
The understanding of chemical bonds is an essential concept in chemistry. Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in a molecule. They are responsible for determining the physical and chemical properties of substances. To help students grasp this fundamental concept, a chemical bonds worksheet is often used. This worksheet provides practice problems and questions for students to solve and helps them reinforce their knowledge and understanding of chemical bonds.
The chemical bonds worksheet answer key is a valuable resource for both teachers and students. It provides the correct answers and explanations for the problems and questions in the worksheet. This answer key allows students to check their work and verify if they have correctly solved the problems. It also helps teachers in assessing students’ understanding of the topic and identifying any misconceptions or areas that need further clarification.
The chemical bonds worksheet answer key covers various types of chemical bonds, such as ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. It includes examples and exercises that require students to identify the type of bond in a given compound or determine the formula and structure of a compound based on its bonding pattern. By practicing these problems, students develop their skills in recognizing different types of chemical bonds and understanding how they are formed.
Overall, the chemical bonds worksheet answer key is a valuable tool in the teaching and learning of chemical bonds. It provides students with the opportunity to practice and reinforce their understanding of this important concept. It also helps teachers in assessing students’ knowledge and guiding their learning process. With the help of the chemical bonds worksheet answer key, students can gain a solid understanding of chemical bonds and their role in the world of chemistry.
Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answer Key: An Overview
Understanding chemical bonds is crucial in the field of chemistry. Chemical bonds form when atoms interact with each other, resulting in the formation of molecules or compounds. The Chemical Bonds Worksheet is designed to test your understanding of the different types of chemical bonds and their properties. In order to fully comprehend the answers on the worksheet, it is important to have a solid understanding of the concepts covered in chemical bonding.
The answer key for the Chemical Bonds Worksheet provides explanations for each question and helps to clarify any misconceptions. It is a valuable resource for students to check their work and ensure they have grasped the concepts correctly. The answer key can also serve as a study guide, allowing students to review the material and reinforce their understanding of chemical bonding.
The answer key covers various topics related to chemical bonds, including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, metallic bonds, and intermolecular forces. It explains the formation, properties, and characteristics of each type of bond, as well as their significance in various chemical reactions. The key also provides examples and diagrams that further illustrate the concepts, making it easier for students to visualize and comprehend the information.
In conclusion, the Chemical Bonds Worksheet Answer Key provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of chemical bonds and their properties. It is an essential tool for students to assess their understanding and reinforce their knowledge of chemical bonding. By studying the answer key and reviewing the explanations, students can improve their comprehension of chemical bonds and apply their knowledge to solve more complex problems in the future.
Understanding Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together within a molecule or compound. They are the result of the interactions between the valence electrons of the atoms involved. Understanding these bonds is crucial in understanding the properties and behaviors of different substances.
There are three main types of chemical bonds: covalent, ionic, and metallic. In a covalent bond, atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. This type of bonding is commonly found in molecules and is responsible for the formation of compounds such as water (H2O) and methane (CH4). Covalent bonds can be polar or nonpolar depending on the electronegativity difference between the atoms involved.
- In an ionic bond, there is a transfer of electrons from one atom to another. This results in the formation of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which are attracted to each other due to electrostatic forces. Ionic bonds are commonly found in compounds such as sodium chloride (NaCl) and calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- In contrast, metallic bonds occur within metals and involve a sea of delocalized electrons. These electrons are free to move throughout the metal lattice, creating a network of positive ions surrounded by a “cloud” of negative charges. This type of bonding contributes to the unique properties of metals, such as their high conductivity and malleability.
In conclusion, understanding chemical bonds is essential in comprehending the nature of substances and their interactions. Whether it is the sharing of electrons in a covalent bond, the transfer of electrons in an ionic bond, or the delocalization of electrons in a metallic bond, these forces play a fundamental role in the formation and stability of compounds.
Types of Chemical Bonds
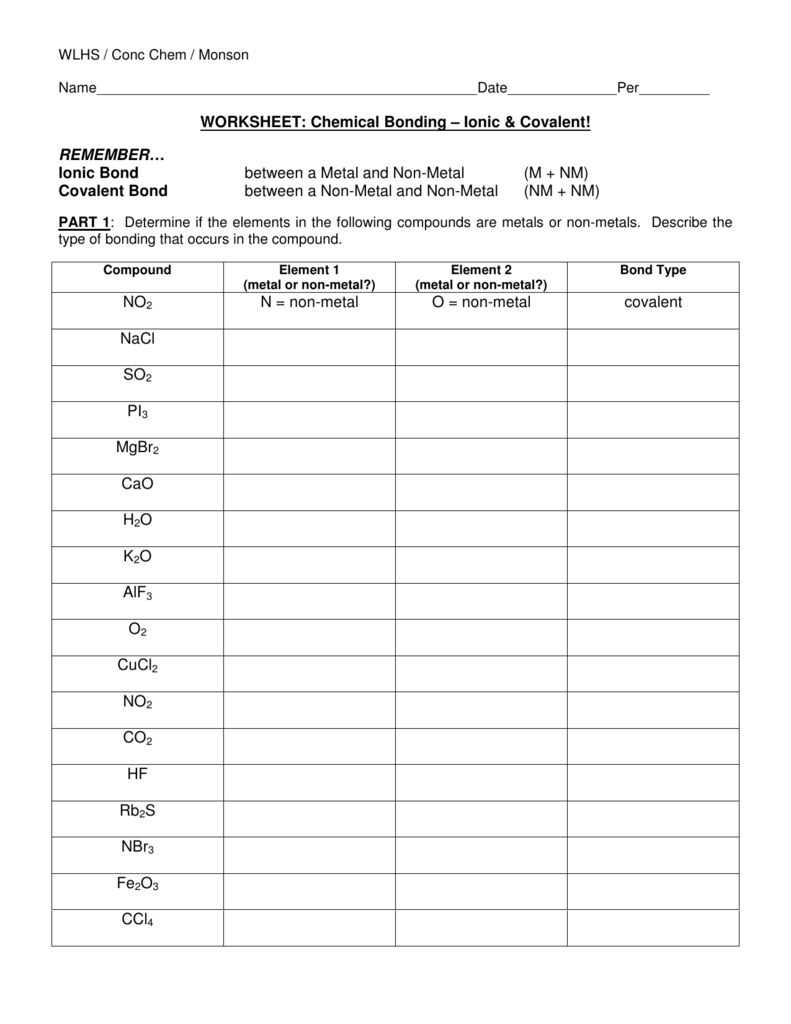
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in a compound. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds.
Ionic Bonds

Ionic bonds form when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another. This creates ions with opposite charges, which attract each other and form a bond. In an ionic bond, one atom becomes a positively charged cation, while the other becomes a negatively charged anion. The attraction between these ions results in a strong bond that holds the compound together.
Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds form when atoms share electrons. Both atoms in a covalent bond contribute one or more electrons to a shared electron pair. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration. Covalent bonds can be further classified as nonpolar or polar, depending on how equally the electrons are shared between the atoms.
Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds occur between metal atoms. In a metallic bond, the outermost electrons of the metal atoms are freely shared among all the atoms in the metal. This creates a “sea” of electrons that are not associated with any specific atom. The delocalized electrons give metals their characteristic properties, such as conductivity and malleability.
Overall, the type of chemical bond that forms between atoms depends on the difference in electronegativity between the atoms. Ionic bonds occur when there is a large difference in electronegativity, covalent bonds occur when there is a moderate difference, and metallic bonds occur when there is a minimal difference. Understanding the different types of chemical bonds is essential for studying and predicting the behavior of compounds in various chemical reactions.
Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key

In the study of chemistry, understanding the concept of ionic bonds is essential. Ionic bonds occur when one atom completely transfers its valence electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of ions with opposite charges. An important tool for learning about ionic bonds is the Ionic Bonds Worksheet. This worksheet provides practice questions and exercises to aid students in understanding the principles and calculations involved in ionic bonding.
The Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key provides students with the solutions to the questions and exercises on the worksheet. It serves as a guide for students to check their work and ensure they have correctly understood the concepts. The answer key assists students in identifying any mistakes they may have made and allows them to correct and learn from them.
The Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key typically includes step-by-step explanations for each question, highlighting the key concepts and calculations required to arrive at the correct answer. It may also include additional information or tips to further help students understand the topic. The answer key is an invaluable resource for self-study and can be used as a reference tool for students to review the material covered.
By providing a clear understanding of the solutions to the ionic bonding questions, the Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key helps students reinforce their knowledge and build confidence in their abilities. It allows them to practice and refine their skills in solving problems related to ionic bonding, an important aspect of chemistry. Overall, the Ionic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key is a valuable tool for both students and teachers in enhancing the learning experience and promoting mastery of the topic.
Covalent Bonds Worksheet Answer Key
When studying chemical bonds, it is important to understand the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. Covalent bonds occur when two or more atoms share electrons, while ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons from one atom to another. This worksheet is designed to help students practice identifying and understanding covalent bonds.
Below is the answer key for the covalent bonds worksheet:
- Question 1: Which of the following compounds has a covalent bond? Answer: Water (H2O).
- Question 2: How many covalent bonds are there in a molecule of methane (CH4)? Answer: Four.
- Question 3: What is the chemical formula for carbon dioxide? Answer: CO2.
- Question 4: True or False: Covalent bonds are formed between metal and non-metal atoms. Answer: False.
- Question 5: Which of the following molecules is polar? Answer: Ammonia (NH3).
By reviewing the answer key, students can check their understanding and correct any misconceptions they may have had while completing the worksheet. This will help reinforce their knowledge of covalent bonding and ensure they are on the right track in their studies.
Overview of Metallic Bonds Worksheet Answer Key
In this worksheet answer key, we will explore the concept of metallic bonds and their characteristics. Metallic bonding occurs between metal atoms and is responsible for the unique properties exhibited by metals, such as conductivity and malleability.
The answer key provides a comprehensive overview of metallic bonding, including its definition and key features. It also includes examples and diagrams to help students visualize the concept and understand how metallic bonds form.
Key Concepts Covered in the Answer Key:
- Definition of Metallic Bond: Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between metal cations and a sea of delocalized electrons.
- Characteristics of Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds are non-directional, meaning that they do not have specific bond lengths or angles. They are also strong and have high melting and boiling points.
- Formation of Metallic Bonds: Metallic bonds form when metal atoms lose their valence electrons to form positive ions, which are surrounded by a sea of delocalized electrons.
- Examples of Metallic Bonds: Examples of metals with metallic bonds include copper, silver, and iron.
- Properties of Metals: Metallic bonding gives metals their unique properties, such as excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, high malleability, and ductility.
The metallic bonds worksheet answer key serves as a useful resource for students to reinforce their understanding of metallic bonding. By providing clear explanations and examples, it helps students grasp the concept and apply it to different scenarios. It also encourages critical thinking and problem-solving skills by including questions that require students to analyze and interpret information related to metallic bonding.
Intermolecular Forces Worksheet Answer Key
Intermolecular forces are the forces of attraction between particles that make up substances. These forces determine the physical properties of substances, such as their boiling points, melting points, and solubility. Understanding intermolecular forces is important in explaining various phenomena, including how substances interact and why certain substances have different properties.
The answer key for the Intermolecular Forces Worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the different types of intermolecular forces and their characteristics. It helps students identify and understand the forces at play in different scenarios. The key covers the three main types of intermolecular forces: London dispersion forces, dipole-dipole forces, and hydrogen bonding.
The answer key provides detailed explanations, examples, and diagrams to help students grasp the concept of intermolecular forces. It includes information on how these forces vary in strength, how they affect molecular polarity, and how they relate to specific compounds and their properties. The key also highlights the importance of intermolecular forces in determining the behavior of substances in different states, such as solid, liquid, and gas.
Understanding intermolecular forces is crucial in fields such as chemistry, physics, and materials science. It enables scientists to predict and explain various phenomena, such as the behavior of substances in different environments, the interaction between molecules, and the formation of different types of compounds. The Intermolecular Forces Worksheet answer key provides students with a solid foundation in this fundamental concept, allowing them to apply their knowledge to a wide range of scientific and practical applications.
Properties of Chemical Bonds
Chemical bonds are the forces that hold atoms together in a molecule or compound. They are formed when electrons are shared, transferred, or attracted between atoms. These bonds determine the physical and chemical properties of substances, as well as their reactivity and stability.
1. Bond Length: The distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms is known as the bond length. It is determined by the size and electronegativity of the atoms involved in the bond. Generally, shorter bond lengths indicate stronger bonds.
2. Bond Energy: Bond energy, also known as bond strength or bond dissociation energy, measures the amount of energy required to break a chemical bond. Bonds with higher bond energy are more stable and require more energy to break.
3. Polarity: Chemical bonds can be classified as polar or nonpolar based on the electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. In polar bonds, electrons are unevenly shared, resulting in a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. Nonpolar bonds have equal sharing of electrons.
4. Bond Angle: The bond angle is the angle formed between two adjacent chemical bonds in a molecule. It depends on the arrangement of atoms around a central atom and affects the molecular shape and properties.
5. Intermolecular Forces: Chemical bonds also influence the interactions between molecules. Intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonding, London dispersion forces, and dipole-dipole interactions, are responsible for the physical properties of substances, such as boiling and melting points.
6. Reactivity: The type and strength of chemical bonds determine the reactivity of substances. Bonds that are easily broken or formed are more reactive. For example, molecules with weak bonds are more likely to undergo chemical reactions.
7. Stability: Chemical bonds contribute to the stability of substances. Strong bonds result in more stable compounds that are less likely to undergo chemical changes. Conversely, weak bonds are more prone to breaking and forming new compounds.
Overall, the properties of chemical bonds are essential in understanding and predicting the behavior of substances, their interactions, and their role in various chemical reactions and processes.