Cardiology is a critical component of paramedic practice, and accurate knowledge and skills in this area can mean the difference between life and death for patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. As a paramedic, it is crucial to have a solid understanding of cardiology principles, diagnostic tests, and treatment modalities to provide effective care in a prehospital setting. To help paramedics assess their knowledge and enhance their clinical practice, the paramedic cardiology practice test offers a comprehensive review of essential concepts.
The paramedic cardiology practice test comprises a series of questions and scenarios that cover various topics related to cardiac anatomy and physiology, rhythm interpretation, and cardiac interventions. By taking this practice test, paramedics can assess their knowledge and identify areas for improvement. The questions are designed to challenge paramedics’ critical thinking skills and help them prepare for real-life situations they may encounter in the field.
The practice test covers a range of cardiac conditions, including acute coronary syndromes (ACS), heart failure, arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. Paramedics will have the opportunity to practice interpreting EKGs, identifying abnormal rhythms, and determining appropriate interventions based on the patient’s condition. This practice test also covers essential pharmacological interventions and emergency procedures for cardiac emergencies.
Whether you are a newly certified paramedic looking to reinforce your cardiology knowledge or an experienced practitioner seeking to enhance your skills, the paramedic cardiology practice test is an invaluable tool. By regularly testing your understanding of essential cardiology concepts, you can consistently improve your clinical judgment and decision-making abilities, ultimately providing better care for your patients.
Overview of Paramedic Cardiology Practice Test
Paramedic cardiology practice tests are designed to assess the knowledge and skills of paramedics in the field of cardiology. These tests are essential for paramedics to ensure they are competent in identifying and managing cardiac emergencies. By passing these tests, paramedics can demonstrate their ability to provide effective care to patients experiencing cardiac-related issues.
Paramedic cardiology practice tests cover various topics, including the anatomy and physiology of the cardiovascular system, electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation, cardiac arrhythmias, and the use of cardiac medications and interventions. They also focus on assessing and managing patients with conditions such as myocardial infarction, heart failure, and cardiac arrest.
Key areas covered in paramedic cardiology practice tests include:
- Understanding the normal cardiac anatomy and physiology
- Identifying different types of cardiac arrhythmias
- Interpreting ECG findings
- Administering appropriate cardiac medications
- Performing advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) protocols
- Managing patients with acute coronary syndromes
- Recognizing signs and symptoms of heart failure
- Responding to cardiac arrest situations
Paramedics can prepare for cardiology practice tests by studying textbooks, attending training courses, and practicing with sample questions and scenarios. It is crucial for paramedics to keep their knowledge and skills up to date in order to provide optimal care for patients with cardiovascular emergencies.
What is a Paramedic Cardiology Practice Test?
A paramedic cardiology practice test is a specialized examination designed to assess the knowledge and skills of paramedics in the field of cardiology. It is an essential tool for evaluating their competency and ensuring that they are prepared to provide effective care to patients experiencing cardiovascular emergencies.
The paramedic cardiology practice test covers various topics related to cardiology, including anatomy and physiology of the cardiovascular system, assessment and recognition of common cardiac conditions, interpretation of electrocardiograms (ECGs), management of cardiac arrest, and administration of appropriate medications. This test plays a crucial role in assessing a paramedic’s ability to effectively respond to cardiac emergencies and make critical decisions in a high-pressure environment.
The paramedic cardiology practice test typically consists of multiple-choice questions that require the paramedic to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-life scenarios. It may also include practical skills assessments, such as performing a proper assessment of a patient with a suspected cardiac condition or demonstrating the correct techniques for administering cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
By successfully completing a paramedic cardiology practice test, paramedics can demonstrate their proficiency in providing advanced cardiovascular care. It helps to ensure that paramedics are equipped with the necessary knowledge and skills to provide lifesaving interventions to patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. This test also serves as a valuable tool for ongoing education and professional development, allowing paramedics to continually improve their cardiology skills and stay up to date with the latest advancements in the field.
Why is it Important for Paramedics to Take Cardiology Practice Tests?
Paramedics are healthcare professionals who provide emergency medical care to patients in critical situations. They are often the first medical responders on the scene and are responsible for making critical decisions regarding patient care. One of the most common and life-threatening emergencies that paramedics encounter is cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks or arrhythmias. In order to effectively manage and treat these cardiac conditions, paramedics must have a strong understanding of cardiology and be able to quickly assess and respond to cardiac emergencies.
Taking cardiology practice tests is essential for paramedics for several reasons. Firstly, these tests help paramedics assess their knowledge and skills in cardiology. By regularly taking practice tests, paramedics can identify areas where they may need further study or improvement. This allows them to focus their efforts on areas of weakness and ensure they are up-to-date with the latest cardiology guidelines and protocols.
- Cardiology practice tests also help paramedics build confidence in their abilities to handle cardiac emergencies. In high-pressure situations, paramedics need to act quickly and decisively. By regularly testing their knowledge and skills, paramedics can develop the confidence needed to make critical decisions and provide appropriate treatments without hesitation.
- In addition, cardiology practice tests help paramedics stay informed about advancements in cardiology. The field of cardiology is constantly evolving, with new research and technologies emerging. By regularly taking practice tests, paramedics can stay up-to-date with the latest advances in the field and ensure they are providing the best possible care to their patients.
- Furthermore, passing cardiology practice tests is often a requirement for paramedics to maintain their certification and licensure. Many certifying bodies and regulatory agencies require paramedics to demonstrate their knowledge and skills in cardiology on a regular basis. By successfully completing these practice tests, paramedics can ensure they meet these requirements and continue practicing as licensed professionals.
In conclusion, taking cardiology practice tests is imperative for paramedics to enhance their knowledge, skills, confidence, and ensure they provide optimal care to patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. These tests allow paramedics to assess their understanding of cardiology, stay up-to-date with advancements in the field, and meet certification requirements. By investing time in practicing and testing their cardiology knowledge, paramedics can make a significant impact on patient outcomes and save lives.
Common Topics Covered in Paramedic Cardiology Practice Tests
Paramedics play a critical role in providing emergency medical care to patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. In order to effectively assess and treat these patients, paramedics must possess a thorough understanding of cardiology principles and practices. As such, paramedic cardiology practice tests often cover a variety of topics related to the cardiovascular system and cardiac emergencies.
One common topic covered in paramedic cardiology practice tests is cardiac anatomy and physiology. Paramedics must have a solid understanding of the structure and function of the heart, as well as how blood flows through the cardiovascular system. This knowledge is essential for accurately assessing and interpreting cardiac rhythms and understanding the underlying causes of cardiac emergencies.
- Cardiac rhythms: Paramedic cardiology practice tests often assess a paramedic’s ability to identify and interpret various cardiac rhythms, including normal sinus rhythm, atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and many others. Paramedics must be able to quickly and accurately identify abnormal rhythms in order to provide appropriate treatment.
- ECG interpretation: Another important topic covered in paramedic cardiology practice tests is electrocardiogram (ECG) interpretation. Paramedics must be able to analyze ECG tracings to identify abnormalities, such as ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and determine the appropriate course of action.
- Cardiac medications: Paramedics must also have a comprehensive knowledge of cardiac medications, their indications, contraindications, and dosages. Paramedic cardiology practice tests often assess a paramedic’s ability to correctly identify and administer medications commonly used in the management of cardiac emergencies, such as nitroglycerin, aspirin, and adenosine.
- CPR and defibrillation: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and defibrillation are essential skills for a paramedic. Paramedic cardiology practice tests often include scenarios where paramedics must demonstrate their ability to effectively perform CPR and use an automated external defibrillator (AED) to deliver a shock when indicated.
In conclusion, paramedic cardiology practice tests cover a range of topics crucial to the effective assessment and treatment of cardiac emergencies. It is essential for paramedics to possess a solid understanding of cardiac anatomy and physiology, as well as the ability to interpret cardiac rhythms, analyze ECG tracings, administer appropriate medications, and perform CPR and defibrillation. By regularly reviewing and practicing these topics, paramedics can enhance their knowledge and skills, ultimately improving patient outcomes in cardiac emergencies.
Understanding Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology
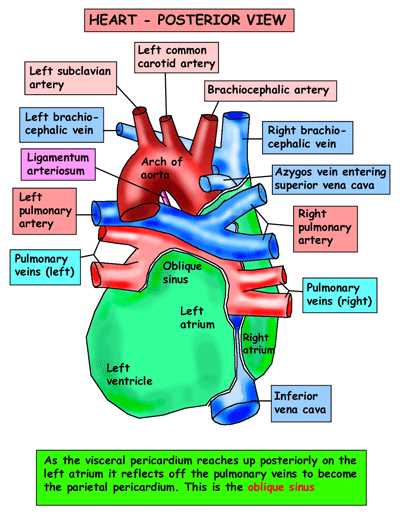
The heart is a complex organ responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. It is located in the thoracic cavity, between the lungs, and is made up of four chambers: the left and right atria, and the left and right ventricles. These chambers are separated by valves that ensure blood flows in the correct direction.
In order to understand cardiac physiology, it is important to understand the flow of blood through the heart. Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium from the body’s tissues and is then pumped into the right ventricle. From there, it is pumped to the lungs to become oxygenated. Oxygenated blood returns to the heart, entering the left atrium and then the left ventricle. The left ventricle pumps the oxygenated blood out to the rest of the body.
Key Terms:
- Atria: The upper chambers of the heart that receive blood.
- Ventricles: The lower chambers of the heart that pump blood.
- Valves: Structures that prevent the backflow of blood.
- Deoxygenated Blood: Blood that is low in oxygen and high in carbon dioxide.
- Oxygenated Blood: Blood that is high in oxygen and low in carbon dioxide.
The heart’s pumping action is regulated by electrical impulses. These impulses are generated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, also known as the heart’s natural pacemaker. The SA node sends electrical signals to the atria, causing them to contract and pump blood into the ventricles. The impulses then pass through the atrioventricular (AV) node, which delays them slightly to allow the ventricles to fill with blood. Finally, the impulses travel down the bundle of His and into the Purkinje fibers, which cause the ventricles to contract and pump blood out of the heart.
Understanding cardiac anatomy and physiology is crucial for paramedics, as they are often the first responders in emergency situations involving the heart. By having a thorough knowledge of the heart’s structure and how it functions, paramedics are better equipped to provide life-saving interventions to patients experiencing cardiac emergencies.
Recognizing Cardiac Arrhythmias and EKG Interpretation
As a paramedic, it is crucial to be able to recognize and interpret cardiac arrhythmias through electrocardiogram (EKG) readings. Cardiac arrhythmias refer to abnormal heart rhythms that can be indicative of underlying heart conditions. By understanding how to interpret EKG readings and recognize different arrhythmias, paramedics can provide appropriate interventions and potentially save lives.
One of the key steps in recognizing cardiac arrhythmias is understanding the normal sinus rhythm, which serves as a baseline for comparison. The normal sinus rhythm is characterized by a regular heart rate, normal P-wave, consistent PR interval, and a normal QRS complex. Deviations from this baseline can indicate various types of arrhythmias.
Some common cardiac arrhythmias include atrial fibrillation, ventricular tachycardia, and atrioventricular block. Atrial fibrillation is characterized by chaotic electrical activity in the atria, leading to an irregular heart rate. Ventricular tachycardia, on the other hand, is a rapid heart rhythm originating from the ventricles. Atrioventricular block refers to a delay or interruption in the electrical conduction between the atria and ventricles.
Interpreting EKG readings involves analyzing different components such as the P-wave, PR interval, QRS complex, and T-wave. The P-wave represents atrial depolarization, while the QRS complex represents ventricular depolarization. The PR interval measures the time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles, and the T-wave represents ventricular repolarization. By analyzing these components and their relationship to each other, paramedics can determine the type of arrhythmia and the appropriate intervention to take.
In summary, recognizing cardiac arrhythmias and interpreting EKG readings is a crucial skill for paramedics. By understanding the normal sinus rhythm and being able to identify deviations from it, paramedics can effectively diagnose and treat different types of arrhythmias. This knowledge is essential in providing timely and appropriate care to patients with cardiac conditions.