Manifest Destiny was a belief held by many Americans in the 19th century that the United States was destined to expand across the North American continent. This belief fueled westward expansion and the acquisition of new territories, often at the expense of Native American tribes and other countries.
One of the key factors that fueled Manifest Destiny was the idea of American exceptionalism. Americans believed that their democratic values and way of life were superior to those of other nations, and that it was their duty to spread these values to other parts of the world. This belief in American exceptionalism justified the expansion of the United States and the displacement of indigenous peoples.
Another factor that contributed to Manifest Destiny was economic opportunity. The West was seen as a land of opportunity, with vast natural resources and fertile land. People believed that by expanding westward, they could improve their economic prospects and create a better life for themselves and their families. This economic motivation played a significant role in driving westward expansion.
However, Manifest Destiny also had its critics. Some argued that it was a justification for imperialism and the subjugation of other peoples. Others believed that the United States should focus on improving conditions at home rather than engaging in colonial expansion. These critics questioned the morality of Manifest Destiny and its impact on indigenous peoples and other countries.
Overall, Manifest Destiny was a complex belief system that shaped the course of American history. It was fueled by a combination of factors, including American exceptionalism and the promise of economic opportunity. However, it also raised ethical questions and led to the displacement and mistreatment of indigenous peoples. Understanding Manifest Destiny is essential for understanding the motivations behind westward expansion in the 19th century.
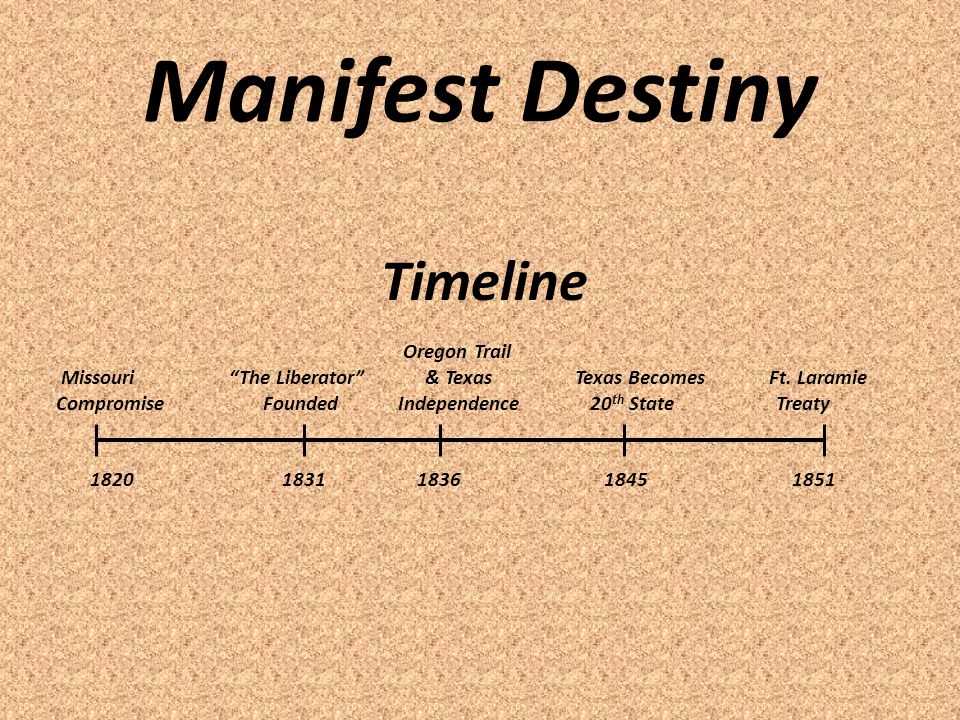
Manifest Destiny DBQ Answer Key

The concept of Manifest Destiny was a prevailing belief in the 19th century United States that God had ordained or destined the American people to expand their territory from coast to coast. This ideology fueled the rapid westward expansion of the United States and justified the displacement and mistreatment of Native American tribes. The documents provided in this DBQ showcase the various perspectives and motivations behind Manifest Destiny, revealing the mindset of the American people during this time period.
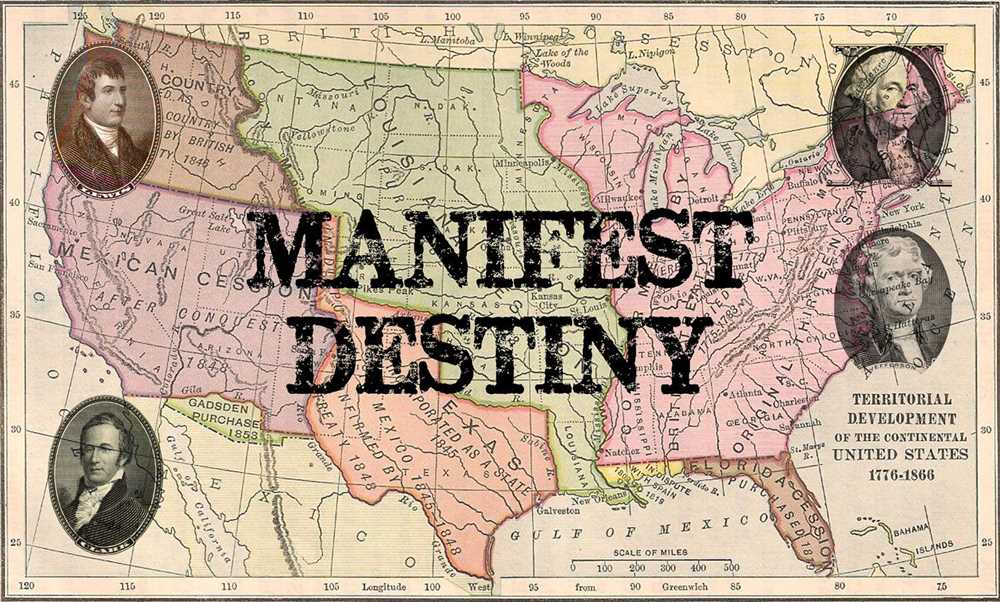
Document A, a map of the United States from 1810 to 1842, illustrates the territorial growth of the country during the early 19th century. The map clearly shows how the United States expanded westward, acquiring new territories such as Texas, Oregon, and California. This expansion was driven by the belief that it was the divine destiny of the American people to spread their civilization across the continent.
- Document B, an excerpt from John O’Sullivan’s article “The Great Nation of Futurity,” highlights the idealistic vision of Manifest Destiny. O’Sullivan argues that the United States has a unique mission to be a beacon of freedom and democracy for the rest of the world. He claims that the American people are destined to spread their principles and institutions to other nations, ultimately creating a global empire of liberty.
- Document C, an excerpt from an 1845 editorial in the Democratic Review, emphasizes the economic motivations behind Manifest Destiny. The editorial argues that the vast resources and fertile lands in the West are essential for the prosperity and growth of the United States. It states that expansion is necessary to provide new markets for American goods and ensure the survival of the nation’s economy.
- Document E, a painting by John Gast titled “American Progress,” portrays a female figure known as Columbia leading pioneers and settlers westward. Columbia symbolizes the spirit of Manifest Destiny, guiding the American people towards their manifest destiny. The painting portrays Native Americans and wild animals fleeing in fear and represents the belief that progress and civilization would inevitably replace the indigenous population and wilderness.
Overall, the documents provided in this DBQ demonstrate the complex motivations behind Manifest Destiny, including religious, idealistic, and economic factors. This belief in the divine destiny of the American people to expand their territory and spread their ideals had far-reaching consequences, shaping the history of the United States and impacting the lives of Native Americans and other groups affected by westward expansion.
Understanding Manifest Destiny
The concept of Manifest Destiny played a significant role in shaping the expansionist policies of the United States during the 19th century. It was a belief that the American nation was destined by God to spread its ideals and institutions across the entire North American continent. This conviction fueled the westward expansion and colonization of the American frontier.
Key Factors:
- Territorial Expansion: Manifest Destiny served as a justification for the acquisition of new territories through various means such as purchase, treaty, or force. The Louisiana Purchase of 1803, the annexation of Texas in 1845, and the Mexican-American War (1846-1848) were all driven by the belief in Manifest Destiny.
- Religious and Cultural Superiority: Many Americans believed that their nation’s expansion was not only a political and economic necessity but also a moral duty. They saw themselves as the chosen people who would bring democracy, Christianity, and civilization to areas considered “uncivilized” or inhabited by Native American tribes.
- Economic Opportunities: The pursuit of wealth and access to new markets were also significant motivators behind Manifest Destiny. The idea that vast natural resources and fertile lands were waiting to be utilized in the West appealed to entrepreneurs, farmers, and settlers, who sought economic opportunities and a better life for themselves and their families.
- Population Growth and National Identity: The rapidly increasing population of the United States further fueled the belief in Manifest Destiny. Americans needed more land for settlement, resources, and to accommodate the influx of immigrants arriving in the country. Expansion became a way to assert national identity and maintain social cohesion.
While the concept of Manifest Destiny provided a unifying vision for the American people during a period of significant growth, it also had its critics. Some saw it as an excuse for imperialistic aggression, while others recognized the negative impact it had on indigenous populations. Nevertheless, understanding Manifest Destiny is crucial to comprehending the motivations and actions of the United States during this transformative period in its history.
| Key Factors | Effects |
|---|---|
| Territorial Expansion | Increased land holdings and geopolitical power |
| Religious and Cultural Superiority | Displacement of Native American tribes and erosion of their cultures |
| Economic Opportunities | Development of new industries and access to valuable resources |
| Population Growth and National Identity | Creation of a diverse and expanding nation |
Historical Context: Westward Expansion
The period of Westward Expansion in the United States, spanning from the early 1800s to the late 1800s, was a time of rapid expansion and territorial acquisition. It was driven by a combination of factors, including a belief in Manifest Destiny, economic opportunities, and a desire for new land. This era saw the United States acquire vast territories, such as the Louisiana Purchase, Florida, Texas, and the Oregon Territory, through treaties, purchases, and military conquest.
The idea of Manifest Destiny, the belief that it was the country’s destiny and a God-given right to expand its territory from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean, played a significant role in motivating westward expansion. This belief was fueled by a sense of American exceptionalism and a desire to spread democracy, Christianity, and American values to new territories. The concept of Manifest Destiny provided a moral justification for the acquisition of land inhabited by Native Americans and other groups.
As Americans moved westward, they encountered diverse cultures and faced conflicts with Native American tribes, often resulting in violence and forced displacement. The westward expansion also led to the expansion of slavery, as southern states sought to maintain a balance of power in Congress by adding more slaveholding territories. This issue would eventually contribute to the tensions that led to the American Civil War.
The economic opportunities presented by the West also fueled westward expansion. The discovery of gold in California and other regions brought thousands of people seeking wealth and a better life. The construction of railroads, such as the Transcontinental Railroad, facilitated the movement of people and goods to the western frontier, opening up new markets and driving economic growth.
In conclusion, Westward Expansion was a defining era in American history, driven by a combination of factors including ideas of Manifest Destiny, economic opportunities, and a desire for new land. It shaped the country’s identity and had a profound impact on Native American communities, the institution of slavery, and the nation’s economic development.
Examining the Doctrine of Manifest Destiny

The Doctrine of Manifest Destiny was a belief that originated in the United States in the 19th century. It stated that it was the divine right and destiny of the American people to spread across the entire continent, from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. This idea was rooted in the belief of American exceptionalism and the notion that the United States was destined to bring democracy, progress, and civilization to the western frontier.
One of the key elements of Manifest Destiny was the sense of destiny and providence that accompanied the expansion of the United States. Americans believed that they were chosen by God to fulfill a special mission and bring their values and way of life to the lands they conquered. This belief in the exceptionalism of the United States fueled the desire for territorial expansion and justified the displacement and mistreatment of Native American populations.
The driving force behind Manifest Destiny

The doctrine of Manifest Destiny was driven by a combination of political, economic, and social factors. Politically, the United States sought to extend its influence and strengthen its position in the world. By expanding its territory, the United States aimed to secure its borders, increase its resources, and gain strategic advantages. Economically, expanding westward offered opportunities for trade, agriculture, and the extraction of natural resources. Socially, the idea of Manifest Destiny appealed to the American spirit of adventure, individualism, and the pursuit of economic and personal freedom.
- Political: securing borders, increasing influence
- Economic: trade, agriculture, natural resources
- Social: adventure, individualism, freedom
However, the doctrine of Manifest Destiny also had its critics. Some argued that it was a justification for imperialism, expansionism, and the mistreatment of indigenous peoples. Others believed that the United States should focus on internal development and prioritize the well-being of its citizens rather than acquiring more land. Additionally, the doctrine of Manifest Destiny led to conflicts with neighboring countries, such as Mexico, as the United States sought to annex their territories.
In conclusion, the Doctrine of Manifest Destiny was a belief that shaped the expansionist policies of the United States in the 19th century. It was driven by a sense of divine right, political ambition, economic opportunities, and social ideals. While it played a significant role in the westward expansion of the United States, it also led to controversy, criticism, and conflicts. The legacy of Manifest Destiny continues to impact American society and the perception of the nation’s role in the world today.
Manifest Destiny and American Identity
The concept of Manifest Destiny played a crucial role in shaping the American identity during the 19th century. From the early years of the United States, it was believed that the nation had a divine mission to expand its borders and spread its democratic values across the continent. This belief provided a sense of purpose and exceptionalism for Americans, driving them to explore, settle, and conquer new territories.
Manifest Destiny was deeply ingrained in American society, shaping the nation’s politics, economy, and social fabric. It justified the expansionist policies pursued by the government, such as the Louisiana Purchase and the annexation of Texas. The ideology fueled the desire to control new lands, which were abundant in resources and offered opportunities for economic growth. It also fueled conflicts with Native American tribes, as settlers and the government saw their presence as obstacles to the fulfillment of the divine mission.
Furthermore, the concept of Manifest Destiny also influenced the construction of American identity. It fostered a sense of adventure and entrepreneurial spirit, as individuals and families embarked on long and often perilous journeys to settle the western frontier. These pioneers saw themselves as courageous and resilient, embodying the American spirit of exploration and expansion. The hardships they faced, such as harsh climates, Native American resistance, and geographic obstacles, became part of the collective narrative of the nation, reinforcing the image of America as a land of opportunity and progress.
In conclusion, Manifest Destiny was a powerful force that shaped the American identity by providing a sense of purpose, driving expansionist policies, and fostering an adventurous spirit. It contributed to the nation’s growth, but it was also accompanied by conflicts and the displacement of indigenous peoples. Understanding the impact of Manifest Destiny is essential to comprehending the historical roots of American exceptionalism and the complexities of the nation’s past.
Impact on Native American Tribes
The concept of Manifest Destiny had a profound impact on Native American tribes, leading to the displacement and destruction of many indigenous communities. As settlers moved westward, their belief in the right to expand their territory and spread their ideologies often clashed with the rights and existence of Native American tribes already living on the land.
One of the key aspects of Manifest Destiny was the idea of erasing Native American culture and assimilating indigenous peoples into white society. This led to policies such as the Indian Removal Act of 1830, which forcibly relocated tribes from their ancestral lands onto reservations in the west. Additionally, Native American children were often sent to boarding schools with the goal of eradicating their cultural practices and languages.
Another consequence of Manifest Destiny was violence and conflict between settlers and Native American tribes. The westward expansion brought about a wave of conflicts, such as the Creek War and the Seminole Wars, as tribes resisted displacement and attempted to protect their territories. Treaties were often violated or disregarded by the US government, leading to further tensions and violence.
The impact on Native American tribes was not only immediate, but also long-lasting. The loss of ancestral lands, resources, and cultural practices had profound effects on the social, economic, and spiritual well-being of Native American communities. Many tribes experienced devastating population declines, loss of traditional livelihoods, and cultural disintegration.
In conclusion, the doctrine of Manifest Destiny had a devastating impact on Native American tribes. It led to the forced relocation and assimilation of indigenous communities, as well as violent conflicts and the lasting loss of land and culture. It is crucial to acknowledge and address this historical injustice, and work towards healing and recognizing the rights of Native American tribes in the present day.