Nasogastric tube posttest is a method used to assess the effectiveness of using a nasogastric tube in patients. This test is usually performed after the insertion of a nasogastric tube to ensure that it is properly placed and functioning correctly.
The purpose of the nasogastric tube posttest is to evaluate whether the tube is in the correct position, whether it is properly draining gastric contents, and whether the patient is tolerating it well. The test involves checking for signs and symptoms of complications, measuring the drainage output, and assessing the patient’s comfort level.
During the nasogastric tube posttest, healthcare providers will observe the patient for any signs of discomfort or distress, such as abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting. They will also monitor the drainage from the tube to ensure that it is clear and free of blood or other abnormal substances.
Overall, the nasogastric tube posttest is an important step in managing patients with a nasogastric tube. It allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of the tube and ensure the patient’s safety and well-being.
Nasogastric Tube Posttest ATI
The Nasogastric Tube Posttest ATI is a test designed to assess the knowledge and skills of healthcare professionals in the use and care of nasogastric tubes. The test consists of multiple-choice questions that cover various aspects of nasogastric tube placement, insertion, maintenance, and troubleshooting. It is a comprehensive assessment tool that helps healthcare professionals evaluate their understanding of this important procedure.
The test assesses the healthcare professional’s ability to correctly identify the appropriate size and type of nasogastric tube for different patient populations, as well as their knowledge of proper insertion techniques. It also evaluates their understanding of the importance of maintaining proper tube placement and their ability to troubleshoot common issues that may arise during nasogastric tube use.
The Nasogastric Tube Posttest ATI is an important tool for healthcare professionals to ensure that they have the necessary knowledge and skills to safely and effectively use nasogastric tubes. By successfully completing this test, healthcare professionals can demonstrate their competency in this area and provide the highest quality care to their patients.
During the test, healthcare professionals are expected to demonstrate their understanding of the indications and contraindications for nasogastric tube placement, as well as their ability to accurately assess and document tube placement and any associated complications. They should also have a comprehensive understanding of the techniques for administration of medications and enteral feedings through a nasogastric tube.
Overall, the Nasogastric Tube Posttest ATI serves as a valuable tool for healthcare professionals to assess their knowledge and skills in the use and care of nasogastric tubes. By successfully completing this test, healthcare professionals can ensure that they are providing safe and effective care for their patients and are up to date with the latest best practices in this important procedure.
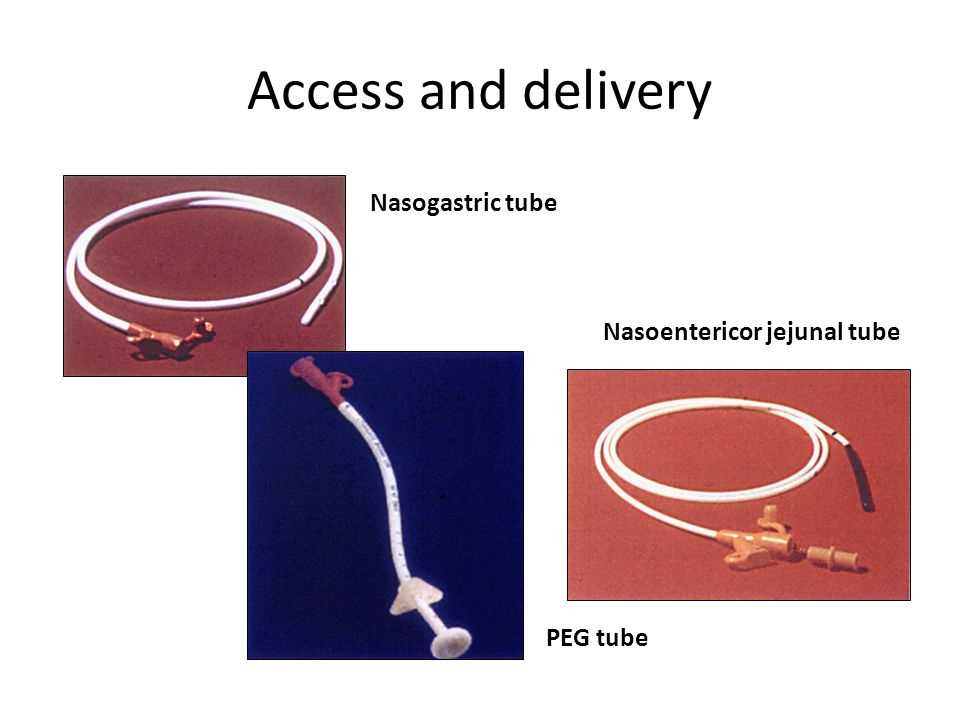
What is a Nasogastric Tube?
A nasogastric tube, also known as an NG tube, is a medical device that is inserted through a patient’s nose and goes down into their stomach. It is commonly used for various medical purposes, including feeding, medication administration, and drainage.
The NG tube is a flexible, hollow tube made of rubber or plastic material. It is usually around 36 inches long and has markings to indicate the depth of insertion. The tube is gently inserted through one nostril and guided down into the patient’s stomach. Once in place, it can be secured with adhesive tape or a specialized tube holder.
The primary purpose of an NG tube is to provide enteral nutrition or feeding for patients who are unable to eat or swallow orally. This can be due to conditions such as dysphagia, oral surgery, or a reduced level of consciousness. The tube allows for the delivery of liquid or crushed food directly into the stomach, ensuring that the patient receives the necessary nutrients.
In addition to feeding, an NG tube can also be used for medication administration. Certain medications, such as those that may irritate the stomach lining, can be given through the NG tube to bypass the oral route. This is particularly useful for patients who are on a temporary or long-term basis and are unable to take medications orally.
Another use of an NG tube is for drainage purposes. If a patient has excessive fluid or air in their stomach or intestines, the tube can be used to remove these substances. This can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications such as bloating, distention, or vomiting. The tube can also be used to empty the stomach before surgery or certain medical procedures.
In summary, a nasogastric tube is a medical device used for feeding, medication administration, and drainage. It is inserted through the nose and into the stomach, providing a safe and efficient way to deliver nutrients, medications, or remove substances when needed.
Purpose of a Nasogastric Tube
A nasogastric tube is a medical device that is used to deliver nutrition, medication, or fluids directly into the stomach. It consists of a long, thin tube that is inserted through the nose and down into the stomach. The primary purpose of a nasogastric tube is to provide essential nutrition and hydration to patients who are unable to eat or drink on their own.
In addition to providing nutrition, a nasogastric tube can also be used to relieve pressure or remove excess fluid or air from the stomach. This can be especially helpful for patients who have undergone abdominal surgery or have gastrointestinal issues such as bloating or distention. The tube can also be used to administer medications, such as painkillers or antibiotics, directly into the stomach, bypassing the digestive system.
When a patient requires a nasogastric tube, it is important for healthcare providers to ensure proper placement and function. The tube should be inserted by a trained professional and verified through an X-ray or pH test to ensure it is correctly positioned in the stomach. Regular assessments and monitoring of the tube’s placement and function should be performed to prevent complications such as aspiration or blockage.
Overall, the purpose of a nasogastric tube is to support the nutritional needs of patients who are unable to eat or drink on their own, as well as to provide relief from gastrointestinal distress and administer medications. Proper placement and monitoring are essential to ensure the tube functions correctly and does not cause any harm to the patient.
Types of Nasogastric Tubes
A nasogastric (NG) tube is a flexible tube that is inserted through the nose and down into the stomach. It is used for various purposes such as feeding, medication administration, decompression of the stomach, and aspiration of gastric contents. There are different types of nasogastric tubes available, each with its own specific characteristics and uses.
1. Levin tube: The Levin tube is a single-lumen tube that is commonly used for gastric decompression. It is made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), which provides flexibility and ease of insertion. The distal end of the tube has multiple side holes to facilitate the removal of gastric contents. The proximal end is typically connected to a suction or collection device.
2. Salem Sump tube: The Salem Sump tube is a double-lumen tube that is used for gastric decompression and aspiration. It consists of an inner lumen for suction and an outer lumen for the venting of air. This design prevents the inner lumen from adhering to the gastric wall and allows for continuous suction without causing trauma. The distal end of the tube has a blue pigtail for the identification of the venting lumen.
- 3. Dobhoff tube: The Dobhoff tube, also known as a weighted feeding tube, is a flexible tube that is used for enteral feeding. It is made of polyurethane and has a weighted tip to facilitate insertion and placement in the small intestine. The distal end of the tube has multiple side holes for the delivery of enteral feedings.
- 4. Miller-Abbott tube: The Miller-Abbott tube is a double-lumen tube that is used for intestinal decompression and suction. It consists of an inflatable balloon at the distal end, which helps to anchor the tube in the small intestine. The proximal end of the tube is typically connected to a suction device. It is commonly used in the treatment of intestinal obstructions.
In conclusion, nasogastric tubes come in various types and are selected based on the specific purpose for which they are used. Careful selection and appropriate insertion techniques are essential to ensure the safe and effective use of these tubes.
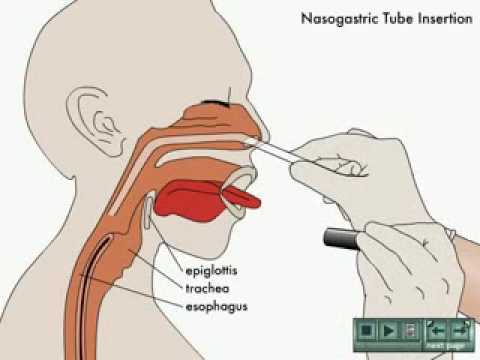
Insertion Procedure for a Nasogastric Tube
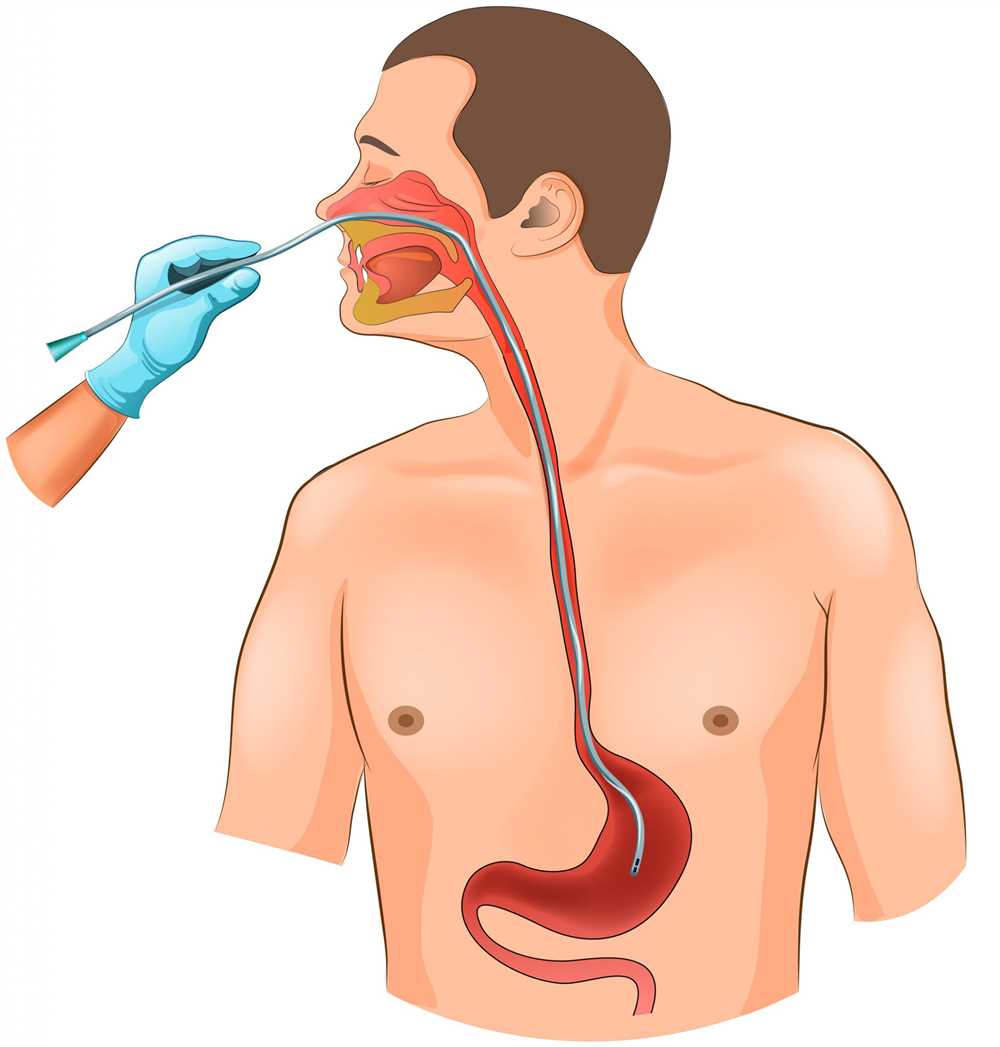
Nasogastric tube insertion is a common procedure performed in healthcare settings to assist with feeding, administration of medication, or removal of gastric contents. The following steps outline the procedure for safely inserting a nasogastric tube:
- Prepare the patient: Explain the procedure to the patient and gain informed consent. Position the patient upright or in a semi-Fowler’s position to facilitate insertion. Ensure that all necessary equipment, including the nasogastric tube, lubricant, and a cup of water, is readily available.
- Gather the necessary supplies: Put on clean gloves and assemble the equipment. Open the packaging of the nasogastric tube and inspect it for any defects or kinks. Lubricate the distal end of the tube with water-soluble lubricant to ease insertion.
- Measure and mark the tube: Measure the length of the tube needed for insertion by extending it from the tip of the patient’s nose to the earlobe and then down to the xiphoid process of the sternum. Mark this length on the tube using adhesive tape or a marker. This step helps ensure that the tube is inserted to the correct depth.
- Assist with tube insertion: Instruct the patient to tilt their head back slightly and guide the tube gently through the nostril. Encourage the patient to sip water or swallow while the tube is being inserted to aid its passage into the esophagus and down to the stomach. Advance the tube gradually, using a rotating motion, until the marked length reaches the patient’s nostril.
- Check tube placement: Connect the nasogastric tube to a syringe filled with air and inject a small amount of air while auscultating the epigastric or left upper quadrant area with a stethoscope. If a gurgling sound is heard, it indicates correct placement in the stomach. Perform a pH test on a sample of gastric contents aspirated from the tube to further confirm placement in the stomach.
- Secure the tube: Once the placement has been verified, secure the tube to the patient’s nose using an adhesive strip or tape. Ensure that it is not too tight, as this could cause discomfort or pressure ulcers. Set up a tube holder to prevent accidental dislodgement.
Following these steps during nasogastric tube insertion can help healthcare providers ensure proper placement and avoid complications. It is essential to monitor the patient closely after the procedure and provide appropriate care and education regarding tube maintenance and potential complications.
Nursing Considerations for a Nasogastric Tube
A nasogastric tube, also known as an NG tube, is a medical device that is inserted through the nose and into the stomach. It is commonly used for various purposes such as feeding, decompression, and administration of medications. As a nurse, there are several important considerations to keep in mind when caring for a patient with a nasogastric tube.
1. Insertion and Placement: It is essential to ensure that the nasogastric tube is inserted correctly and in the proper position. This involves verifying the correct insertion length, securing the tube with tape, and confirming its placement using radiography or pH testing. Incorrect insertion or placement can lead to complications such as aspiration or inadequate delivery of medications or nutrients.
2. Monitoring and Assessment: Regular monitoring and assessment of the nasogastric tube and the patient’s response to tube feeding or other interventions are crucial. This includes observing for signs of infection, such as redness or drainage at the insertion site, assessing bowel sounds and abdominal distension, and monitoring intake and output. Any changes in the patient’s condition should be promptly reported to the healthcare team.
3. Comfort and Safety: Nursing care should focus on ensuring the patient’s comfort and safety related to the nasogastric tube. This includes providing frequent mouth care to alleviate dryness or irritation, maintaining the integrity of the nasogastric tube by avoiding unnecessary manipulation or dislodgement, and ensuring that the patient is correctly positioned to prevent accidental pulling or displacement of the tube.
4. Patient Education: It is important to educate the patient and their family about the purpose of the nasogastric tube, its care, and potential complications. This includes teaching them how to flush or administer medications through the tube, recognizing signs of infection or complications, and providing instructions on proper tube placement and securement. Clear and concise education can empower the patient and promote adherence to the prescribed treatment plan.
5. Collaboration and Communication: Collaboration and effective communication with the healthcare team are essential when caring for a patient with a nasogastric tube. Nurses should collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as dietitians, to ensure proper nutrition and feeding regimen, and communicate changes in the patient’s condition or any concerns related to the nasogastric tube promptly. This facilitates coordinated care and improves patient outcomes.
In summary, nursing considerations for a nasogastric tube include ensuring correct insertion and placement, monitoring and assessing the patient’s response, prioritizing comfort and safety, providing patient education, and fostering collaboration and communication with the healthcare team. By addressing these considerations, nurses can contribute to the safe and effective management of patients with nasogastric tubes.