
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch, also known as Plastic Paradise, is a massive collection of marine debris located in the central North Pacific Ocean. This vast expanse of plastic waste is estimated to be twice the size of Texas and is a cause of great concern for environmentalists and scientists.
The Plastic Paradise Worksheet aims to provide answers to the key questions surrounding this environmental issue. It explores the origins of the garbage patch, the impact it has on marine life, and the efforts being made to clean it up.
One of the main causes of the Plastic Paradise is the improper disposal of plastic waste by humans. Plastics that are not properly recycled or disposed of end up in rivers and oceans, where they are carried by currents and eventually gather in large concentrations. This accumulation of plastic waste poses a significant threat to marine ecosystems and wildlife.
The Plastic Paradise Worksheet provides an insight into the devastating effects of plastic pollution on marine life. It highlights the dangers posed by plastic debris, including entanglement and ingestion. Marine animals, such as birds, turtles, and dolphins, mistake plastic for food and can suffer from internal injuries or even death as a result.
Plastic Paradise: The Great Pacific Garbage Patch Worksheet Answer Key

In the documentary “Plastic Paradise: The Great Pacific Garbage Patch,” the key answers to the worksheet provided important insights into the issue of plastic pollution in the ocean. Students were asked to watch the film and answer questions related to the causes, impact, and potential solutions of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch.
The causes of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch: The worksheet highlighted several key causes of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. One of the primary causes is plastic waste that is improperly disposed of or not recycled. This includes items such as single-use plastic bottles, bags, and packaging materials. Another cause mentioned is the use of plastic microbeads in personal care products, which can easily enter waterways and contribute to the patch’s growth.
The impact of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch: The worksheet emphasized the devastating impact of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch on marine life and ecosystems. It highlighted that marine animals often mistake plastic debris for food, leading to ingestion and entanglement. This can result in injury, suffocation, and even death. The patch also affects the overall health of the ocean and poses a threat to human health, as microplastics can enter the food chain.
Potential solutions to the Great Pacific Garbage Patch:

- Reducing plastic consumption and waste: The worksheet stressed the importance of reducing plastic consumption and waste by using alternatives to single-use plastics, such as reusable bags and bottles. It also emphasized the need for individuals to be conscious consumers and make choices that minimize plastic waste.
- Improving recycling and waste management: The worksheet highlighted the need for effective recycling and waste management systems to ensure that plastic waste is properly disposed of and recycled. It mentioned the importance of recycling programs and the need for individuals, communities, and governments to invest in these solutions.
- Advocating for policy changes: The worksheet encouraged students to take action and advocate for policy changes that address the issue of plastic pollution. This includes supporting and promoting legislation that bans or regulates single-use plastics and encourages the use of sustainable alternatives.
- Supporting research and innovation: The worksheet mentioned the importance of supporting research and innovation in finding solutions to the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. This includes funding scientific studies, investing in technology that can remove plastics from the ocean, and supporting initiatives that promote the development of biodegradable plastics.
The answers provided in the “Plastic Paradise: The Great Pacific Garbage Patch” worksheet shed light on the causes, impact, and potential solutions to this environmental crisis. It emphasized the need for collective action, from individuals to governments, to address plastic pollution and protect our oceans for future generations.
What is the Great Pacific Garbage Patch?
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a vast accumulation of plastic debris floating in the Pacific Ocean. It is located between Hawaii and California and is estimated to be twice the size of Texas, covering an area of approximately 1.6 million square kilometers. The garbage patch consists of various types of plastic waste, including bottles, straws, fishing nets, and microplastics.
The trash in the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is not visible from the surface, as most of the debris is made up of tiny plastic particles. These particles are often less than 5 millimeters in size and are suspended in the water column, making it difficult to clean up. The patch is constantly growing and is fueled by the ocean currents and the disposal of plastics into the ocean.
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch has detrimental effects on marine life and ecosystems. Plastic debris can entangle marine animals, such as sea turtles and seals, causing injury or death. The ingestion of plastic by marine organisms can lead to digestive issues and can disrupt the food chain. Additionally, the chemicals found in plastics can leach into the ocean, posing a threat to the health of marine life.
Efforts are being made to address the issue of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. Clean-up initiatives and awareness campaigns aim to reduce plastic waste and promote recycling. However, solving the problem requires a collective effort, including the reduction of plastic production, improved waste management systems, and the development of biodegradable alternatives to plastic.
How was the Great Pacific Garbage Patch discovered?

In the late 1980s, an oceanographer named Captain Charles Moore accidentally stumbled upon a massive collection of floating debris while sailing through the North Pacific Ocean. He was returning to California from a sailing race in Hawaii when he decided to take a shortcut through an area known as the “Eastern Garbage Patch.” What he encountered shocked him.
As Captain Moore sailed through the waters, he noticed an alarming amount of plastic debris floating on the surface. He observed discarded fishing nets, water bottles, and other plastic items, stretching as far as the eye could see. Intrigued by this alarming sight, Captain Moore decided to devote his time and resources to further studying this phenomenon and raising awareness about the issue.
This accidental discovery marked the beginning of scientific exploration and research into what is now known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch. Over the years, researchers have conducted numerous expeditions to study the size, composition, and environmental impacts of this massive accumulation of plastic waste. The Great Pacific Garbage Patch has since gained widespread attention and has become a symbol of the global plastic pollution crisis.
What causes the formation of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch?
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch is a massive collection of floating plastic debris that has formed in the North Pacific Ocean. It is an alarming environmental issue, and understanding the factors that contribute to its formation is crucial in developing effective solutions. Several key factors are responsible for the creation and growth of this immense garbage patch.
One of the main causes is the sheer volume of plastic waste that is improperly disposed of or not recycled. Every year, millions of tons of plastic end up in the ocean from various sources, including coastal cities, shipping containers, and fishing equipment. The accumulation of this plastic waste, such as bottles, bags, and microplastics, contributes significantly to the formation of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch.
The ocean currents play a vital role in the concentration and movement of the debris. The North Pacific Gyre, a large system of rotating ocean currents, creates a vortex effect that traps and accumulates floating debris in one area. This gyre acts as a circulating system, continuously bringing in new plastic waste and preventing it from dispersing across the ocean. The combination of the gyre’s circular movement and the abundance of plastic pollution contributes to the patch’s formation.
Additionally, the durability of plastic plays a significant role in the persistence of the garbage patch. Unlike organic materials, plastic takes hundreds of years to degrade completely. As a result, the plastic waste that enters the ocean remains present for an extended period, contributing to the growth of the patch over time. The slow degradation of plastic combined with continuous pollution exacerbates the problem and makes it challenging to address.
In summary, the formation of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch is primarily caused by the improper disposal and lack of recycling of plastic waste, the ocean currents’ circulation patterns, and the long-lasting nature of plastic. These factors create a perfect storm for the accumulation and persistence of plastic debris in the North Pacific Ocean, highlighting the urgent need for effective waste management and conservation efforts.
Consequences of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch
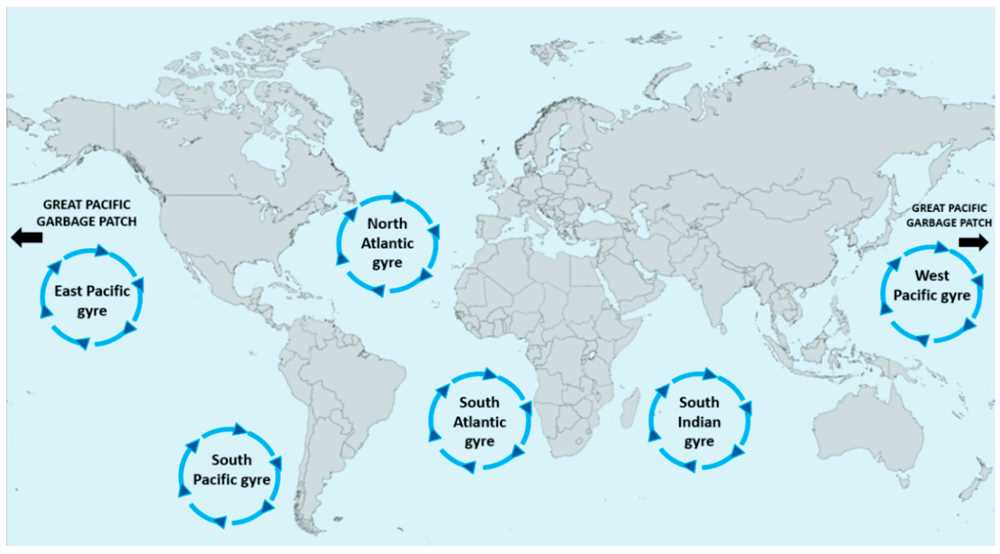
The Great Pacific Garbage Patch, also known as the Pacific Trash Vortex, is a massive collection of floating debris, primarily consisting of plastic, in the North Pacific Ocean. The consequences of this pollution are far-reaching and have serious implications for the environment, marine life, and human health.
Ecosystem disruption: The presence of the Great Pacific Garbage Patch disrupts the delicate balance of marine ecosystems. The floating debris blocks sunlight from reaching the underlying marine plants and organisms, affecting their ability to photosynthesize and grow. This disruption has a cascading effect on the entire food chain, as it impacts the availability of food and habitats for marine animals.
Marine life entanglement and ingestion: The debris in the garbage patch poses a significant threat to marine life. Animals such as sea turtles, seabirds, and marine mammals often mistake plastic pieces for food or become entangled in plastic nets and ropes. This leads to injury, suffocation, and even death. The ingestion of plastic by marine animals can also have long-term negative effects on their reproductive and digestive systems.
Harmful chemical release: Plastic in the ocean gradually breaks down into smaller pieces called microplastics. These microplastics can absorb and release harmful chemicals, such as PCBs and DDTs, which can then enter the marine food web. As these chemicals accumulate in the tissues of marine organisms, they can have toxic effects on both animals and humans who consume contaminated seafood.
Disruption of coastal communities: The pollution caused by the Great Pacific Garbage Patch affects not only marine ecosystems but also coastal communities. Beaches become littered with plastic debris, impacting their aesthetic value and tourism potential. Fishing industries may suffer as plastic entanglement and ingestion affects fish populations, leading to decreased catches and economic losses for fishing communities.
In conclusion, the Great Pacific Garbage Patch has severe consequences for the environment, marine life, and human health. It is crucial to address this issue through increased awareness, improved waste management practices, and the development of sustainable alternatives to plastic to mitigate the long-lasting effects of this harmful pollution.
How does plastic pollution impact marine life?
Plastic pollution has a devastating impact on marine life, causing serious harm and even death to various species that inhabit our oceans. The ocean is home to an incredible array of creatures, including fish, marine mammals, sea turtles, birds, and many others, all of which are affected by plastic pollution in different ways.
One of the most significant impacts of plastic pollution on marine life is ingestion. Many marine animals mistake plastic debris for food and ingest it, leading to obstruction of their digestive systems. This can result in starvation, malnutrition, and a complete disruption of their natural behaviors and lifecycles. Additionally, the toxic chemicals present in plastic can leach into the bodies of marine organisms, causing long-term health issues and even death.
Furthermore, marine animals often become entangled in plastic waste, such as fishing nets and six-pack rings. This entanglement can cause injuries, limb amputations, and suffocation, ultimately leading to death. For example, sea turtles often mistake plastic bags for jellyfish and end up choking on them. Seabirds may get entangled in fishing lines and be unable to fly or feed properly, leading to severe consequences for their survival.
Overall, plastic pollution poses a significant threat to marine life, endangering entire ecosystems and biodiversity. It is crucial for individuals, businesses, and governments to take action to reduce plastic waste and adopt sustainable practices to protect our oceans and the incredible creatures that call them home.
Steps to Reduce Plastic Pollution in the Ocean
Plastic pollution in the ocean has become a major environmental issue, but there are steps that can be taken to reduce its impact. By implementing these measures, we can help protect marine life and preserve the health of our oceans for future generations.
1. Reduce Single-Use Plastics: One of the most effective ways to combat plastic pollution is to reduce the amount of single-use plastics we use in our daily lives. This includes items such as plastic bags, straws, and water bottles. By opting for reusable alternatives, such as cloth bags and metal or glass containers, we can significantly decrease the amount of plastic waste that ends up in the ocean.
2. Recycle Properly: Proper recycling is crucial in preventing plastic waste from entering the ocean. It is important to follow local recycling guidelines and separate plastics from other types of waste. By ensuring that plastics are recycled correctly, we can minimize their environmental impact and promote the reuse of these materials.
3. Support Bans and Regulations: Governments and organizations around the world are taking action to reduce plastic pollution by implementing bans and regulations on single-use plastics. Supporting these initiatives and advocating for stronger regulations can help create a cleaner and healthier ocean environment.
4. Clean-Up Initiatives: Participating in clean-up initiatives, such as beach clean-ups or river clean-ups, can help remove plastic waste from the environment before it reaches the ocean. These initiatives not only help clean up existing pollution but also raise awareness about the issue and educate others about the importance of reducing plastic waste.
5. Education and Awareness: Educating ourselves and others about the impacts of plastic pollution in the ocean is key to driving behavioral change. By spreading awareness about the issue and promoting sustainable alternatives, we can inspire others to take action and reduce their own plastic consumption.