may lead to incorrect conclusions.
Troubleshooting: Double-check chromosome identification
To troubleshoot this issue, reviewers should double-check their chromosome identification against the provided reference material or other reliable sources. Comparing the banding patterns and sizes of the chromosomes with the known characteristics can help ensure that the correct chromosomes are selected for the karyotype analysis.
Mistake: Missing or misplaced chromosomes

Another common mistake is missing or misplacing chromosomes during the karyotyping process. If a chromosome is accidentally left out or placed in the wrong position, it can significantly impact the karyotype analysis results and interpretation.
Troubleshooting: Carefully count and place chromosomes
To troubleshoot this issue, reviewers should carefully count the number of chromosomes present in the karyotype and compare it to the expected number for the organism being analyzed. They should also pay close attention to the position and arrangement of the chromosomes to ensure they are correctly placed.
Mistake: Incorrect interpretation of anomalies
Interpreting karyotype anomalies incorrectly is another common mistake that can lead to inaccurate conclusions. It’s important to have a strong understanding of karyotype analysis and the significance of different anomalies before making any interpretations.
Troubleshooting: Consult reliable sources and expert opinions
To troubleshoot this issue, reviewers should consult reliable sources such as textbooks, scientific articles, or experts in the field. It’s important to gather as much information as possible about the specific anomaly in question before making any conclusions or interpretations.
By being aware of these common mistakes and knowing how to troubleshoot them, users of the Karyotyping Gizmo can ensure accurate and meaningful results from their karyotype analyses. It’s important to exercise caution and attention to detail throughout the process to minimize errors and obtain reliable data.
Analyzing and Comparing Chromosomes

The process of analyzing and comparing chromosomes is a crucial step in understanding genetic information and studying genetic disorders. Chromosomes are structures within cells that contain the DNA, the genetic material that carries the instructions for the development and functioning of living organisms. By examining chromosomes, scientists can identify abnormalities and variations that may be associated with certain genetic conditions or diseases.
One method used for analyzing and comparing chromosomes is karyotyping. Karyotyping involves arranging and pairing chromosomes according to their size, shape, and banding patterns. This technique allows scientists to visualize the entire set of chromosomes in an individual’s cells and identify any structural or numerical abnormalities. Karyotyping can be done using various techniques, such as staining the chromosomes to make them more visible under a microscope.
Comparing Chromosomes
When analyzing and comparing chromosomes, scientists look for similarities and differences between different individuals or populations. One key aspect of chromosome comparison is identifying any variations in the number of chromosomes or the structure of specific chromosomes. For example, Down syndrome is a condition caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21, which can be identified through karyotyping. Comparing chromosomes can also help in determining the evolutionary relationships between different species.
Another aspect of chromosome analysis is studying the banding patterns on chromosomes. Each chromosome has unique banding patterns, which are created by staining techniques. These banding patterns can be used to identify specific regions or genes within the chromosomes, helping scientists understand the role of these genes in health and disease. By comparing the banding patterns of chromosomes in different individuals or populations, scientists can gain insights into genetic variations and the potential impact on phenotype.
In conclusion, analyzing and comparing chromosomes is a valuable tool in genetic research. It allows scientists to identify abnormalities, study genetic disorders, determine evolutionary relationships, and understand the functions of specific genes. Karyotyping and examining banding patterns are important techniques in this process, providing valuable information for both diagnostic and research purposes.