
When it comes to choosing their candidates for elections, political parties in the United States employ a variety of methods and processes. One of the most important steps in this process is the parties’ primaries, caucuses, and conventions. These events play a crucial role in determining which candidates will represent the party in the general elections.
Primaries are essentially elections held within a specific party to choose its candidate for an upcoming election. They are open to registered party members, who vote for the candidate they believe best represents their interests and values. Primaries can be either closed, meaning only members of that specific party can participate, or open, allowing any registered voter to cast a ballot.
Caucuses, on the other hand, are local meetings where party members gather to discuss and choose their preferred candidate. These meetings often involve passionate debates and discussions that help shape the party’s platform and direction. Unlike primaries, caucuses require participants to physically attend the meeting and openly voice their support for a candidate.
Finally, conventions are large-scale events where party members from across the country come together to officially nominate their candidate for the general election. Conventions also serve as platforms for party leaders and members to rally their base, outline their party’s agenda, and show unity and support for their chosen candidate. These events are often filled with speeches, endorsements, and other political festivities.
Understanding the processes of parties’ primaries, caucuses, and conventions is essential for anyone interested in American politics. These events determine who will be on the ballot, shape party platforms, and ultimately influence the course of the nation’s political landscape.
Understanding the Electoral Process: Parties, Primaries, Caucuses, and Conventions
The electoral process in the United States is complex and involves several stages, including parties, primaries, caucuses, and conventions. These processes play a vital role in selecting candidates for political office and shaping the country’s political landscape.
Political parties are crucial in the electoral process as they serve as the main vehicle through which candidates run for office. There are two major parties in the United States: the Democratic Party and the Republican Party. Parties develop platforms and mobilize voters to support their candidates.
Primaries are an important part of the electoral process, offering voters the opportunity to choose their preferred candidate within their own party. Primaries can be open or closed, meaning that they either allow all registered voters or only registered party members to participate. Candidates compete in primaries to secure delegates who will represent them at the national convention.
Caucuses are another method used by political parties to select candidates. Unlike primaries, caucuses are party-run meetings where participants discuss and debate the candidates before voting. Caucuses tend to be more time-consuming and involve a higher level of engagement from participants.
Conventions mark the culmination of the electoral process, where delegates from each party gather to officially nominate their candidate for the presidential election. Conventions also serve as a platform to showcase the party’s platform and allow attendees to network and strategize for the upcoming general election.
All of these processes are critical in shaping the electoral landscape and determining who ultimately runs for office. Understanding the role of parties, primaries, caucuses, and conventions helps citizens participate effectively in the democratic process and have a voice in selecting their leaders.
Parties: The foundation of the American political system
Political parties play a vital role in the American political system, serving as the foundation of the democratic process. With their distinct ideologies, platforms, and strategies, parties provide voters with a choice and help to connect citizens with the government. Understanding the functions and operations of political parties is essential for comprehending the complexities of the American political landscape.
Organizing and mobilizing voters: One of the key roles of political parties is to organize and mobilize voters. Parties work to identify potential supporters, register voters, and develop strategies to encourage voter turnout. They engage in various campaign activities, such as door-to-door canvassing, phone banking, and fundraising, to rally support for their candidates. Through these efforts, parties help to ensure that citizens are informed and actively participate in the electoral process.
Developing and promoting policy agendas: Political parties serve as vehicles for developing and promoting policy agendas. Each party has its own set of values and priorities, which are reflected in their platforms. The platform outlines the party’s stance on various issues, from healthcare and education to national security and the economy. By advocating for their policy agendas, parties strive to shape public opinion and influence the policy-making process.
Choosing candidates: Another crucial function of political parties is the selection of candidates for elections. Through primaries, caucuses, and conventions, parties allow their members to participate in the candidate selection process. This internal process helps parties to identify strong candidates who align with their values and have the potential to win elections. By choosing candidates, parties play a significant role in shaping the pool of politicians and leaders who represent their interests and values.
Fostering political discourse and debate: Political parties provide a platform for political discourse and debate. They serve as a space where individuals with diverse perspectives can come together and engage in discussions on various issues. By facilitating these conversations, parties help to shape public opinion, encourage the exchange of ideas, and promote democratic deliberation. Through debates, party platforms, and public campaigns, parties foster dialogue and create opportunities for citizens to participate in the democratic process.
In conclusion, political parties are the foundation of the American political system. They mobilize voters, develop policy agendas, choose candidates, and foster political discourse. Understanding the role of parties is essential for active participation in the democratic process and shaping the future of the country.
What are political parties?
Political parties are organized groups of people who share similar political beliefs and goals. They play a crucial role in the democratic system by representing citizens’ interests and competing for political power. Political parties serve as a bridge between the government and the people, helping to shape public policy and make decisions on behalf of their members and supporters.
Political platforms: Political parties develop political platforms, which are sets of ideas and principles that guide their policies and actions. These platforms can include stances on various issues such as the economy, social issues, foreign policy, and more. They provide a framework for the party’s agenda and serve as a basis for campaigning and attracting voters.
Election support: One of the main roles of political parties is to support candidates during elections. Parties endorse and nominate candidates to run for different political offices, such as president, governor, or mayor. They provide financial and logistical support, campaign strategies, and help mobilize voters to increase the chances of their candidates winning.
Promoting democracy: Political parties help promote democracy by encouraging citizen participation. They provide a way for individuals to express their political views and become involved in the political process. Parties organize events such as primary elections, caucuses, and conventions, where members and supporters can have a direct say in selecting candidates and shaping party platforms.
Countering opposing parties: Political parties often compete with each other, presenting their own ideas and challenging the policies of opposing parties. They engage in debates, campaigns, and public discourse to convince voters of their positions and criticize their opponents. This healthy competition helps ensure a balance of power and prevents any one party from dominating the political landscape.
Overall, political parties are essential components of democratic systems, providing representation, organizing elections, promoting citizen engagement, and offering a platform for political ideologies to be debated and put to the test.
The role of political parties in the electoral process

Political parties play a crucial role in the electoral process of a country. They serve as a key mechanism for organizing and mobilizing voters, as well as shaping public opinion and policy agendas. Parties provide a platform for candidates to run for office, allowing them to articulate their positions on various issues and gain public support. Through party primaries, caucuses, and conventions, parties select their nominees for general elections, ensuring a competitive and democratic process.
One of the main functions of political parties is to facilitate the participation of citizens in the electoral process. They serve as intermediaries between the government and the people, helping to translate the concerns and preferences of citizens into policy decisions. Parties are responsible for recruiting and training candidates, providing them with the necessary resources and support to run effective campaigns. They also play a crucial role in educating voters, disseminating information about candidates and their policy proposals to help voters make informed choices.
Furthermore, political parties contribute to the stability and continuity of the political system. They provide a framework for policy development and implementation, allowing for the peaceful transition of power between different governments. Parties act as a check on the government, holding it accountable for its actions and providing an avenue for citizens to express their grievances. They also facilitate the compromise and consensus-building necessary for the functioning of a democratic society.
In conclusion, political parties play a vital role in the electoral process by organizing and mobilizing voters, selecting candidates, facilitating citizen participation, and ensuring the stability of the political system. They are essential for the functioning of a democratic society, providing a platform for political competition and representation of diverse interests. Without political parties, the electoral process would lack structure, accountability, and the ability to translate the will of the people into policy decisions.
The History and Evolution of Political Parties in the United States
Political parties have played a significant role in shaping the United States’ political landscape since the nation’s founding. The first political parties emerged in the 1790s, with the formation of the Federalist Party and the Democratic-Republican Party. These parties represented differing ideologies and views on key issues such as the role of the federal government, economic policies, and the interpretation of the Constitution.
Over time, the names and ideologies of political parties in the United States have changed, reflecting shifting political dynamics and the evolving priorities of the American electorate. The Democratic-Republican Party eventually split into the Democratic Party and the Whig Party, while the Federalist Party dissolved in the early 1820s. The Whig Party later disbanded, paving the way for the emergence of the modern-day Republican Party in the 1850s. The Democratic Party, on the other hand, has endured as one of the two major political parties in the United States throughout its history.
Throughout the 19th and 20th centuries, new parties would occasionally emerge, challenging the dominance of the two main parties. These third parties, such as the Populist Party and the Progressive Party, often focused on specific issues or represented disenfranchised groups. While they rarely achieved significant electoral success, third parties have influenced political discourse and policy agendas, advocating for important changes such as women’s suffrage and workers’ rights.
Today, the United States operates under a two-party system, with the Democratic Party and the Republican Party as the primary political forces. These parties compete in elections at all levels of government and have significant influence over policy-making and political discourse. However, in recent years, there has been growing interest and support for alternative parties, indicating a potential shift in the American political landscape. The history and evolution of political parties in the United States highlight the dynamic nature of democracy and the ongoing struggle for representation and diverse viewpoints within the country’s political system.
Primaries: The battle within the parties
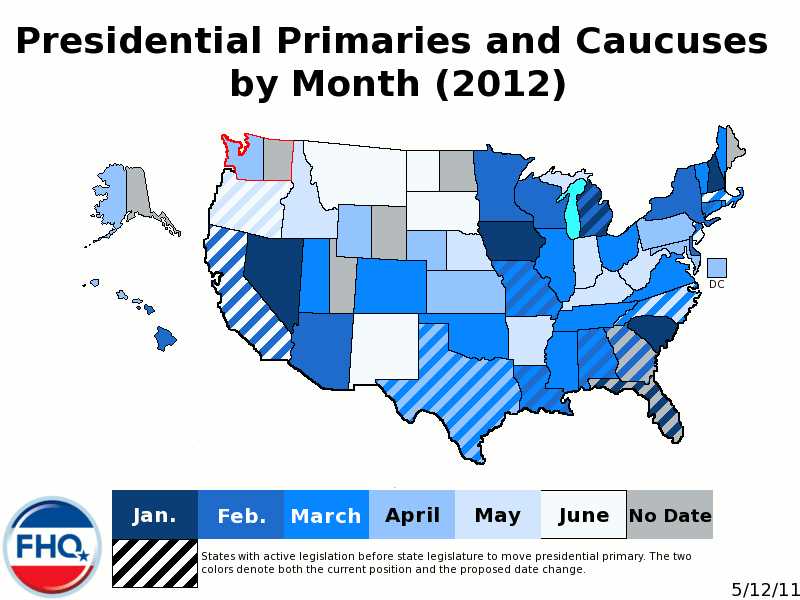
Primaries are an essential part of the American political system, as they allow party members to choose their preferred candidate for the general election. However, primaries are not just about selecting a nominee; they also reflect the internal battles within the parties.
Each party has its own primary process, with different rules and regulations. In the Democratic Party, for example, candidates compete in state-level primaries to earn delegates who will eventually vote for the nominee at the national convention. Likewise, the Republican Party holds primaries and caucuses to determine its candidate. This internal competition can be fierce, as candidates fight for the support of party members and try to distinguish themselves from others.
The primary season is an opportunity for candidates to present their platforms and policies to the party’s base, hoping to gain their support. This often leads to intense campaign rhetoric and aggressive strategies as candidates try to appeal to different factions within their parties. For example, in the Democratic primaries, we often see candidates vying for support from progressive voters, moderate Democrats, and minority communities. Similarly, in the Republican primaries, candidates may target conservative voters, establishment Republicans, or evangelicals, depending on the state and its electorate.
Primaries also reveal the ideological divisions within the parties. In recent years, we have seen a shift towards more progressive policies within the Democratic Party, with candidates like Bernie Sanders advocating for Medicare for All and free college tuition. On the other hand, the Republican Party has seen a rising influence of populism and nationalism, with candidates like Donald Trump appealing to conservative voters with anti-immigration and America-first policies. These ideological battles within the parties can shape the direction and priorities of the eventual nominee and the party as a whole.
In conclusion, primaries are not just a process of selecting a presidential nominee; they also serve as battlegrounds for the internal struggles and ideological debates within the parties. They allow party members to choose their preferred candidate, and through this process, we can observe the diverse factions, policy priorities, and political strategies within the American political landscape.