
In the world of chemistry, naming molecular compounds is a crucial skill that helps scientists communicate and understand the properties of various substances. Molecular compounds are formed when atoms of different elements come together and share electrons to form bonds. Having a solid understanding of how to name these compounds is essential for studying and researching different chemical reactions and reactions.
One way to practice and test your knowledge of naming molecular compounds is through a worksheet. A naming molecular compounds worksheet provides a series of questions and prompts for you to identify and name different compounds based on their chemical formulas. These worksheets often include both simple and complex compounds, allowing you to challenge yourself and strengthen your skills.
Answering a naming molecular compounds worksheet requires a good understanding of the rules and conventions for naming compounds. These rules involve identifying the different elements present in the compound, determining their oxidation states, and using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound. The answers to the worksheet will provide you with feedback and help you identify any areas where you may need further practice or clarification.
By regularly practicing with a naming molecular compounds worksheet, you can improve your ability to quickly and accurately name different compounds. This skill is particularly important in fields such as organic chemistry, where the ability to identify and name specific molecules is crucial for understanding their reactivity and function. So, whether you are a student studying chemistry or a researcher working in a lab, dedicating time to practicing naming molecular compounds is a valuable way to enhance your chemical knowledge and skills.
Naming Molecular Compounds Worksheet with Answers
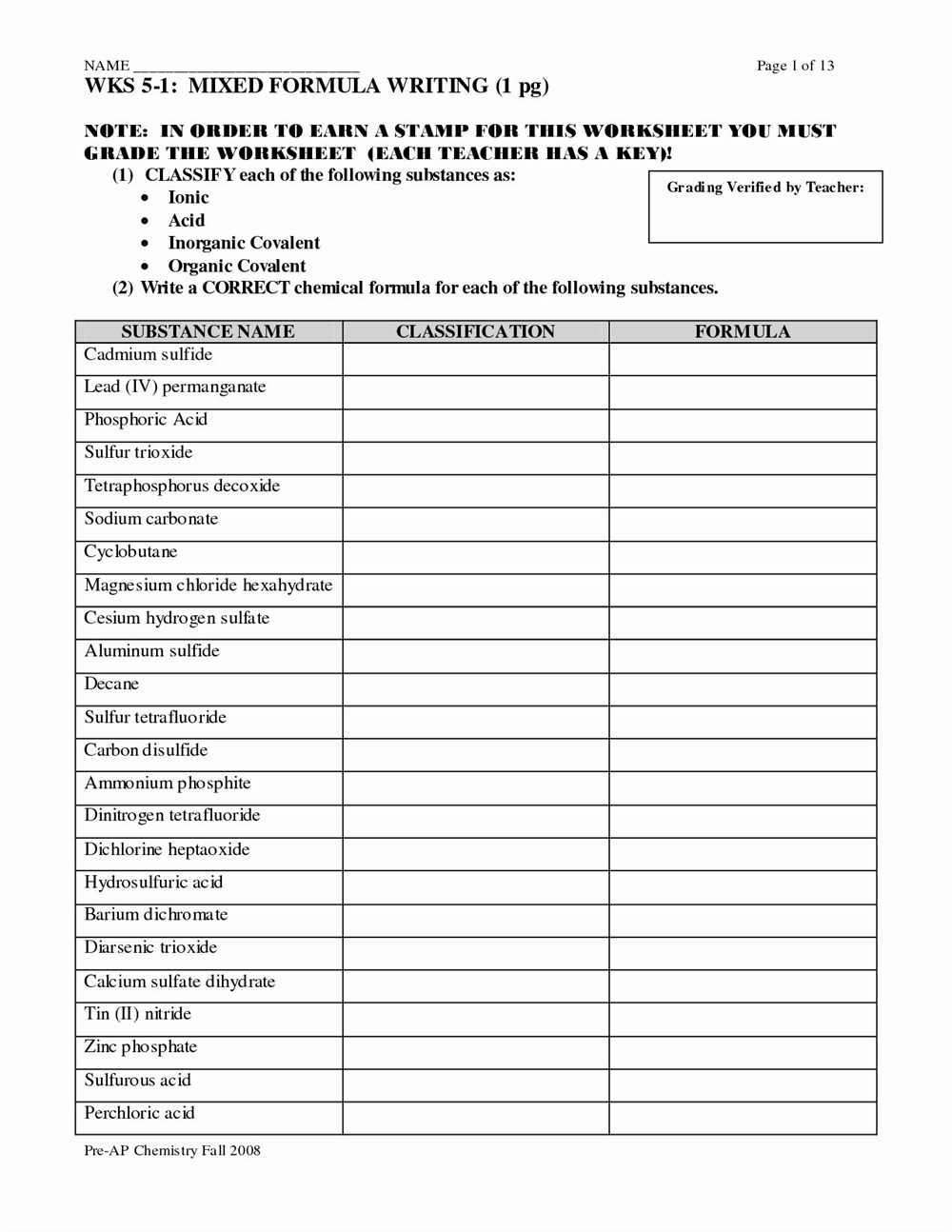
Naming molecular compounds can be a challenging task for students learning chemistry. A naming molecular compounds worksheet with answers can be a useful resource to help students practice and reinforce their understanding of the rules for naming these compounds.
This worksheet typically provides a series of molecular compounds, and students are required to write the correct names for each compound. The answers are usually included at the end of the worksheet, allowing students to check their work and identify any mistakes they may have made.
To successfully complete the worksheet, students need to understand the rules for naming molecular compounds. They need to know how to identify the elements present in a compound and determine the number of atoms of each element. They also need to understand how to use prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element in the compound.
The naming molecular compounds worksheet with answers provides students with an opportunity to practice these skills and reinforce their understanding of the naming conventions. By completing the worksheet and checking their answers, students can identify any areas where they need further review or clarification. This worksheet can also serve as a valuable study tool for upcoming tests or exams.
- Example Question: Write the name for the compound CO2.
- Answer: Carbon dioxide.
In conclusion, a naming molecular compounds worksheet with answers is a valuable resource for students learning chemistry. It allows them to practice and reinforce their understanding of the rules for naming molecular compounds while also providing a tool for self-assessment and review. By using this worksheet, students can improve their proficiency in naming molecular compounds and enhance their overall knowledge of chemistry.
Basics of Molecular Compound Naming

When it comes to naming molecular compounds, there are a few basic rules that need to be followed. These rules are based on the chemical formula and structure of the compound, and they help to ensure that compounds can be easily identified and differentiated from one another.
One of the first things to consider when naming a molecular compound is the type of bonding present. Molecular compounds are made up of nonmetals, and they are held together by covalent bonds. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, which results in the formation of molecules. Understanding the type of bonding present is important because it can help determine the prefixes used in the compound name.
Next, it is important to identify the elements present in the compound and their respective numbers. The element with the lesser electronegativity is typically listed first in the compound name, followed by the element with the greater electronegativity. The names of the elements are specified using their standard chemical symbols. In some cases, it may be necessary to use the name of the element followed by a numerical prefix to indicate the number of atoms present.
Once the elements and their numbers have been identified, the final step is to determine the prefix that corresponds to the number of atoms. These prefixes indicate the number of atoms present and are added to the beginning of the names of the elements. For example, if there are two oxygen atoms present in the compound, the prefix “di-” would be added before the name of oxygen, resulting in the name “dioxide.”
In conclusion, naming molecular compounds involves understanding the type of bonding, identifying the elements and their numbers, and determining the appropriate prefixes. By following these basic rules, it becomes easier to accurately name and differentiate between different molecular compounds.
Naming Molecular Compounds Worksheet
When it comes to naming molecular compounds, it’s important to understand the basic rules and guidelines. This naming system helps chemists identify and communicate the specific compounds they are working with. It involves using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms present in each element within the compound.
The Naming Molecular Compounds Worksheet provides practice for students to apply these rules and learn how to name different compounds correctly. The worksheet typically contains a series of questions, each presenting a different molecular compound. Students are required to analyze the elements present in the compound and use the appropriate prefixes to name it.
The worksheet often includes examples to help students understand the naming process. It may also provide a table of prefixes to reference when naming compounds. Students are encouraged to practice naming compounds with different combinations of elements to reinforce their understanding of the naming rules.
Answering the questions on the worksheet helps students develop their knowledge of molecular compounds and improve their ability to identify and name them correctly. It also enhances their understanding of chemical nomenclature and the use of prefixes to indicate the number of atoms in a compound.
In conclusion, the Naming Molecular Compounds Worksheet is a valuable tool for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of naming molecular compounds. By answering the questions and applying the naming rules, students can develop their skills in chemical nomenclature and improve their ability to communicate effectively within the field of chemistry.
Naming Binary Molecular Compounds
Binary molecular compounds are formed when two nonmetal atoms bond together to share electrons. These compounds are also known as covalent compounds since the bond between the atoms is a covalent bond, meaning that the electrons are shared between the atoms.
When naming binary molecular compounds, the first element in the compound is named first, followed by the second element. The naming rules for binary molecular compounds involve using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present.
The prefixes used to indicate the number of atoms in a binary molecular compound are as follows:
- Mono-: used only when there is one atom of the first element
- Di-: used for two atoms of the first element
- Tri-: used for three atoms of the first element
- Tetra-: used for four atoms of the first element
- Penta-: used for five atoms of the first element
- Hexa-: used for six atoms of the first element
- Hepta-: used for seven atoms of the first element
- Octa-: used for eight atoms of the first element
- Nona-: used for nine atoms of the first element
- Deca-: used for ten atoms of the first element
After indicating the number of atoms with the appropriate prefix, the second element in the compound is named using its elemental name and the suffix “-ide”. For example, if the compound is composed of two oxygen atoms and one carbon atom, it is named carbon dioxide.
In summary, when naming binary molecular compounds, remember to use the appropriate prefixes to indicate the number of atoms and the suffix “-ide” for the second element. By following these naming rules, you can accurately name binary molecular compounds.
Naming Molecular Compounds with Polyatomic Ions
In the world of chemistry, molecules are formed when two or more atoms combine together. These molecules can have different types of atoms, and they can also contain polyatomic ions. Polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that are covalently bonded together and carry a charge. When naming molecular compounds with polyatomic ions, it is important to understand the naming conventions and rules that apply.
1. Naming binary compounds with polyatomic ions:
- When a binary compound contains a polyatomic ion, the positive ion is named first, followed by the name of the polyatomic ion.
- For example, if the compound contains the ammonium ion (NH4+) and the nitrate ion (NO3–), the compound would be named ammonium nitrate.
2. Naming ternary compounds with polyatomic ions:
- Ternary compounds are compounds that contain three different elements, including a polyatomic ion.
- When naming ternary compounds, the name of the positive ion is listed first, followed by the name of the polyatomic ion, and finally the negative ion.
- For example, if the compound contains the calcium ion (Ca2+), the carbonate ion (CO32-), and the hydrogen ion (H+), the compound would be named calcium hydrogencarbonate.
3. Paying attention to the charges:
- When naming molecular compounds with polyatomic ions, it is crucial to consider the charges of the ions.
- The charges must balance out to achieve overall neutrality in the compound.
- If necessary, parentheses are used to indicate the number of each ion needed to balance the charges.
In conclusion, naming molecular compounds with polyatomic ions requires a good understanding of the naming conventions and rules. By correctly identifying the positive and negative ions, considering their charges, and following the specific naming order, one can accurately name these compounds. It is important to practice and familiarize oneself with the common polyatomic ions and their names to master this skill.
Naming Molecular Compounds with Prefixes

In the world of chemistry, molecular compounds are created when two or more nonmetals combine. These compounds are named using prefixes to indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
The prefixes used in naming molecular compounds include:
- Mono-: Used only when there is one atom of the first element in the compound.
- Di-: Used when there are two atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Tri-: Used when there are three atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Tetra-: Used when there are four atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Penta-: Used when there are five atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Hexa-: Used when there are six atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Hepta-: Used when there are seven atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Octa-: Used when there are eight atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Nona-: Used when there are nine atoms of the first element in the compound.
- Deca-: Used when there are ten atoms of the first element in the compound.
After the first element is named using the appropriate prefix, the second element in the compound is named with a prefix indicating the number of atoms of that element, followed by the suffix “-ide”. It is important to note that the prefix “mono-” is not used for the second element.
For example, if we have a compound with one atom of oxygen and two atoms of nitrogen, it would be named “Dinitrogen Monoxide”.
This naming scheme helps chemists accurately and systematically identify and communicate the composition of molecular compounds, allowing for clear understanding and effective communication in the field of chemistry.
Common Mistakes in Naming Molecular Compounds
In the world of chemistry, accurately naming molecular compounds is crucial for clear communication and understanding. However, there are several common mistakes that can be made when trying to name these complex substances. Understanding and avoiding these errors can help ensure accurate and consistent naming practices.
1. Incorrect use of prefixes: One common mistake is using incorrect prefixes when naming molecular compounds. Molecular compounds are composed of two or more nonmetal atoms, and the prefixes indicate the number of each element present in the compound. For example, “mono-” is only used when there is more than one atom of the first element present. Using the wrong prefix can lead to confusion and inaccurate naming.
2. Ignoring charge considerations: Another mistake is not considering the charges of the elements in the compound. Some elements can have multiple charges, and it is important to account for these charges when naming the compound. Failure to do so can lead to incorrect and misleading names.
3. Confusing element names: Mixing up the names of elements is another common error in naming molecular compounds. Each element has a specific name and symbol, and using the wrong name can result in confusion and misunderstanding. It is important to double-check the names of the elements in the compound before naming it.
4. Neglecting to specify the type of compound: For certain molecular compounds, it is necessary to specify the type of compound, such as acid or base. Neglecting to include this information can lead to ambiguity and difficulty in understanding the compound’s properties and characteristics.
In conclusion, accurate naming of molecular compounds is crucial for clear communication and understanding in the field of chemistry. By avoiding common mistakes such as incorrect prefix usage, ignoring charge considerations, confusing element names, and neglecting to specify compound type, chemists can ensure accurate and consistent naming practices.