Setting up a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) network requires careful planning and proper installation of networking devices. One crucial component of a SOHO network is the router, which serves as the central hub for directing and managing data traffic. In Lab 7-4, we will focus on testing mode, where we will learn how to install and configure a SOHO router effectively.
Installing a SOHO router involves physically connecting it to the network, ensuring all cables are properly plugged in, and verifying the power supply. Once the hardware installation is complete, the next step is to configure the router’s settings. This includes configuring the network address, setting up the wireless network, enabling security features, and creating user accounts.
In testing mode, we will simulate various scenarios and perform tests to ensure the router functions correctly. Through these tests, we can identify any potential issues, troubleshoot connectivity problems, and optimize the router’s performance. By thoroughly testing the router, we can ensure that it is working as intended before deploying it in a production environment.
Lab 7 4 Testing Mode Install and Configure a SOHO Router
Lab 7 4 Testing Mode Install and Configure a SOHO Router is a practical exercise that focuses on installing and configuring a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) router in a testing mode. The purpose of this lab is to provide hands-on experience in setting up and customizing a router for a small office or home network.
The lab begins by introducing the concept of a SOHO router and its role in a small office or home network. It covers the basic features and functions of a router, such as NAT (Network Address Translation), DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol), and port forwarding. The lab also explores the different types of interfaces available on a SOHO router, including Ethernet, USB, and wireless.
During the lab, students are given the opportunity to install and configure a SOHO router in a testing mode. They learn how to connect the router to the existing network, assign IP addresses, set up DHCP, and configure port forwarding. The lab also includes exercises on configuring wireless settings, such as creating a wireless network name (SSID) and setting a password.
By the end of the lab, students should have a clear understanding of how to install and configure a SOHO router in a testing mode. They should be able to customize the router settings to meet the specific needs of a small office or home network. Overall, Lab 7 4 Testing Mode Install and Configure a SOHO Router is a valuable hands-on exercise that provides practical skills in setting up and managing a router for a small office or home network.
Purpose and Objectives
In the Lab 7 4 testing mode install and configure a soho router, the main purpose is to gain hands-on experience in setting up and configuring a small office/home office (SOHO) router for testing purposes. This lab provides an opportunity to understand the basic functionalities and configurations of a router in a small network environment.
The objectives of this lab include:
- Installing and connecting a SOHO router to the network
- Configuring basic settings such as IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway
- Enabling DHCP server functionality on the router
- Setting up port forwarding and NAT (Network Address Translation)
- Testing connectivity between devices within the network and to the internet
By completing these objectives, participants will gain a better understanding of the role of a router in a small network setup and enhance their networking skills. This lab is designed to provide hands-on experience, allowing participants to practice configuring and troubleshooting router settings in a simulated environment.
Equipment and Materials Needed
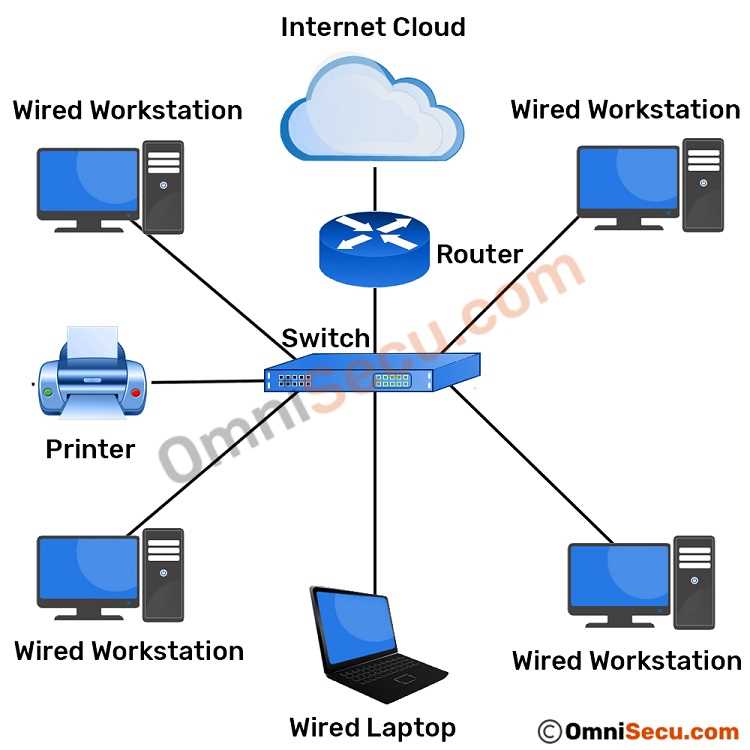
In order to successfully install and configure a SOHO (Small Office/Home Office) router, you will need the following equipment and materials:
- SOHO Router: It is essential to have a SOHO router, which acts as the central hub for your network. Make sure the router supports the necessary features, such as Wi-Fi and Ethernet connectivity.
- Ethernet Cables: Ethernet cables are essential for connecting devices to the router, especially for devices that do not have Wi-Fi capabilities. Make sure you have enough cables of appropriate length.
- Modem: If your ISP (Internet Service Provider) requires a separate modem, make sure you have one that is compatible with your router. This modem will provide the internet connection to your router.
- Computer or Laptop: You will need a computer or laptop to access the router’s configuration settings. Make sure it has an Ethernet port or Wi-Fi capabilities to connect to the router.
- Power Cables: Ensure you have power cables for both the router and the modem. These cables will provide the necessary power supply to the devices.
Additionally, it is important to have a basic understanding of networking concepts and the ability to follow instructions provided by the router’s manufacturer. Having access to the router’s user manual or online resources can also be helpful during the installation and configuration process.
Steps to Install and Configure a SOHO Router
Installing and configuring a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) router is essential for setting up a secure and reliable network in your home or small business. Follow the steps below to ensure a successful installation and configuration process.
Step 1: Hardware Setup

- Connect Power: Plug your SOHO router into a power source using the provided power adapter.
- Connect WAN Port: Connect one end of an Ethernet cable to the WAN port of the router and the other end to your modem or internet source.
- Connect LAN Ports: Connect your devices, such as computers or switches, to the LAN ports of the router using Ethernet cables.
Step 2: Access Router Configuration
- Open a web browser: Launch a web browser on a connected device and enter the default IP address of the router. This information can be found in the router’s user manual.
- Log in: Enter the default username and password provided by the manufacturer. It is recommended to change the default credentials for security reasons.
Step 3: Basic Configuration
- Internet Connection Type: Select the appropriate internet connection type, such as Dynamic IP, Static IP, or PPPoE, based on your internet service provider’s requirements.
- Wireless Settings: Configure the wireless network name (SSID) and password for secure wireless access. Consider enabling encryption, such as WPA2, to protect your network.
- Network Address Translation (NAT): Enable NAT to allow multiple devices to share a single public IP address.
Step 4: Advanced Configuration (Optional)

- Port Forwarding: If you need to access specific services or applications from the internet, configure port forwarding to direct incoming traffic to the appropriate device on your local network.
- DMZ: Set up a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone) if you have devices that require direct access from the internet while still having some level of network security.
- VPN: If you require secure remote access or want to connect multiple locations, configure a Virtual Private Network (VPN) on your SOHO router.
Following these steps will help you install and configure your SOHO router properly, ensuring a reliable and secure network for your home or small office. Remember to save your settings and test your network connectivity after completing the configuration process.
Testing Mode Configuration
The testing mode configuration is an essential step in the installation and configuration process of a Small Office/Home Office (SOHO) router. This mode allows for a thorough testing of the router’s functionality and ensures that it is properly configured to meet the needs of the network.
During the testing mode configuration, several key aspects are addressed to ensure the router’s performance and security. These include:
- Network connectivity: The testing mode allows for the verification of network connectivity by ensuring that the router can establish a connection to the internet and can communicate with other devices on the network.
- Firewall settings: The firewall settings of the router are tested to ensure that they are configured properly to protect the network from unauthorized access and attacks. This includes testing port forwarding rules, access control lists, and intrusion detection systems.
- Quality of Service (QoS): The QoS settings are tested to ensure that the router can prioritize network traffic based on specific criteria, such as bandwidth, latency, and application requirements. This helps to optimize network performance and ensure a consistent user experience.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN) configuration: If the router supports VPN functionality, the testing mode configuration includes testing the VPN settings to ensure that remote access and secure communication are functioning correctly.
- Wireless network configuration: If the router includes wireless capabilities, the testing mode configuration involves testing the wireless network settings to ensure proper connection, signal strength, and security measures, such as encryption and access control.
Overall, the testing mode configuration is a critical step in the installation and configuration process of a SOHO router. It ensures that the router is functioning correctly, secure, and capable of meeting the network requirements of the small office or home office environment.
Troubleshooting
When setting up and configuring a SOHO router, there may be instances where troubleshooting is required to resolve any issues that may arise. Here are some common problems you may encounter and steps you can take to troubleshoot them:
No internet connection
If you are unable to establish an internet connection through your SOHO router, there are several things you can check. First, ensure that your modem is connected to the router’s WAN or Internet port. Make sure that all cables are securely connected and that there are no loose connections. Verify that your modem is properly configured and functioning correctly. Restarting both your modem and router can often resolve connectivity issues. Additionally, check the router’s settings to ensure that it is properly configured for your internet service provider.
If you are using wireless connectivity, check to see if other devices can connect to the router. If they can, the issue may be with the device you are trying to connect. Try restarting the device and reconnecting to the wireless network. If the problem persists, it may be worth resetting the router to its factory settings and setting it up again.
Slow internet connection
If you are experiencing slow internet speeds, there are a few steps you can take to troubleshoot the issue. First, check the speed of your internet connection using an online speed test. If the speed is significantly lower than what you are paying for, contact your internet service provider to see if there are any service issues in your area.
Next, check the placement of your router. Make sure it is positioned in a central location and away from any obstructions that may interfere with the signal. You can also try changing the wireless channel on your router to avoid any interference from other nearby devices.
If you have multiple devices connected to your router, make sure none of them are consuming a large amount of bandwidth. This can be done by accessing the router’s admin console and checking the connected device list. If one device is using a disproportionate amount of bandwidth, you may need to limit its usage or prioritize other devices.
Finally, ensure that your router’s firmware is up to date. Manufacturers often release firmware updates that can improve performance and fix any known issues. Check the manufacturer’s website for any available updates and follow the instructions to install them.