Pediatric nursing is a specialized field of nursing that focuses on the care of infants, children, and adolescents. It requires specialized knowledge and skills, as children have unique physiological, psychological, and developmental needs. Pediatric nurses play a crucial role in promoting the health and well-being of children, both in hospital settings and in the community.
When preparing for a pediatric nursing exam, it is important to have a solid understanding of the principles and concepts of pediatric nursing. This includes knowledge of growth and development, pediatric assessment, common pediatric illnesses and disorders, and interventions for pediatric patients. The exam assesses your ability to apply this knowledge in various clinical scenarios, making it essential to study and practice critical thinking and clinical reasoning skills.
The first pediatric nursing exam is often considered a landmark in a nursing student’s academic journey. It covers a wide range of topics, including concepts related to child growth and development, nutritional needs, immunizations, communication with children and their families, and ethical considerations in pediatric care. It requires a thorough understanding of pediatric nursing theories and the ability to apply them in real-life situations. Studying for this exam involves reviewing lecture notes, textbooks, and practicing with pediatric nursing questions and case studies.
By thoroughly preparing for the pediatric nursing exam, nursing students can gain the knowledge and confidence necessary to provide safe and effective care to pediatric patients. It is important to utilize various study resources, seek help from professors or mentors, and engage in active learning strategies such as group discussions or simulation exercises. With diligent preparation and a solid understanding of pediatric nursing principles, one can excel in the pediatric nursing exam and embark on a fulfilling career in pediatric nursing.
Pediatric Nursing Exam 1
Pediatric nursing is a specialized field of nursing that focuses on providing healthcare to infants, children, and adolescents. Nurses in this field are trained to address the unique needs and challenges of pediatric patients, including their physical, emotional, and developmental needs. Pediatric nursing exam 1 is an important milestone for nursing students pursuing a career in this field, as it serves as a comprehensive assessment of their knowledge and skills.
The Pediatric nursing exam 1 covers various topics related to the care of pediatric patients, including growth and development, common childhood illnesses, medical and surgical interventions, and family-centered care. It assesses the student’s understanding of pediatric nursing theories, principles, and best practices, as well as their ability to apply this knowledge in clinical settings.
During the Pediatric nursing exam 1, students may be asked to demonstrate their knowledge through multiple-choice questions, case studies, and practical skills assessments. They may also be required to perform calculations related to medication dosages and fluid balance in pediatric patients. The exam is designed to evaluate the student’s critical thinking, clinical reasoning, and ability to make sound nursing judgments in the care of pediatric patients.
Preparing for the Pediatric nursing exam 1 requires a combination of studying foundational pediatric nursing textbooks, attending lectures and clinical rotations, and participating in hands-on skill labs. Students are encouraged to form study groups, utilize online resources, and seek guidance from their instructors to enhance their understanding of the material and improve their chances of success on the exam.
Overview of Pediatric Nursing
Pediatric nursing is a specialized area of nursing that focuses on the care of infants, children, and adolescents. This branch of nursing involves providing comprehensive healthcare services to this specific population, including preventive care, health education, and treatment of acute and chronic illnesses. Pediatric nurses play a crucial role in promoting the growth and development of children, while also supporting their families.
One of the main responsibilities of a pediatric nurse is to assess the physical, emotional, and social needs of their patients. They conduct thorough examinations, collect health histories, and monitor vital signs to identify any deviations from normal growth and development. Through their assessments, pediatric nurses can identify potential health problems and develop individualized care plans to address them.
Pediatric nurses are also responsible for administering medications, providing treatments, and managing various medical devices, such as intravenous lines or feeding tubes. They are trained to provide age-appropriate care to their patients, taking into consideration their unique physical and emotional needs. This includes adapting their communication style, administering medications in a child-friendly manner, and creating a comforting and child-friendly environment.
In addition to providing direct patient care, pediatric nurses also collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as doctors, therapists, and social workers, to ensure the holistic care of their patients. They advocate for their patients’ needs, coordinate care across different healthcare settings, and provide support to families throughout the healthcare journey. Pediatric nurses have a deep understanding of child development and family dynamics, allowing them to effectively communicate and support their patients and their families.
In summary, pediatric nursing is a specialized area that focuses on providing comprehensive healthcare services to infants, children, and adolescents. Through their assessments, care plans, and direct patient care, pediatric nurses play a vital role in promoting the health and well-being of children. Their knowledge and expertise in child development and family dynamics make them valuable healthcare providers in the field of pediatric nursing.
Growth and Development
Understanding growth and development is crucial in pediatric nursing, as it allows nurses to assess and provide appropriate care for children of different ages and developmental stages. Growth refers to the increase in physical size, while development refers to the acquisition of skills and abilities over time. Both growth and development are influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, nutrition, and environmental factors.
During the first year of life, infants undergo rapid growth and development. They triple their birth weight by the age of one and achieve significant milestones such as rolling over, sitting up, and crawling. As they enter toddlerhood, children continue to develop fine motor skills, such as using utensils, and gross motor skills, such as walking and running. Cognitive development also progresses, with toddlers starting to understand simple concepts and develop language skills.
- Physical growth: Physical growth in children involves an increase in height, weight, and head circumference. It is important for nurses to monitor these measurements to ensure that children are growing within normal ranges. Any significant deviations may signal underlying health issues.
- Cognitive development: Cognitive development refers to the ability to think, reason, and understand. It involves the development of memory, attention, problem-solving skills, and language. Nurses can support cognitive development by providing age-appropriate activities and stimulating environments.
- Social and emotional development: Children’s social and emotional development involves the development of relationships, self-awareness, and emotional regulation. Nurses play a vital role in promoting healthy social and emotional development by providing a nurturing and supportive environment.
- Moral development: Moral development involves the development of values, beliefs, and a sense of right and wrong. Nurses can support moral development by teaching children about empathy, kindness, and respect for others.
By understanding the principles of growth and development, pediatric nurses can provide holistic care and support for children at different stages of their lives. They can identify potential developmental delays or concerns and intervene early to promote optimal growth and development.
Common Pediatric Health Issues
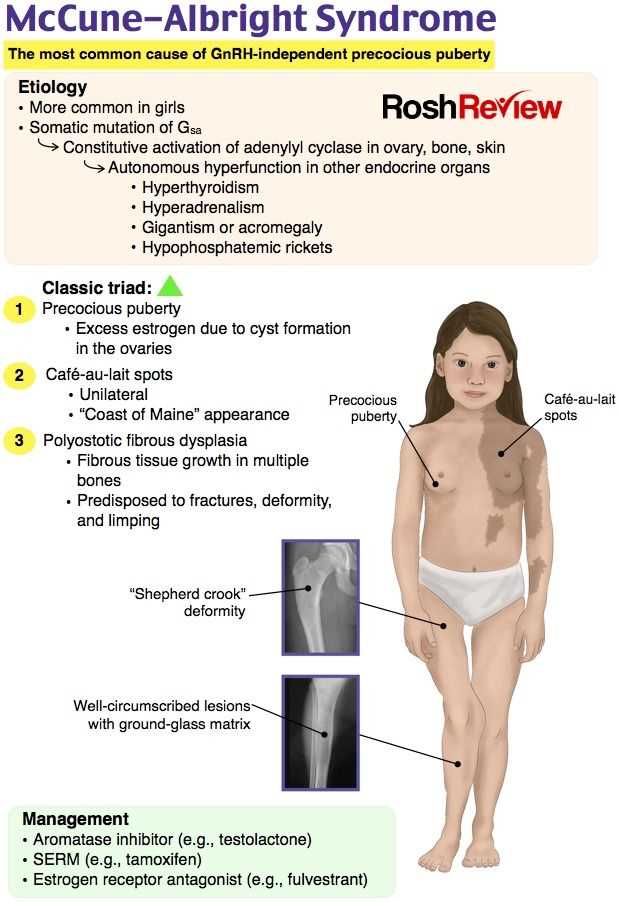
When it comes to pediatric health, there are several common issues that nurses need to be familiar with. This knowledge helps them provide the best care and support for pediatric patients. Some of the commonly encountered pediatric health issues include:
- Respiratory infections: Respiratory infections such as bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and croup are quite common in children. These infections can range from mild to severe and may require various treatments depending on the severity.
- Gastrointestinal disorders: Pediatric patients often experience gastrointestinal disorders like gastroenteritis, appendicitis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). These conditions can cause discomfort, pain, and sometimes require interventions such as medication or surgical procedures.
- Allergies: Allergies, particularly food allergies and allergic rhinitis, are prevalent among pediatric patients. Nurses need to be aware of these allergies and be prepared to help manage them in case of an allergic reaction.
- Ear infections: Ear infections, known as otitis media, are a common issue in children, especially in infants and toddlers. These infections can cause pain and discomfort in the ear and may require antibiotic treatment if severe.
Additionally, other common pediatric health issues include asthma, skin infections, urinary tract infections, and mental health disorders such as attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and anxiety. It is crucial for pediatric nurses to stay updated on the latest research, guidelines, and best practices related to these health issues to provide optimal care to their young patients. By being knowledgeable about common pediatric health issues, nurses can effectively identify symptoms, provide appropriate interventions, and educate parents and caregivers on preventive measures and management strategies.
Pediatric Assessment

The pediatric assessment is a crucial part of nursing care for children. It involves gathering information about the child’s current health status, as well as past medical history and family history, in order to develop an accurate picture of their overall health. This information is important for identifying any potential health issues or developmental concerns, and for developing an appropriate plan of care.
During the pediatric assessment, the nurse will gather information through a variety of methods. This can include interviewing the child and their parents or caregivers, conducting a physical examination, and reviewing any available medical records. The nurse will also assess the child’s growth and development, including their height, weight, and head circumference. This information helps to monitor the child’s overall health and identify any potential issues.
It’s important for the nurse to approach the pediatric assessment with sensitivity and age-appropriate communication techniques. This may involve using toys, games, or storytelling to engage with younger children, or using open-ended questions and active listening techniques to communicate with older children and adolescents. The nurse should also take into account the child’s cultural and social background when conducting the assessment, as this can influence their health beliefs and practices.
The pediatric assessment is an ongoing process that should be conducted at regular intervals to monitor the child’s health and development over time. By gathering accurate and comprehensive information, nurses can make informed decisions about the child’s care and provide appropriate interventions or referrals as needed. Effective pediatric assessments are essential for promoting the health and well-being of children and ensuring they receive the best possible care.
Nursing Interventions in Pediatric Care
Nursing interventions play a crucial role in providing comprehensive and individualized care to pediatric patients. These interventions aim to promote the child’s well-being, prevent complications, and maximize health outcomes. By employing evidence-based practices and a holistic approach, nurses can optimize the care provided to children across various healthcare settings.
One key nursing intervention is the assessment of the child’s physical, emotional, and developmental needs. This involves conducting a thorough health history, performing physical examinations, and using age-appropriate tools to evaluate growth and development. By understanding the child’s unique needs, nurses can create tailored care plans that address any potential issues and promote optimal growth and development.
Nurses play a vital role in implementing and monitoring therapeutic interventions. Administering medication, performing treatments, and monitoring vital signs are just a few examples of interventions nurses provide on a daily basis. It is important for nurses to have a solid understanding of pediatric pharmacology and safe medication administration practices to ensure the child’s safety and efficacy of treatment. Additionally, nurses closely monitor the child’s response to interventions, assess for any adverse reactions, and communicate any changes to the healthcare team.
Nurses also provide education and support to children and their families. This includes teaching parents about proper nutrition, hygiene, and immunizations, as well as facilitating communication between the child and parents. By providing education and support, nurses empower families to actively participate in their child’s care and make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, nurses play a crucial role in advocating for the child’s rights and ensuring their needs are met within the healthcare system.
In summary, nursing interventions in pediatric care are multifaceted and encompass assessing the child’s needs, implementing and monitoring therapeutic interventions, and providing education and support to children and their families. Through these interventions, nurses contribute to promoting the health and well-being of pediatric patients, while also empowering families to actively participate in their child’s care.