
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in the field of chemistry, providing a systematic arrangement of all known elements. With its distinctive layout and unique properties, it serves as a comprehensive reference guide for scientists, students, and enthusiasts alike.
One common question about the periodic table is how it is organized. The table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number, with elements grouped into periods and groups. Each element is represented by a symbol, which consists of one or two letters, often derived from the element’s name. The rows in the table, known as periods, correspond to the number of electron shells an element’s atoms possess. The columns, or groups, indicate the number of valence electrons an element has, which determines its chemical properties.
Another question often asked is why the periodic table is important. The periodic table provides a visual representation of the relationship between elements, allowing scientists to identify patterns and trends in their properties. It serves as a foundation for understanding chemical reactions, as elements with similar properties often behave in predictable ways. Additionally, the periodic table is essential for predicting and synthesizing new elements, as well as for studying the composition of various substances.
When examining the individual elements on the periodic table, questions may arise about their atomic structure and properties. For instance, what determines an element’s atomic mass? An element’s atomic mass is determined by the total number of protons and neutrons in its nucleus. Additionally, questions about an element’s physical and chemical properties, such as its boiling point or reactivity, can be answered by consulting the periodic table.
In conclusion, the periodic table is a vital tool in the field of chemistry, providing a structured arrangement of elements and their properties. Its organization allows scientists to analyze and understand the behavior of elements, predict their reactions, and even discover new elements. By answering common questions about the periodic table, we can enhance our understanding of the building blocks of the universe.
What is the periodic table?

The periodic table is a way of organizing the elements, which are the building blocks of all matter. It is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. The table’s structure allows for the identification and classification of elements based on their properties and relationships with other elements.
The periodic table consists of rows called periods and columns called groups. Each element is represented by its chemical symbol, usually consisting of one or two letters derived from its name. The elements are organized in a way that reflects their atomic structure, with elements in the same period having the same number of electron shells and those in the same group having similar electron configurations.
The periodic table provides valuable information about each element, such as its atomic mass, atomic number, and chemical properties. It also showcases patterns and trends in these properties as you move across the rows and down the columns. The table allows scientists to predict an element’s behavior, understand its reactivity, and determine its potential chemical interactions.
Overall, the periodic table is an essential tool for chemists, physicists, and other scientists, providing a comprehensive overview of the elements and their properties. Its organization and structure have been refined over time, resulting in a vital resource for understanding the fundamental building blocks of the universe.
Understanding the basic structure
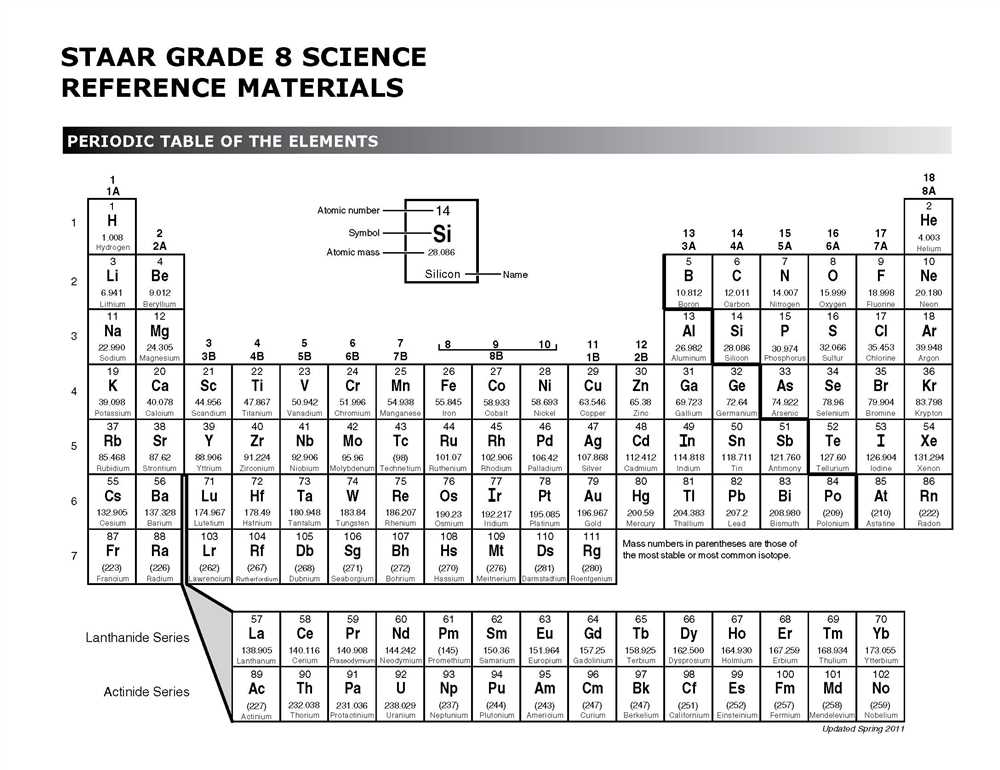
The periodic table is a visual representation of the basic building blocks of matter. It is an organized arrangement of all known elements, which are the fundamental substances that make up everything around us. By understanding the basic structure of the periodic table, we can gain insights into the properties and behaviors of elements, and how they interact with each other.
The periodic table is divided into several key sections:
- Periods: These are the horizontal rows on the periodic table. There are seven periods, denoted by the numbers 1 to 7. Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
- Groups: These are the vertical columns on the periodic table. There are 18 groups, denoted by the numbers 1 to 18 or by specific names. Elements in the same group share similar chemical properties.
- Blocks: The periodic table is also divided into four blocks: s-block, p-block, d-block, and f-block. These blocks represent the different types of orbitals where the outermost electrons of an element are located.
Each element in the periodic table is represented by a unique symbol. This symbol typically consists of one or two letters, derived from the element’s name. The elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, which is the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus.
By studying the periodic table, scientists have been able to identify patterns and trends in element properties. For example, elements on the left side of the periodic table tend to be metals, while elements on the right side tend to be nonmetals. Elements in the same group often have similar reactivity and bonding behavior. These insights into the basic structure of the periodic table have contributed to our understanding of chemistry and the behavior of matter.
Why is the periodic table important?
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry that organizes all the known elements in a systematic manner. It provides a wealth of information about the properties, behaviors, and relationships of different elements, allowing scientists to better understand and study the building blocks of matter.
One of the key reasons why the periodic table is important is that it helps in predicting the chemical behavior of elements. By observing the position of an element in the table, scientists can anticipate its reactivity, valency, and other important characteristics. This information is crucial for designing and synthesizing new compounds, as well as understanding chemical reactions and their underlying mechanisms.
The periodic table also allows scientists to identify patterns and trends in element properties. Elements in the same group or period often exhibit similar properties due to their similar electronic configurations. This knowledge helps in classifying elements and predicting their properties based on their position in the table. It also enables scientists to understand and explain the periodicity of properties like atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity across different elements.
Furthermore, the periodic table is essential for communication and standardization in the field of chemistry. It provides a universal system for labeling and referring to elements, ensuring that scientists worldwide can easily understand and communicate about specific elements or groups of elements. This standardization is crucial for collaborations, research publications, and educational materials, facilitating the exchange of knowledge and advancements in the field of chemistry.
In summary, the periodic table plays a vital role in chemistry by organizing and categorizing elements, predicting their properties, identifying trends, and facilitating communication and standardization in the field. It serves as a powerful tool for scientists to explore the vast world of elements and deepen our understanding of the fundamental principles of chemistry.
Exploring the significance of the periodic table in chemistry
The periodic table is an essential tool in the field of chemistry, serving as a foundation for understanding and organizing the elements. It provides a systematic and comprehensive overview of the elements, their properties, and their relationships with one another.
One of the primary significance of the periodic table is its ability to predict and explain the chemical behavior of elements. By arranging the elements in order of increasing atomic number and grouping them based on similar properties, scientists can make predictions about an element’s reactivity, valence electrons, and even its physical appearance. This predictive power allows chemists to understand the behavior of elements that have not yet been discovered and to design experiments to test hypotheses based on the periodic trends.
The periodic table also helps chemists understand the underlying principles of chemical bonding. By looking at the electron configurations of elements, chemists can determine how atoms interact with one another and form chemical compounds. The arrangement of elements in the periodic table highlights patterns in electron configuration and valence electrons, which are crucial in understanding the formation of chemical bonds and the stability of compounds. This knowledge of bonding allows chemists to design and synthesize new materials with specific properties for various applications.
Furthermore, the periodic table acts as a roadmap for discovering new elements and expanding our understanding of the universe. Gaps in the periodic table indicate elements that have not yet been synthesized or discovered. By studying the trends and patterns in the known elements, scientists can predict the properties of these undiscovered elements and work towards their synthesis. The periodic table serves as a guide for research and exploration, fueling the discovery of new elements and expanding our knowledge of the building blocks of matter.
Overall, the periodic table is a fundamental tool in chemistry that enables scientists to understand and manipulate the behavior of elements. Its significance lies in its ability to organize and predict the properties of the elements, explain chemical bonding, and guide the discovery of new elements. Without the periodic table, the study of chemistry would lack the systematic framework necessary for advancing our understanding of the natural world.
What are elements?
The concept of elements is fundamental to understanding the periodic table. Elements are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. They are the building blocks of matter and are composed of atoms with the same number of protons.
Elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic number, which represents the number of protons in an atom’s nucleus. Each element has a unique atomic number, symbol, and name. The periodic table consists of rows called periods and columns called groups or families.
Atoms are the smallest units of elements and possess unique properties that distinguish one element from another. Atoms consist of a central nucleus, which contains protons and neutrons, surrounded by electrons in energy levels or shells.
The periodic table contains information about each element, such as its atomic number, atomic mass, symbol, and electronic configuration. It also provides valuable information about the properties and characteristics of elements, such as their physical state at room temperature, reactivity, and common uses.
The periodic table is an invaluable tool for scientists, chemists, and students alike, as it helps in understanding the relationships between elements and predicting their properties. It is constantly expanding as new elements are discovered and added to the table.
- The concept of elements is essential for understanding the periodic table.
- Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
- Elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic number.
- Atoms are the smallest units of elements.
- The periodic table contains information about each element’s properties and characteristics.
Defining the building blocks of matter
The periodic table is a visual representation of the building blocks of matter. It organizes all known elements based on their atomic structure and properties. This table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups or families. Each element is represented by its chemical symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass.
Atoms are the smallest units of matter that retain the properties of a particular element. Atoms are composed of three main particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons have a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons have a negative charge. The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number, while the total number of protons and neutrons determines its atomic mass.
Key terms:
- Periods: The rows of the periodic table that represent the number of electron shells an element’s atoms have.
- Groups or families: The columns of the periodic table that share similar chemical properties.
- Chemical symbol: A shorthand representation of an element’s name.
- Atomic number: The number of protons in an atom.
- Atomic mass: The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
The periodic table is an essential tool for chemists and scientists studying the properties of elements and their interactions. It helps in identifying elements, predicting their chemical behavior, and understanding their role in various chemical reactions. By organizing elements based on their atomic structure and properties, the periodic table provides a framework for studying and exploring the world of matter.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
In the periodic table, elements are organized based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and chemical properties. The table is divided into rows called periods and columns called groups. Each element is represented by its atomic symbol, atomic number, and atomic mass.
The periodic table is arranged in such a way that elements with similar properties are placed in the same group. There are a total of 18 groups in the table. The elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons, which determines their chemical reactivity. For example, the elements in Group 1, also known as the alkali metals, have one valence electron and are highly reactive.
The table also shows a recurring pattern of physical and chemical properties as you move from left to right across a period. Elements on the left side of the table are metals, while elements on the right side are non-metals. The transition metals are located in the middle of the table. This arrangement allows for easy comparison and identification of elements based on their properties.
The periodic table also provides valuable information about the structure of atoms. Each row represents a shell of electrons, with the first row (row 1) containing the first shell, the second row (row 2) containing the second shell, and so on. The number of shells increases as you move down the table.
In summary, the periodic table is organized in a systematic manner, allowing scientists to classify and study the properties of elements. It provides a wealth of information about the atomic structure, electron configuration, and chemical behavior of each element.