Whether you’re studying to become a nurse or preparing for a Moderate Sedation Exam, having access to well-crafted test questions and answers can greatly enhance your chances of success. Understanding and mastering the principles of moderate sedation is crucial for anyone working in a medical field, as it involves the use of medications to induce a state of relaxation and analgesia during medical procedures.
Our comprehensive collection of moderate sedation test questions and answers covers a variety of topics, from the pharmacology of sedative drugs to the assessment and management of sedated patients. By familiarizing yourself with these questions, you’ll be better equipped to handle real-world scenarios and demonstrate your knowledge on the exam.
In addition to multiple-choice questions, our test bank also includes detailed explanations for each answer, helping you understand the reasoning behind the correct response. This will not only help you in your exam preparation but also provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter, which can be applied in clinical practice.
Moderate Sedation Test Questions and Answers
Are you preparing for a test on moderate sedation? Here are some commonly asked questions and their answers to help you study and be well-prepared.
1. What is moderate sedation?
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is a type of sedation used during medical procedures to help patients relax and feel comfortable. It involves administering medications to induce a depressed level of consciousness while allowing the patient to maintain the ability to respond to verbal commands and physical stimulation.
2. How is moderate sedation administered?
Moderate sedation can be administered through various routes, including intravenous (IV), oral, intramuscular (IM), and inhalation. The choice of administration route depends on the specific procedure, patient’s condition, and healthcare provider’s preference.
3. What are the common medications used for moderate sedation?
The most commonly used medications for moderate sedation are benzodiazepines, such as midazolam and diazepam, and opioids, such as fentanyl. These medications have sedative and analgesic properties, helping to reduce anxiety and pain during the procedure.
4. What are the potential risks and complications of moderate sedation?
Although moderate sedation is generally considered safe, there are some potential risks and complications associated with its use. These include respiratory depression, airway obstruction, hypotension, allergic reactions, and rare instances of cardiac events. It is crucial for healthcare providers administering sedation to monitor patients closely and be prepared to manage any potential complications.
5. What are the guidelines for monitoring patients during moderate sedation?
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) and the American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ASGE) have developed guidelines for monitoring patients during moderate sedation. These guidelines include monitoring essential vital signs such as blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate, as well as evaluating the level of sedation and the patient’s ability to maintain a patent airway.
Remember to consult and study from reputable sources in addition to these questions and answers. Good luck with your test!
What is moderate sedation?
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is a type of anesthesia that is used to relax a patient during medical procedures or surgeries. It is a state between minimal sedation and deep sedation, where the patient is in a calm and relaxed state but is still able to respond to verbal or physical stimulation. This level of sedation is commonly used for procedures that require some level of discomfort or pain, such as dental procedures, endoscopies, or minor surgeries.
In moderate sedation, the patient remains conscious and can communicate with the healthcare provider, but they experience decreased anxiety and pain. The sedatives used for moderate sedation are typically administered orally, intramuscularly, or intravenously. The dosage and type of sedative are carefully chosen to achieve the desired level of sedation while minimizing potential risks and side effects.
During moderate sedation, the patient’s vital signs, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen saturation, are closely monitored to ensure the patient’s safety. An anesthesiologist or a trained healthcare professional is present throughout the procedure to administer the sedative, monitor the patient’s response, and manage any potential complications.
Moderate sedation provides a relaxed and comfortable experience for patients undergoing various medical procedures, allowing them to undergo necessary treatments while minimizing discomfort and anxiety.
Why is moderate sedation used?
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is a type of sedation used in medical and dental procedures to help patients relax and reduce pain or discomfort. It is commonly used for minor surgical procedures, such as dental work, endoscopy, and colonoscopy, as well as for diagnostic procedures, such as MRI scans and cardiac catheterizations.
Moderate sedation is used to:
- Reduce anxiety: Moderate sedation helps to alleviate fear and anxiety related to the procedure, making it easier for patients to undergo necessary medical or dental treatments.
- Relieve pain: By providing a moderate level of sedation, patients are able to experience reduced or minimal pain during the procedure, enhancing their comfort and overall experience.
- Facilitate cooperation: Moderate sedation helps patients remain calm and cooperative during medical or dental procedures, allowing healthcare providers to perform the necessary interventions more effectively.
- Amnesia: In some cases, moderate sedation can induce temporary amnesia, wherein patients may not remember the details of the procedure or any discomfort experienced during the sedation.
- Enhance safety: By keeping patients sedated and relaxed, moderate sedation can contribute to a safer environment for both patients and healthcare providers, minimizing the risk of adverse events or complications.
Overall, moderate sedation is a valuable tool in medical and dental settings, as it helps patients receive necessary treatments without experiencing excessive pain or anxiety. It is important for healthcare providers to carefully monitor patients during sedation to ensure their safety and well-being throughout the procedure.
Who can administer moderate sedation?
In the context of moderate sedation, administration of sedation medications should be performed by licensed healthcare professionals who have received appropriate training and certification in sedation techniques. These professionals include anesthesiologists, nurse anesthetists, and other qualified healthcare providers who have the necessary knowledge and expertise to safely administer and monitor moderate sedation.
Anesthesiologists are medical doctors who specialize in the administration of anesthesia and are specifically trained in the use of sedation medications. They are highly skilled in assessing patients’ medical conditions, managing anesthesia-related complications, and adjusting sedation levels as necessary to ensure patient comfort and safety during procedures.
Nurse anesthetists, on the other hand, are advanced practice registered nurses (APRNs) who have completed additional education and training in anesthesia. They work under the supervision of anesthesiologists or other physicians and have the authority to administer sedation medications, monitor patients, and manage anesthesia care.
In addition to anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists, other qualified healthcare providers such as dentists, oral surgeons, and gastroenterologists may also be trained and certified to administer moderate sedation. These professionals undergo specific training in sedation techniques and must adhere to strict guidelines governing sedation administration to ensure patient safety.
It is important for healthcare facilities and providers to adhere to applicable state and local regulations regarding the administration of sedation. This includes ensuring that the healthcare professionals who administer moderate sedation are properly trained, certified, and have the necessary credentials to safely provide sedation services.
Risks and Complications of Moderate Sedation
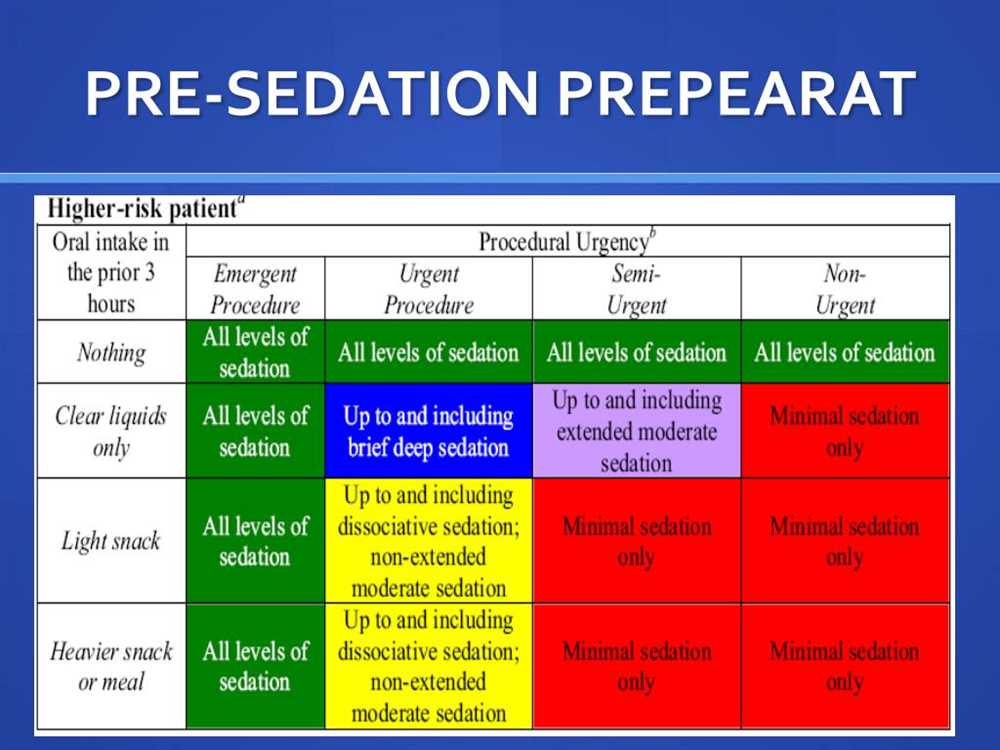
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is commonly used in medical procedures to help patients relax and minimize discomfort. While it is generally safe and effective, there are risks and complications that can arise during or after the administration of moderate sedation.
One of the potential risks is oversedation, which can lead to respiratory depression or even respiratory arrest. This can happen if the dose of the sedative medication is too high or if the patient’s respiratory function is compromised. Continuous monitoring of the patient’s vital signs, including oxygen saturation, heart rate, and blood pressure, is essential to detect any signs of oversedation and intervene promptly if necessary.
Another complication that can occur is an allergic reaction to the sedative medication. Some patients may develop symptoms such as rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing as a result of an allergic response. It is important for healthcare providers to obtain a thorough medical history and perform an allergy assessment before administering any sedative medications to minimize the risk of an allergic reaction.
In rare cases, patients may experience cardiovascular complications during moderate sedation. This can include changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or rhythm. Patients with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions may be at a higher risk for these complications. Close monitoring of cardiac function and appropriate interventions, such as administration of vasopressor medications or fluid resuscitation, may be necessary in such cases.
Other potential risks and complications include nausea, vomiting, headache, and prolonged recovery time. It is important for healthcare providers to educate patients about these potential side effects and provide appropriate post-procedure care instructions to minimize their impact.
In conclusion, while moderate sedation is generally a safe and effective technique, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring patients and managing potential risks and complications. By implementing appropriate protocols and interventions, the chances of adverse events can be minimized, ensuring the well-being and safety of patients undergoing moderate sedation.
What medications are commonly used for moderate sedation?
When it comes to moderate sedation, there are several medications that are commonly used to achieve the desired level of sedation and anxiolysis. These medications are carefully selected based on their ability to induce relaxation and reduce anxiety, while ensuring the safety and comfort of the patient.
One of the most commonly used medications for moderate sedation is midazolam, a benzodiazepine with sedative, anxiolytic, and amnesic properties. Midazolam is preferred for its rapid onset of action and short duration of effect, allowing for better control of the sedation level. It can be administered orally, intranasally, intramuscularly, or intravenously, depending on the patient’s needs and preferences.
In addition to midazolam, opioids such as fentanyl or remifentanil are often used as adjunct medications for moderate sedation. These opioids provide pain relief and enhance the sedative effects of other medications, without causing excessive respiratory depression. They can be administered intravenously or through other routes, depending on the patient’s condition and the procedure being performed.
Other medications commonly used for moderate sedation include propofol, a short-acting intravenous sedative-hypnotic agent, and dexmedetomidine, an alpha-2 adrenergic agonist with sedative and analgesic properties. Both these medications are known for their fast onset and offset of action, allowing for precise titration of sedation levels.
In summary, the medications commonly used for moderate sedation include midazolam, opioids such as fentanyl or remifentanil, propofol, and dexmedetomidine. Each of these medications has its own unique properties and administration routes, allowing healthcare professionals to tailor the sedation approach to the specific needs of the patient.
How is moderate sedation monitored during a procedure?
Moderate sedation, also known as conscious sedation, is a type of anesthesia that is used during certain diagnostic or therapeutic procedures to help patients relax and feel comfortable. While under moderate sedation, patients remain conscious and able to respond to verbal commands, but they may experience decreased anxiety, pain relief, and a possible loss of memory of the procedure.
To ensure the safety and effectiveness of moderate sedation, it is important to carefully monitor the patient throughout the procedure. This involves the use of various monitoring techniques and equipment to assess the patient’s vital signs and level of sedation. These may include:
- Continuous monitoring of blood pressure: Blood pressure is one of the key vital signs that is monitored during a procedure under moderate sedation. It helps to determine the patient’s overall cardiovascular health and the effect of the sedation medication on their blood pressure.
- Continuous monitoring of heart rate and rhythm: By monitoring the patient’s heart rate and rhythm throughout the procedure, healthcare providers can identify any significant changes or abnormalities that may require immediate intervention.
- Pulse oximetry: A pulse oximeter is a non-invasive device that is commonly used to monitor the patient’s oxygen saturation levels during the procedure. It measures the percentage of oxygen in the blood and can alert the healthcare team to any potential respiratory issues.
- End-tidal carbon dioxide monitoring: This type of monitoring involves measuring the carbon dioxide levels in the patient’s exhaled breath. It helps to assess the adequacy of the patient’s ventilation and can detect any potential respiratory problems.
- Capnography: Capnography is a more advanced monitoring technique that provides continuous monitoring of carbon dioxide levels, respiratory rate, and waveform. It can help detect changes in the patient’s breathing patterns and provide immediate feedback on their respiratory status.
- Intraoperative reassessment: Throughout the procedure, healthcare providers will periodically assess the patient’s level of consciousness, pain levels, and response to stimuli. This helps to ensure that the sedation is effective and the patient is comfortable.
By continuously monitoring the patient’s vital signs and level of sedation during a procedure under moderate sedation, healthcare providers can promptly identify and manage any potential complications to ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.