
When we think about the food we eat, we often focus on its taste and nutritional value. However, there is much more to our food than meets the eye. Macromolecules, or large molecules, play a crucial role in the composition and functions of our food. Understanding the role of macromolecules in our diet can help us make healthier food choices and optimize our overall well-being.
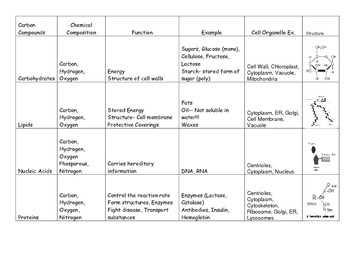
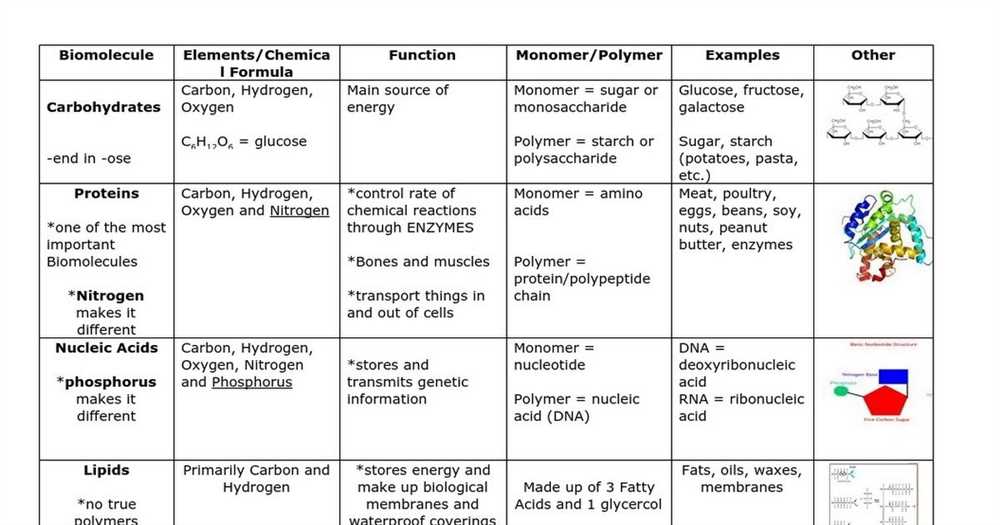
One of the main macromolecules found in our food is carbohydrates. Carbohydrates are a source of energy for our body and can be found in various forms, such as sugars and starches. They are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and provide us with the fuel we need to carry out daily activities. By understanding the types and amounts of carbohydrates in our food, we can better manage our blood sugar levels and maintain a balanced diet.
Proteins are another important class of macromolecules in our food. They are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of our body tissues. Proteins are composed of amino acids, and different combinations of these amino acids give rise to a wide variety of proteins with different structures and functions. By consuming foods rich in protein, we can support muscle growth, strengthen our immune system, and promote overall health and well-being.
The Importance of Macromolecules in Our Food
Macromolecules play a vital role in maintaining the overall health and well-being of our bodies. These large, complex molecules are found in the food we consume and are essential for various physiological processes, such as energy production, tissue repair, and immune function. Understanding the importance of macromolecules in our diet can help us make informed choices when it comes to our nutrition.
One of the key macromolecules in our food is carbohydrates. These molecules, composed of sugar units, serve as the primary source of energy for our bodies. They are broken down into glucose during digestion and are then used by our cells to fuel their activities. Carbohydrates are found in many foods, such as fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Including a variety of carbohydrates in our diet ensures a steady supply of energy and helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Proteins are another important macromolecule found in our food. These molecules are made up of amino acids and are vital for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues. They are involved in various processes, including the formation of enzymes, hormones, and antibodies. Consuming an adequate amount of protein helps support muscle development, aids in wound healing, and contributes to the overall functioning of our immune system. Good sources of protein include lean meats, fish, dairy products, legumes, and nuts.
Lipids, or fats, are macromolecules that provide long-term energy storage and insulation for our bodies. They also play a crucial role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and the production of hormones. While fats are often associated with weight gain, they are an essential component of a balanced diet. Including healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can help support brain function, protect organs, and regulate body temperature.
Nucleic acids are macromolecules responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. They are essential for the production of proteins and the proper functioning of our cells. While nucleic acids are not found in abundance in our food, consuming a balanced diet that includes foods rich in vitamins and minerals is crucial for supporting the synthesis of these important molecules.
In conclusion, macromolecules in our food are essential for maintaining our overall health and well-being. Carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids all play crucial roles in various physiological processes, from energy production to tissue repair. Including a balanced variety of these macromolecules in our diet ensures that our bodies receive the necessary nutrients to function optimally.
Carbohydrates: The Fuel for Our Bodies
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for our bodies. They are the main source of fuel for the brain and muscles, and they are essential for maintaining proper bodily functions. Carbohydrates are made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen and are found in various forms in the foods we eat.
There are two types of carbohydrates: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. Simple carbohydrates, also known as sugars, are found in fruits, milk, and processed foods. They provide quick energy but are quickly digested and can cause a spike in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, complex carbohydrates, found in whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, are made up of longer chains of sugar molecules and provide a slower and more sustained release of energy. They also contain important vitamins, minerals, and fiber.
Our bodies break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then used by the cells as a source of energy. Excess glucose is stored in the liver and muscles as glycogen to be used when needed. When we engage in physical activity, our bodies rely on stored glycogen to provide energy. It is important to consume an adequate amount of carbohydrates to maintain glycogen stores and support optimal physical performance.
Carbohydrates are not only vital for providing energy, but they also play a role in other physiological processes. They are needed for proper brain function, as the brain relies on glucose as its main source of fuel. Additionally, carbohydrates have a sparing effect on protein, meaning that they help preserve protein for other functions, such as building and repairing tissues.
In conclusion, carbohydrates are an essential macronutrient that serves as the primary fuel for our bodies. They provide energy, support brain function, and help preserve protein. It is important to consume a balanced diet that includes both simple and complex carbohydrates to ensure optimal health and performance.
Proteins: Essential Building Blocks for Growth and Repair
Proteins are an essential macromolecule found in a wide variety of foods that we consume on a daily basis. They are vital for the growth and repair of tissues and organs in our bodies. In fact, proteins are often referred to as the building blocks of life because they play such a crucial role in maintaining our overall health.
One of the key functions of proteins is their role in growth and development. During periods of growth, such as childhood and adolescence, proteins are necessary for the formation of new tissues and the production of hormones and enzymes. Without an adequate intake of protein, growth can be stunted and development can be impaired. In addition, proteins are also important for maintaining and repairing tissues throughout our lives. When we exercise or engage in physical activity, our muscles undergo stress and damage. Proteins help to repair this damage and promote muscle growth and strength.
Proteins are made up of amino acids, which are the building blocks that form long chains. There are 20 different types of amino acids, and they can be combined in various ways to create different types of proteins. Some of these amino acids can be produced by our bodies, while others must be obtained through our diet. These are known as essential amino acids, and they are crucial for our overall health and well-being.
It is important to include a variety of protein sources in our diet to ensure that we are getting all of the essential amino acids. Foods such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, and legumes are excellent sources of protein. Additionally, plant-based sources of protein such as tofu, quinoa, and lentils can also provide the necessary amino acids.
Summary:
- Proteins are essential for growth and repair of tissues in our bodies.
- They play a crucial role in the formation of new tissues and the production of hormones and enzymes.
- Proteins help to repair damage and promote muscle growth and strength.
- Proteins are made up of amino acids, including essential amino acids that must be obtained through our diet.
- A variety of protein sources should be included in our diet to ensure we are getting all of the necessary amino acids.
Lipids: The Powerhouses of Energy
Lipids, also known as fats, are an essential component of our diet and play a crucial role in providing us with energy. Unlike carbohydrates and proteins, which provide 4 calories per gram, lipids provide more than twice the energy at 9 calories per gram. This makes lipids the powerhouses of energy in our bodies.
One of the main functions of lipids is to serve as a concentrated source of energy. Our bodies store excess energy from the food we consume in the form of lipids, primarily in adipose tissue. When our body needs energy, it can convert these stored lipids back into usable fuel. This ability to store and release energy efficiently allows lipids to provide a sustained source of energy for longer periods of time compared to carbohydrates and proteins.
Lipids are also important for the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin A, D, E, and K. These vitamins cannot be absorbed by our bodies unless they are consumed with dietary fats. Lipids act as carriers for these vitamins, assisting in their absorption and utilization within our bodies.
Lastly, lipids play a crucial role in maintaining cell structure and function. Phospholipids, a type of lipid, are an essential component of cell membranes. They form a lipid bilayer that acts as a barrier, regulating the movement of molecules in and out of the cell. Lipids also form protective insulation around cells, helping to maintain their integrity.
In conclusion, lipids are not only a rich source of energy but also serve essential functions in our bodies. From providing sustained energy to aiding in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and maintaining cell structure, lipids are truly the powerhouses of energy.
Nucleic Acids: The Blueprint of Life
Nucleic acids are essential macromolecules that play a critical role in living organisms. They are responsible for storing, transmitting, and expressing genetic information, making them the blueprint of life. There are two types of nucleic acids: deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
DNA: DNA is found in the nucleus of cells and contains the genetic instructions for the development and functioning of living organisms. It is made up of two strands of nucleotides that form a double helix structure. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The sequence of these bases determines the genetic code. DNA replication allows for the transmission of genetic information during cell division.
RNA: RNA is involved in protein synthesis and has multiple forms. Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized. Transfer RNA (tRNA) helps in the assembly of amino acids during protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is a component of the ribosomes, which are the cellular structures where protein synthesis occurs.
In summary, nucleic acids are crucial macromolecules that hold the genetic information necessary for the development, functioning, and reproduction of living organisms. DNA acts as a stable repository of genetic information, while various forms of RNA are involved in the translation of this information into functional proteins.
Understanding the Role of Enzymes in Digestion

In order to understand the role of enzymes in digestion, it is important to first understand the process of digestion itself. Digestion is the process by which our body breaks down the food we eat into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by our cells. This process begins in the mouth, where enzymes produced by the salivary glands start to break down carbohydrates. The food then travels down the esophagus and into the stomach, where it is further broken down by stomach acid and enzymes.
Enzymes are proteins that act as catalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body. In digestion, enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down the macromolecules found in food into smaller molecules that can be absorbed. For example, amylase is an enzyme that breaks down carbohydrates into simple sugars like glucose. Lipase is another enzyme that breaks down fats into glycerol and fatty acids. Proteases, on the other hand, break down proteins into amino acids.
Each enzyme is specific to the molecule it breaks down, meaning that there are specific enzymes for carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. This specificity ensures that each type of molecule is broken down efficiently and effectively. Additionally, enzymes have optimal conditions under which they function best. For example, the enzyme amylase works best in a slightly acidic environment, which is why it is most active in the stomach.
Without enzymes, digestion would be a slow and inefficient process. Enzymes break down macromolecules into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and used by our cells. They play a vital role in ensuring that our body gets the nutrients it needs from the food we eat. Understanding the role of enzymes in digestion is crucial for understanding how our bodies process and utilize the macromolecules found in our food.
Common Sources of Macromolecules in our Daily Diet

The three main macromolecules found in our daily diet are carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids. These macromolecules provide us with the necessary energy and nutrients to perform various bodily functions.
Carbohydrates: Carbohydrates are the main source of energy in our diet. They can be found in foods such as grains, bread, rice, pasta, fruits, and vegetables. These foods are rich in complex carbohydrates, which are broken down into simple sugars during digestion. Simple sugars, such as glucose, are then used by our cells to produce energy.
Proteins: Proteins are essential for the growth, repair, and maintenance of tissues in our body. They are found in foods such as meat, poultry, fish, eggs, dairy products, legumes, and nuts. These foods are rich in amino acids, which are the building blocks of proteins. When we consume proteins, our body breaks them down into amino acids, which are then used to build and repair tissues.
Lipids: Lipids, also known as fats, are an important source of energy and essential nutrients. They are found in foods such as oils, butter, margarine, meats, cheese, nuts, and seeds. Lipids provide more than twice the amount of energy as carbohydrates and proteins. They also serve as an important structural component of cell membranes and help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
In conclusion, a balanced daily diet should include sources of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids to provide us with the necessary energy and nutrients for optimal health. It is important to choose a variety of foods from each macromolecule group to ensure a well-rounded diet.