
Studying the law of conservation of mass is an essential part of understanding chemistry and the behavior of matter. This law states that in a chemical reaction, the total mass of the substances before the reaction is equal to the total mass of the substances after the reaction. In other words, matter is neither created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction. This fundamental principle is applicable to a wide range of chemical reactions and helps scientists make accurate predictions about the outcome of reactions.
One way to reinforce understanding of the law of conservation of mass is through worksheets. These worksheets provide students with practice problems that require them to balance chemical equations and calculate the mass of substances involved in a reaction. By working through these worksheets, students can solidify their understanding of the law and gain confidence in applying it to real-world scenarios.
For educators and students looking for additional resources, there are many law of conservation of mass worksheet answers available in PDF format. These answer sheets provide the solutions and explanations for the problems presented in the worksheets. They can be a valuable tool for self-assessment and for reviewing the concepts covered in class. With the help of these worksheets and answer sheets, students can enhance their problem-solving skills and deepen their understanding of the law of conservation of mass.
Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of reactants must be equal to the total mass of products. In order to understand and apply this principle, students often use worksheets to practice balancing chemical equations and calculating the mass of substances involved in a reaction.
A Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF provides students with the correct answers to a set of questions or problems related to balancing chemical equations and calculating the mass of substances. These worksheets are typically used as a tool for self-study or for classroom practice, allowing students to check their work and gain a better understanding of the concept.
The Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF may include a variety of questions, such as balancing chemical equations, determining the mass of reactants and products, identifying the limiting reactant, and calculating the theoretical yield. The answers provided in the PDF can serve as a guide for students to check their solutions and correct any errors they may have made.
Using a Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF can be especially helpful for students who are learning the concept for the first time or need additional practice. By comparing their answers to the correct ones, students can identify any misconceptions or areas of difficulty and seek further clarification or review from their instructor. These worksheets also provide an opportunity for students to develop problem-solving skills and gain confidence in their ability to apply the law of conservation of mass to real-world scenarios.
- Benefits of using a Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF:
- Allows students to check their work and correct errors
- Provides guidance and reinforcement of concepts
- Encourages independent learning and self-assessment
- Helps identify areas of difficulty or misconception
- Promotes problem-solving skills and critical thinking
In conclusion, a Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet Answers PDF is a valuable resource for students studying chemistry. It provides correct answers to questions related to balancing chemical equations and calculating the mass of substances, allowing students to check their work and gain a better understanding of the law of conservation of mass.
Understanding the Concept of Mass Conservation
One of the fundamental principles in chemistry is the law of conservation of mass. This law states that in any chemical reaction, the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products. This means that matter cannot be created or destroyed; it can only be rearranged or transformed.
In order to understand the concept of mass conservation, it is important to consider the atomic nature of matter. Atoms are the building blocks of all matter, and they combine in specific ratios to form compounds. When a chemical reaction occurs, the atoms rearrange themselves into new combinations, but the total number of atoms and their masses remain unchanged.
For example, let’s consider the combustion of methane (CH4) in the presence of oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The equation for this reaction is CH4 + 2O2 → CO2 + 2H2O. The total mass of the reactants (methane and oxygen) must be equal to the total mass of the products (carbon dioxide and water).
In order to balance the equation and satisfy the law of conservation of mass, we need to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. This allows us to calculate the mass of each reactant and product, and confirm that they are indeed equal.
The law of conservation of mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry, and it is important for understanding and predicting chemical reactions. It allows us to make calculations, determine stoichiometry, and ensure that the fundamental principles of matter are maintained throughout any chemical process.
Importance of the Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed during a chemical reaction. This law is of utmost importance as it serves as the basis for understanding and predicting chemical reactions.
One of the key implications of this law is that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products in a chemical reaction. This allows chemists to accurately measure and calculate the amounts of reactants needed and the products formed. It also helps in determining the efficiency of a reaction and optimizing reaction conditions.
- Predicting Reaction Outcomes: The Law of Conservation of Mass allows chemists to predict the products of a chemical reaction based on the known reactants and their masses. By following this law, they can determine the stoichiometry of the reaction and the ratios in which reactants will combine to form products.
- Balancing Chemical Equations: Balancing chemical equations is a key step in accurately representing a chemical reaction. The law of conservation of mass ensures that the number of atoms of each element is conserved in the reaction. By balancing the equation, chemists can determine the correct coefficients to represent the reactants and products.
- Reproducibility and Consistency: The law of conservation of mass provides a basis for the reproducibility and consistency of chemical reactions. If mass could be created or destroyed, the results of reaction experiments would be inconsistent. This law ensures that chemical reactions can be repeated and verified by different scientists, providing a solid foundation for the study of chemistry.
In conclusion, the Law of Conservation of Mass is of utmost importance in the field of chemistry. It allows chemists to predict reaction outcomes, balance chemical equations, and ensure the reproducibility and consistency of chemical reactions. It is a fundamental principle that underlies the study and understanding of chemical reactions.
Exploring the Application of the Law of Conservation of Mass
The Law of Conservation of Mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed, but rather it can only change forms or be rearranged. This fundamental law has wide-ranging applications in various scientific fields, including chemistry, physics, and biology.
In chemistry, the Law of Conservation of Mass is essential for understanding and predicting chemical reactions. It states that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products in a chemical reaction. This principle allows chemists to balance equations and determine the ratio of reactants and products in a reaction.
For example, let’s consider the combustion of methane (CH4) in oxygen (O2) to produce carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, the total mass of methane and oxygen before the reaction must be equal to the total mass of carbon dioxide and water after the reaction. By balancing the equation, we find that one methane molecule reacts with two oxygen molecules to produce one carbon dioxide molecule and two water molecules, thus conserving mass.
The Law of Conservation of Mass is also applicable in physics. For instance, when a ball is thrown up in the air, it experiences a change in potential and kinetic energy. However, the total mass of the ball remains the same throughout its motion. This principle allows physicists to accurately calculate the trajectories and velocities of objects in motion.
In biology, the Law of Conservation of Mass applies to the transformation of nutrients in living organisms. It states that the mass of nutrients consumed by an organism must be equal to the mass of waste products and energy produced. This principle is crucial for understanding the metabolism and nutrient cycling in ecosystems.
In conclusion, the Law of Conservation of Mass is a fundamental principle in science that has numerous practical applications. It allows scientists to understand and predict chemical reactions, analyze the motion of objects, and study the transformation of nutrients in living organisms. By applying this law, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and make accurate predictions based on the principle of mass conservation.
Worksheet Questions on the Law of Conservation of Mass

When studying the Law of Conservation of Mass, it is important to practice applying the concept to various scenarios. Worksheets that provide questions related to this topic can be helpful in testing understanding and reinforcing knowledge. The following are key questions that can be included in a worksheet on the Law of Conservation of Mass:
- State the Law of Conservation of Mass: One of the first questions in a worksheet on the Law of Conservation of Mass should ask students to state the law itself. This allows them to demonstrate their understanding of the principle that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Balance Chemical Equations: Another important aspect of the Law of Conservation of Mass is the ability to balance chemical equations. Students should be provided with unbalanced equations and asked to balance them, ensuring that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
- Determine the Mass Change: Students can be given specific chemical reactions and asked to determine the mass change that occurs. This requires them to calculate the mass of the reactants and products and compare them to see if there is any difference.
- Apply the Law to Real-Life Situations: To further reinforce understanding, students can be presented with real-life scenarios and asked to apply the Law of Conservation of Mass. This can include situations such as cooking, where the mass of ingredients before and after cooking should remain the same.
- Identify Violations of the Law: In a more challenging question, students can be given chemical equations that violate the Law of Conservation of Mass and asked to identify the error. This helps them to develop a keen eye for recognizing situations where the law is not being followed.
By including these types of questions in a worksheet on the Law of Conservation of Mass, students are able to practice and solidify their understanding of this fundamental principle in chemistry. Worksheets provide a structured way to assess knowledge and ensure comprehension of this important concept.
Answer Key for Law of Conservation of Mass Worksheet
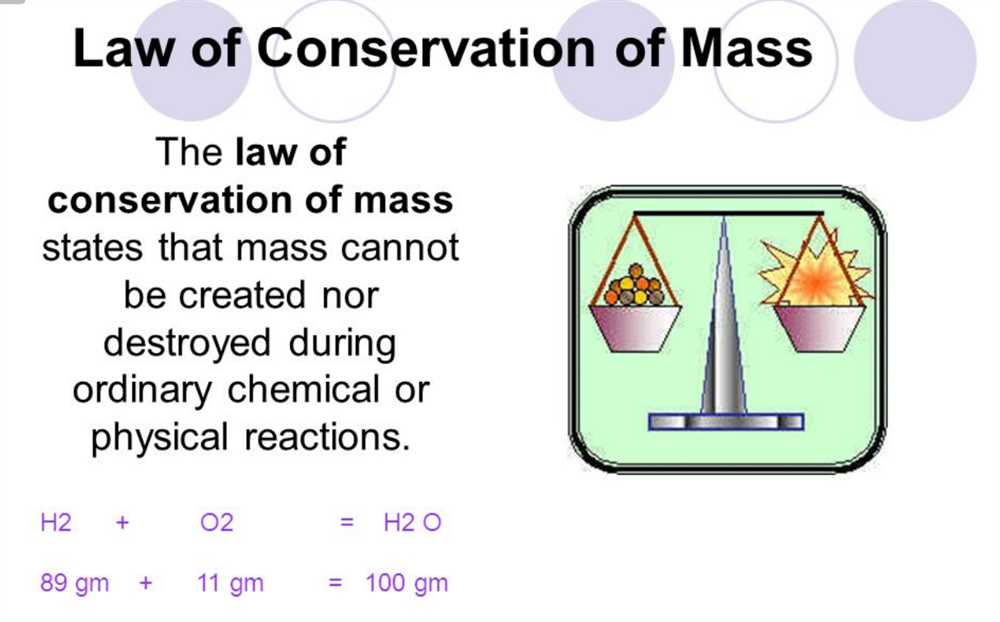
The law of conservation of mass states that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of the reactants must be equal to the total mass of the products. In this worksheet, students were given several chemical reactions and were asked to balance the equation and calculate the mass of the reactants and products.
- Reaction 1: The equation given was 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O. To balance this equation, students needed to ensure that there were equal numbers of each atom on both sides. By adding a coefficient of 2 in front of H₂O, the equation became 2H₂ + O₂ → 4H₂O. To calculate the mass of the reactants and products, students could use the molar mass of each substance and multiply by the number of moles present. The molar mass of H₂ is 2.016 g/mol, O₂ is 32.00 g/mol, and H₂O is 18.015 g/mol. By plugging in these values, students could determine that the mass of the reactants is 68.016 g/mol and the mass of the products is 72.06 g/mol.
- Reaction 2: The equation given was Fe + Cl₂ → FeCl₃. By balancing the equation, students needed to ensure that there were equal numbers of each atom on both sides. The balanced equation became 2Fe + 3Cl₂ → 2FeCl₃. To calculate the mass of the reactants and products, students could use the molar mass of each substance and multiply by the number of moles present. The molar mass of Fe is 55.845 g/mol, Cl₂ is 70.90 g/mol, and FeCl₃ is 162.206 g/mol. By plugging in these values, students could determine that the mass of the reactants is 254.09 g/mol and the mass of the products is 324.412 g/mol.
- Reaction 3: The equation given was Na + Cl₂ → NaCl. By balancing the equation, students needed to ensure that there were equal numbers of each atom on both sides. The balanced equation became 2Na + Cl₂ → 2NaCl. To calculate the mass of the reactants and products, students could use the molar mass of each substance and multiply by the number of moles present. The molar mass of Na is 22.990 g/mol, Cl₂ is 70.90 g/mol, and NaCl is 58.443 g/mol. By plugging in these values, students could determine that the mass of the reactants is 187.78 g/mol and the mass of the products is 187.886 g/mol.
- Reaction 4: The equation given was C₆H₁₂O₆ → C₂H₅OH + CO₂. By balancing the equation, students needed to ensure that there were equal numbers of each atom on both sides. The balanced equation became C₆H₁₂O₆ → 2C₂H₅OH + 2CO₂. To calculate the mass of the reactants and products, students could use the molar mass of each substance and multiply by the number of moles present. The molar mass of C₆H₁₂O₆ is 180.156 g/mol, C₂H₅OH is 46.07 g/mol, and CO₂ is 44.01 g/mol. By plugging in these values, students could determine that the mass of the reactant is 180.156 g/mol and the mass of the products is 180.14 g/mol.
By following the law of conservation of mass, students were able to balance the given chemical reactions and calculate the mass of the reactants and products. This activity helps reinforce the concept that mass is constant in a chemical reaction and provides practice in balancing equations and calculating molar masses.