
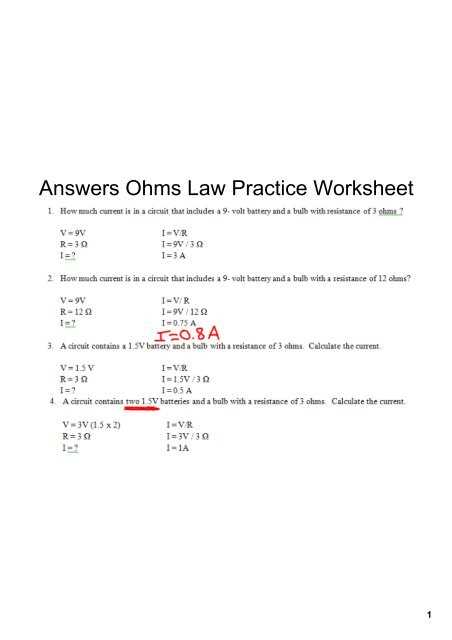
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering and physics that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit. Understanding Ohm’s Law is crucial for anyone working with electronics, as it allows them to calculate and predict the behavior of electrical circuits.
A worksheet on Ohm’s Law is a valuable tool for students and professionals alike to practice applying the principles of Ohm’s Law to solve electrical problems. This worksheet typically contains a series of questions that require the student to calculate the unknown values of voltage, current, or resistance in different electrical circuits.
Having access to the answers to an Ohm’s Law worksheet can be beneficial for students as it allows them to check their work and ensure they have understood the concepts correctly. These answers provide a step-by-step solution to each problem, guiding the student through the process of applying Ohm’s Law and reaching the correct answer.
By reviewing the Ohm’s Law worksheet answers, students can identify any mistakes they may have made and learn from them. They can also gain a better understanding of the different variables and their relationships in an electrical circuit. Additionally, having access to these answers can save time for instructors by eliminating the need to individually check each student’s work.
The Basics of Ohm’s Law

Ohm’s Law is a fundamental principle in electrical engineering and is used to calculate the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electric circuit. The law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor.
In mathematical terms, the equation for Ohm’s Law is given as:
V = I * R
Where V represents the voltage across the two points, I represents the current flowing through the conductor, and R represents the resistance of the conductor.
Ohm’s Law can be understood using the analogy of water flow. Imagine a pipe with water flowing through it. The voltage can be considered as the pressure difference across the two ends of the pipe, the current can be considered as the flow rate of the water, and the resistance can be considered as the size of the pipe. According to Ohm’s Law, if the pressure difference (voltage) increases, the flow rate (current) will also increase, while an increase in the size of the pipe (decrease in resistance) will also result in an increase in flow rate.
To apply Ohm’s Law, one must have knowledge of at least two out of the three variables: voltage, current, and resistance. By rearranging the equation, one can solve for the unknown variable. For example, if the voltage and resistance are known, the current can be calculated by dividing the voltage by the resistance.
- Example calculation: To find the current flowing through a circuit with a voltage of 12V and a resistance of 4Ω:
- Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
- I = 12V / 4Ω = 3A
By understanding Ohm’s Law, engineers and technicians can analyze and design electrical circuits, calculate power requirements, and troubleshoot circuit issues. It serves as a fundamental tool in the field of electrical engineering and plays a crucial role in the understanding and application of electricity.
Understanding Ohm’s Law Equation

Ohm’s Law is a fundamental equation in electrical engineering that relates current, voltage, and resistance. It states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. The equation can be expressed as:
I = V / R
Where:
- I is the current in amperes (A)
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
This equation is a fundamental tool for understanding and analyzing electrical circuits. By manipulating the equation, engineers and electricians can calculate and predict the behavior of electrical systems. It allows them to determine the voltage drop across a resistor, the amount of current flowing through a circuit, or the resistance required to achieve a desired current.
For example, if we know the voltage applied across a circuit and the resistance, we can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the current. Conversely, if we know the current and resistance, we can determine the voltage. This equation is invaluable in troubleshooting electrical problems, designing circuits, and ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical systems.
How to Calculate Voltage using Ohm’s Law

Ohm’s Law is an important equation in electrical engineering that relates the voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. It states that the current passing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage across the conductor and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. This law is expressed mathematically as:
V = I * R
To calculate voltage using Ohm’s Law, you need to know the current flowing through the circuit and the resistance of the conductor. By rearranging the equation, you can solve for voltage:
V = I * R
Where:
- V is the voltage across the conductor (in volts)
- I is the current passing through the conductor (in amperes)
- R is the resistance of the conductor (in ohms)
Let’s say you have a circuit with a current of 2 amps and a resistance of 10 ohms. Using Ohm’s Law, you can calculate the voltage as follows:
V = 2A * 10Ω
V = 20V
Therefore, the voltage across the conductor in this circuit is 20 volts.
How to Calculate Current using Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electrical engineering that relates the current flowing through a circuit to the voltage and resistance. It states that the current (I) flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage (V) applied across it and inversely proportional to the resistance (R) of the conductor. Mathematically, it can be represented as:
I = V/R
To calculate the current flowing through a circuit using Ohm’s Law, you need to know the voltage across the circuit and the resistance of the circuit. Using the equation above, you can rearrange it to solve for current:
I = V/R
where I is the current in amperes (A), V is the voltage in volts (V), and R is the resistance in ohms (Ω).
To calculate the current:
- Determine the voltage across the circuit (V).
- Determine the resistance of the circuit (R).
- Plug the values of V and R into the equation I = V/R.
- Perform the division to calculate the current (I) in amperes (A).
For example, let’s say you have a circuit with a voltage of 12 volts and a resistance of 4 ohms. To calculate the current flowing through the circuit, you can use Ohm’s Law:
| Voltage (V) | Resistance (Ω) | Current (A) |
|---|---|---|
| 12 | 4 | 3 |
Thus, the current flowing through the circuit is 3 amperes (A).
Ohm’s Law is a powerful tool that allows engineers and electricians to analyze and design electrical circuits. By understanding the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance, you can accurately calculate the current flowing through a circuit and make informed decisions about the design, safety, and operation of electrical systems.
How to Calculate Resistance using Ohm’s Law
Ohm’s Law is an essential principle in the study of electrical circuits and is used to calculate the amount of resistance in a circuit. Resistance is a measure of how much a material or component opposes the flow of electric current, and it is measured in ohms (Ω). Understanding how to calculate resistance using Ohm’s Law is fundamental to understanding and analyzing electrical circuits.
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
V = I * R
where V is the voltage across the conductor, I is the current flowing through the conductor, and R is the resistance of the conductor. To calculate the resistance, you can rearrange the formula as:
R = V / I
This formula allows us to calculate the resistance of a conductor when the voltage and current are known. Simply divide the voltage by the current to find the resistance. For example, if the voltage across a conductor is 12 volts and the current flowing through it is 2 amps, the resistance would be:
R = 12V / 2A = 6Ω
If you have a circuit with multiple resistors in series or parallel, you can still use Ohm’s Law to calculate the total resistance. In series circuits, the total resistance is the sum of the individual resistances, while in parallel circuits, the reciprocal of the total resistance is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances. By applying Ohm’s Law to these circuit configurations, you can determine the equivalent resistance.
In summary, calculating resistance using Ohm’s Law is a straightforward process once you understand the basic formula. By knowing the voltage across a conductor and the current flowing through it, you can easily determine the resistance. This knowledge is essential for analyzing and designing electrical circuits.
Ohm’s Law Worksheet Examples
Here are some examples of Ohm’s Law worksheets that can help you practice and understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance:
Example 1:
- In a circuit, the voltage is measured to be 12 volts and the resistance is 4 ohms. Calculate the current flowing through the circuit.
- Solution:
- Using Ohm’s Law formula: I = V / R
- Substituting the given values: I = 12 V / 4 Ω
- Calculating: I = 3 A
- The current flowing through the circuit is 3 amperes.
Example 2:
- A circuit has a current of 2.5 amperes flowing through it and a resistance of 6 ohms. Calculate the voltage across the circuit.
- Solution:
- Using Ohm’s Law formula: V = I * R
- Substituting the given values: V = 2.5 A * 6 Ω
- Calculating: V = 15 V
- The voltage across the circuit is 15 volts.
Example 3:
- A circuit has a voltage of 24 volts and a current of 3 amperes. Calculate the resistance in the circuit.
- Solution:
- Using Ohm’s Law formula: R = V / I
- Substituting the given values: R = 24 V / 3 A
- Calculating: R = 8 Ω
- The resistance in the circuit is 8 ohms.
These examples demonstrate how Ohm’s Law can be applied to calculate the voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. By practicing similar problems, you can improve your understanding of the relationship between these electrical quantities.
Worksheet Example 1: Calculating Voltage
In this example, we will practice calculating voltage using Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s Law states that the voltage across a resistor is equal to the current flowing through it multiplied by its resistance.
Given Information:
- Current (I): 2.5 Amps
- Resistance (R): 10 Ohms
Step 1: Identify the Given Values
We have been given the current (I) as 2.5 Amps and the resistance (R) as 10 Ohms.
Step 2: Apply Ohm’s Law
Using the formula V = I * R, we can calculate the voltage:
| Voltage (V) | = | Current (I) | * | Resistance (R) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | = | 2.5 Amps | * | 10 Ohms |
| Voltage (V) | = | 25 Volts |
Step 3: Interpret the Result
The voltage across the resistor is calculated to be 25 Volts.
By following these steps and applying Ohm’s Law, we were able to determine the voltage in this example. Repeat the same process for other given values to practice calculating voltage in different scenarios.
Worksheet Example 2: Calculating Current
In this example, we will calculate the current flowing through a circuit using Ohm’s law. Ohm’s law states that the current (I) in a circuit is equal to the voltage (V) divided by the resistance (R).
Let’s consider a circuit where the voltage is 12 volts and the resistance is 4 ohms. We can calculate the current by dividing the voltage by the resistance:
Step 1: Write down the given values:
Voltage (V) = 12 volts
Resistance (R) = 4 ohms
Step 2: Apply Ohm’s law:
Current (I) = Voltage (V) / Resistance (R)
Step 3: Calculate the current:
Current (I) = 12 volts / 4 ohms = 3 amperes
So, the current flowing through the circuit is 3 amperes. It is important to note that the unit of measurement for current is amperes (A).
This example demonstrates how Ohm’s law can be used to calculate the current in a circuit when the voltage and resistance are known.
Worksheet Example 3: Calculating Resistance
Let’s take a look at a practical example of calculating resistance using Ohm’s Law. This worksheet will help you understand the concept and improve your problem-solving skills in electrical circuits.
Problem Statement:
You have a circuit with a voltage of 12 V and a current of 2 A flowing through it. You need to calculate the resistance of the circuit using Ohm’s Law.
Solution:
- Identify the given values: In this problem, we are given the voltage (V = 12 V) and the current (I = 2 A).
- Apply Ohm’s Law: Ohm’s Law states that resistance (R) is equal to voltage (V) divided by current (I), i.e., R = V / I.
- Substitute the values: Substituting the given values, we have R = 12 V / 2 A = 6 Ω.
- Interpret the result: The resistance of the circuit is 6 ohms.
So, the resistance of the circuit is 6 ohms, which means that for every 1 volt applied to the circuit, a current of 2 amperes will flow through it.
This example illustrates the application of Ohm’s Law to calculate resistance in a simple circuit. By practicing similar problems, you will become more comfortable with solving electrical circuit equations and gain a better understanding of the concepts involved.