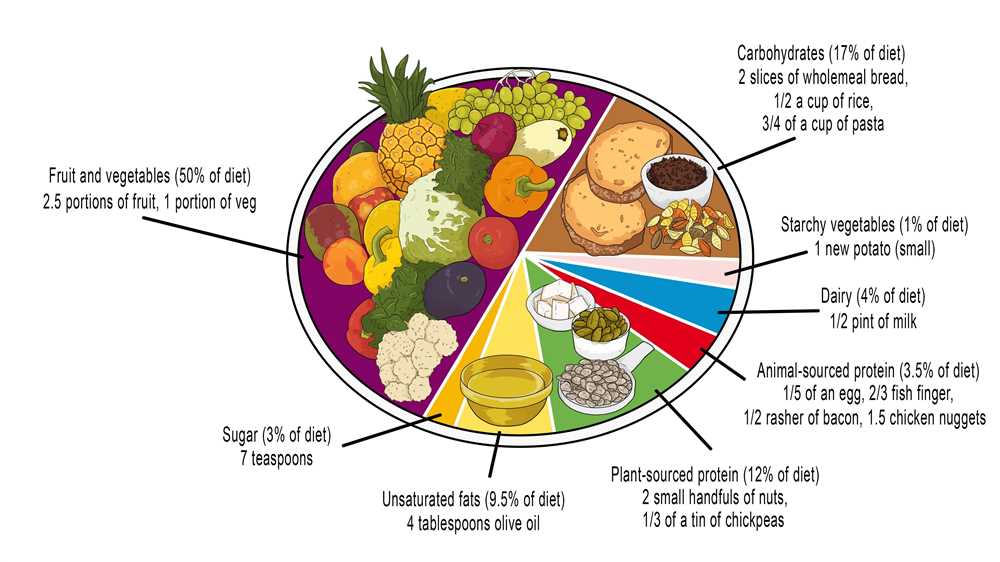
Elephants are recognized as one of the largest land mammals on Earth. They are known for their distinct and impressive size, as well as their unique dietary habits. The question of whether elephants consume carbohydrates has been a topic of interest and debate among scientists and researchers.
A prevailing model suggests that elephants, as herbivores, primarily obtain their energy from consuming plant material. However, recent studies have introduced a different perspective by proposing the possibility of elephants incorporating carbohydrates into their diet. This alternative model challenges the traditional understanding of the elephant’s dietary preferences and offers new insights into their nutritional needs.
Advocates of the carbohydrate inclusion model argue that elephants may consume carbohydrates through their consumption of certain types of plant material, such as fruits and roots. These plant-based sources of carbohydrates can provide elephants with essential energy and nutrients that support their overall well-being. Furthermore, it is suggested that carbohydrates may play a crucial role in elephants’ ability to regulate their metabolism and maintain their energy levels throughout the day.
Understanding the Diet of Model 2 Elephants: The Role of Carbohydrates
In the wild, elephants consume a diverse range of plant material as the main source of their diet. However, when modeling the diet of elephants in captivity, it is important to consider their specific nutritional needs. Model 2 elephants, in particular, require a careful balance of nutrients, including an adequate amount of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy for elephants. They are broken down into simple sugars during digestion and absorbed into the bloodstream, where they are utilized to fuel various bodily functions such as movement, reproduction, and growth. For model 2 elephants, carbohydrates form a significant part of their diet, providing the needed energy for their daily activities.
In order to meet the carbohydrate requirements of model 2 elephants, their diet typically consists of a variety of plant-based foods rich in this nutrient. These include grasses, leaves, fruits, and vegetables. Grasses, in particular, are a staple food for elephants as they are high in complex carbohydrates.
It is important to note that elephants have a unique digestive system that allows them to efficiently break down and extract nutrients from fibrous plant material. They have large hindgut fermenters which house a variety of bacteria and other microorganisms responsible for fermenting cellulose. This enables them to access the energy stored in the carbohydrate-rich plant material that is otherwise indigestible for many other animals.
In conclusion, carbohydrates form a vital part of the diet of model 2 elephants. They serve as a primary source of energy and are obtained from a diverse range of plant-based foods. Understanding the role of carbohydrates in the diet of model 2 elephants is essential for providing them with a nutritionally balanced diet that supports their overall health and well-being.
Importance of Carbohydrates in Model 2 Elephant’s Diet
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in the diet of a Model 2 elephant. These majestic creatures require a constant supply of energy to support their large bodies and active lifestyles. Carbohydrates serve as the primary source of fuel for their muscles and provide the necessary energy for daily activities such as walking, running, and foraging.
One of the key reasons carbohydrates are important in an elephant’s diet is their ability to provide quick and easily accessible energy. The body breaks down carbohydrates into glucose, which is then transported to the muscles to be used as energy. Without an adequate intake of carbohydrates, an elephant may experience fatigue and have difficulty performing its daily tasks.
Carbohydrates also contribute to the overall health and well-being of a Model 2 elephant. Fiber, a type of carbohydrate found in plant-based foods, is essential for maintaining a healthy digestive system. It helps regulate bowel movements and prevents constipation. Additionally, a diet rich in complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and fruits, provides essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and immune function.
It is important for caretakers of Model 2 elephants to ensure a balanced and varied diet that includes an adequate amount of carbohydrates. This can be achieved by providing a combination of fibrous plants, such as hay and grasses, along with supplemental sources of carbohydrates like fruits and vegetables. By meeting their carbohydrate needs, caretakers can help support the energy levels, digestion, and overall health of these magnificent creatures.
Types of Carbohydrates Found in Model 2 Elephant’s Diet
Model 2 elephants have a diverse diet that consists of various types of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates provide them with the necessary energy to sustain their large bodies and active lifestyle.
1. Starch: Starch is a complex carbohydrate found in abundance in the diet of model 2 elephants. It is primarily derived from plants such as grains, legumes, and tubers. Starch is broken down into glucose molecules during digestion, which is then used as a source of energy by the elephants. Grains like corn and wheat, as well as root vegetables like potatoes, are rich sources of starch.
2. Cellulose: Cellulose is another type of carbohydrate that forms the structural component of plant cell walls. While cellulose cannot be digested by most animals, model 2 elephants have a specialized digestive system that allows them to break down cellulose with the help of bacteria present in their gut. This allows them to extract the energy stored in cellulose-rich foods such as grasses and other fibrous plant materials.
3. Sugars: Model 2 elephants also consume sugars as part of their carbohydrate intake. Sugars provide a readily available source of energy and are found in fruits, nectars, and some plants. Fruits like bananas and berries are a common source of sugars in the elephant’s diet. The digestion of sugars is relatively simple and enables quick energy release for the elephants.
4. Glycogen: Glycogen is a complex carbohydrate that functions as a storage form of glucose in animals, including model 2 elephants. It is stored in the liver and muscles and can be rapidly broken down into glucose when there is a need for additional energy. Glycogen is mainly obtained from the digestion of carbohydrates in the diet, and it provides a backup source of energy for the elephants during periods of increased activity or limited food availability.
5. Hemicellulose: Hemicellulose is a type of carbohydrate that is similar to cellulose but is more easily broken down by animals. It is a major component of the plant cell wall and is found in foods such as grains, fruits, and vegetables. Hemicellulose provides a source of energy for model 2 elephants and is digested in their specialized digestive system.
In conclusion, model 2 elephants consume a variety of carbohydrates in their diet, including starch, cellulose, sugars, glycogen, and hemicellulose. These carbohydrates provide essential energy for the elephants and are obtained from a wide range of plant-based foods.
Digestion of Carbohydrates in Model 2 Elephant’s System
In Model 2 Elephant’s digestive system, carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy and nutrients. The process of carbohydrate digestion begins in the mouth, where enzymes like amylase break down complex carbohydrates into simpler forms.
Once in the stomach, the carbohydrates are further broken down with the help of gastric acid. From there, the partially digested carbohydrates move into the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption takes place. Here, enzymes like maltase, sucrase, and lactase break down specific types of carbohydrates, such as maltose, sucrose, and lactose, into their individual sugar molecules.
These sugar molecules, including glucose, fructose, and galactose, are then absorbed into the bloodstream through the lining of the small intestine. They are transported to the liver, where they are either stored as glycogen or released into the bloodstream to be used as immediate energy.
It is worth noting that elephants, as herbivores, have a specialized digestive system that allows them to efficiently break down and utilize the carbohydrates found in plant matter. Their large molars and powerful jaws help grind the plant material, increasing the surface area for enzymatic action. Additionally, elephants have a unique fermentation chamber in their digestive tract, known as the cecum, which allows for the breakdown of fibrous carbohydrates by bacteria.
In summary, the digestion of carbohydrates in Model 2 Elephant’s system involves enzymatic breakdown in the mouth, stomach, and small intestine, with absorption and utilization occurring in the liver.
The Role of Carbohydrates in Providing Energy to Model 2 Elephants
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in providing energy to Model 2 elephants. These majestic creatures require a constant and reliable source of energy to sustain their massive size and perform their daily activities. The digestion of carbohydrates in their digestive system enables them to efficiently convert these complex molecules into glucose, which serves as the primary source of fuel for their cells.
One important component of the Model 2 elephant’s diet is cellulose, a type of carbohydrate found in plant cell walls. While they cannot break down cellulose on their own, they rely on the symbiotic relationship with bacteria in their digestive tracts to ferment these carbohydrates and release usable energy. This process of fermentation allows Model 2 elephants to extract essential nutrients and energy from plant material that would otherwise be indigestible to them.
In addition to cellulose, Model 2 elephants also consume other types of carbohydrates, such as starches and sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and grains. These carbohydrates are readily digested and converted into glucose, which is then transported through the bloodstream to provide energy to all cells in the elephant’s body. Glucose is particularly important for fueling the muscles during physical exertion and supporting the metabolic processes necessary for the elephant’s growth, reproduction, and overall well-being.
To ensure optimal energy intake, Model 2 elephants have evolved a specialized digestive system that is efficient in extracting as much energy as possible from carbohydrates. They have a large and complex digestive tract, which allows for prolonged and thorough fermentation of cellulose by the resident bacteria. This, combined with their ability to digest other carbohydrates, enables Model 2 elephants to maintain their energy levels and sustain their impressive size and strength.
In conclusion, carbohydrates, especially cellulose, play a critical role in providing energy to Model 2 elephants. Their unique digestive system allows them to efficiently extract energy from plant material, ensuring their constant supply of fuel for all physiological processes. Without an adequate intake of carbohydrates, these magnificent creatures would struggle to meet their energy demands and maintain their health and vitality.
Optimal Carbohydrate Intake for Model 2 Elephants
Model 2 elephants have unique dietary requirements, including an optimal carbohydrate intake that supports their health and wellbeing. Carbohydrates are essential for energy production and play a crucial role in various physiological processes within an elephant’s body. It is important to understand the optimal carbohydrate intake for model 2 elephants to ensure their nutritional needs are met.
Research suggests that model 2 elephants should consume carbohydrates from a variety of sources, including fruits, vegetables, and grains. These foods provide a range of complex carbohydrates, such as fiber and starch, which are broken down in the digestive system to release glucose for energy. Additionally, consuming carbohydrates from diverse sources ensures a sufficient intake of essential nutrients and vitamins necessary for a model 2 elephant’s overall health.
Furthermore, it is recommended to monitor the quantity of carbohydrates consumed by model 2 elephants. Overconsumption of carbohydrates may lead to weight gain and related health issues. On the other hand, a deficiency in carbohydrates can result in a lack of energy and hinder the elephant’s performance and overall well-being.
An optimal carbohydrate intake for model 2 elephants can be achieved through a balanced diet that includes a variety of carbohydrates from different sources. It is important for elephant caretakers and experts to carefully monitor and adjust the carbohydrate intake based on individual needs and activity levels of model 2 elephants to ensure their optimal health and functioning.
Sources of Carbohydrates in Model 2 Elephant’s Natural Habitat
In the natural habitat of Model 2 elephants, there are several sources of carbohydrates that contribute to their diet. These sources include various plant species that are abundant in the region. Elephants are herbivores, and their diet mainly consists of plant matter, including leaves, fruits, stems, and roots. These plant sources are rich in carbohydrates, which provide elephants with the energy they need to thrive in their environment.
One of the primary sources of carbohydrates in the natural habitat of Model 2 elephants is grass. Grass is readily available and is a staple food for elephants. It is low in fat and high in fiber and carbohydrates, making it an ideal source of energy for these animals. Elephants can consume large quantities of grass in a single day, allowing them to meet their carbohydrate requirements.
In addition to grass, elephants in this habitat also consume a variety of other plant species that are rich in carbohydrates. This includes trees and shrubs, which provide a diverse range of nutrients for the elephants. Many of these plants produce fruits or seeds that are high in carbohydrates and serve as an important food source, especially during certain seasons when grass may be scarce.
Moreover, elephants also feed on the bark and roots of certain trees, which contain significant amounts of carbohydrates. These parts of the plants often provide elephants with valuable nutrients and energy, especially during periods when other food sources are limited. Elephants have large molars and strong jaws that allow them to break down and digest these tougher plant materials effectively.
In conclusion, the natural habitat of Model 2 elephants offers a variety of sources of carbohydrates in the form of grass, trees, shrubs, fruits, seeds, bark, and roots. These plant species provide the necessary energy for elephants to thrive and maintain their active lifestyle. The ability of elephants to consume and digest these carbohydrates-rich plant materials is key to their survival in their natural habitat.