
Population pyramids provide valuable insights into the distribution and composition of a population. They are graphical representations that display the age and sex structure of a population, allowing for a visual analysis of demographic trends. In this article, we will provide answers to common questions related to population pyramids and help you understand how to interpret them.
One key aspect of analyzing population pyramids is understanding the shape and characteristics they exhibit. A pyramid with a wide base and narrowing top indicates a high birth rate and young population, while a pyramid with a narrow base and wider top suggests a low birth rate and an aging population. By analyzing these variations, we can gain insights into the age and sex patterns within a population.
Moreover, population pyramids help us understand the dependency ratio, or the ratio of dependents (typically children and elderly) to the working-age population. A population with a larger proportion of dependents may face challenges in providing adequate healthcare, social security, and economic stability. Therefore, analyzing the dependency ratio using population pyramids is crucial for formulating appropriate policy interventions.
In this article, we will provide detailed answers to questions such as “What does a population pyramid tell us?”, “How do we interpret the dependency ratio?”, and “What are the implications of an aging population?” By understanding the answers to these questions, you will be better equipped to comprehend population pyramids and their significance in demographic analysis and policymaking.
What are Population Pyramids?
A population pyramid is a graphical representation of the age and sex distribution of a population. It shows the number or percentage of people in different age groups, typically grouped by 5-year intervals, and separated by gender. The shape of the population pyramid can provide valuable insights into the demographic characteristics of a population and its future prospects.
Population pyramids consist of a horizontal axis for the age groups and two vertical axes for the number or percentage of people. The left side of the pyramid represents the male population, while the right side represents the female population. The shape of the pyramid can have different patterns, such as a triangular shape, an inverted triangle, or even rectangular.
The shape of a population pyramid reflects the birth rate, death rate, and migration trends of a population. A wide base indicates a large number of young people and a high birth rate. A bulge in the middle suggests a large group of people in their prime working age. A tapering top indicates a decline in the older population and a low life expectancy. These patterns can provide insights into the social and economic challenges that a population might face.
Population pyramids are commonly used by demographers, economists, and policymakers to study and analyze population trends. They help in understanding the age structure, dependency ratio, labor force participation, and potential future changes in population size. By analyzing population pyramids, policymakers can make informed decisions regarding healthcare, retirement planning, education, and social security.
Definition and Purpose

The population pyramids worksheet is a tool used by demographers and statisticians to analyze and visualize the distribution of a population by age and gender. It consists of two bar graphs, one representing the male population and the other representing the female population, with age categories displayed on the horizontal axis and the number or percentage of individuals in each age group shown on the vertical axis.
The main purpose of population pyramids is to provide a visual representation of the age and gender structure of a population, allowing for an in-depth analysis of demographic trends and patterns. By examining the shape and characteristics of the population pyramid, researchers can gain insights into various aspects of a population, such as its growth rate, fertility rate, mortality rate, and overall age distribution.
Age and Gender Distribution: Population pyramids provide a clear visual representation of the distribution of a population by age and gender. The width of each age group bar indicates the proportion of individuals in that age group, while the horizontal separation of the male and female bars allows for a comparison of the gender ratio within each age group.
Demographic Trends: By analyzing the shape and characteristics of the population pyramid, demographers can identify various demographic trends. For example, a pyramid with a wide base indicates a young and growing population, while a pyramid with a narrower base and broader middle section suggests a population with declining birth rates and increasing life expectancy.
Policy and Planning: Population pyramids are valuable tools for policymakers and planners. They provide crucial insights into the age and gender structure of a population, which can inform decisions related to healthcare, education, social security, and other essential services. By understanding the population structure, policymakers can develop targeted interventions and allocate resources effectively.
Forecasting and Projection: Population pyramids can also be used to forecast and project future population trends. By analyzing the demographic patterns, researchers can estimate future changes in population size, age distribution, and other demographic indicators. These projections play a crucial role in long-term planning and policy development.
How to Interpret Population Pyramids
Population pyramids are graphical representations that depict the distribution of a population by age and gender. They provide valuable insights into the demographic characteristics of a population and help in the analysis and understanding of various social, economic, and health-related phenomena.
When interpreting population pyramids, it is important to consider several key factors. Firstly, the shape of the pyramid indicates the population growth or decline. A pyramid with a wide base and narrow top suggests a rapidly growing population, whereas a pyramid with a narrow base and broad top indicates a declining population.
Furthermore, the horizontal axis of the pyramid represents the age groups, typically divided into five-year intervals, while the vertical axis represents the percentage or number of individuals in each age group. This allows for a visual comparison of the distribution across different age groups and provides insights into the age structure of the population.
In addition, the population pyramid allows for the examination of gender differences in different age groups. By comparing the distribution of males and females, it is possible to identify variations in fertility rates, life expectancy, and migration patterns.
Overall, population pyramids are powerful tools for demographic analysis and provide a comprehensive visual representation of a population’s age and gender composition. They enable policymakers, researchers, and individuals to understand population dynamics, plan for future resource allocation, and address social and economic challenges.
Age Distribution
The age distribution of a population refers to the proportion of individuals in different age groups within a given population. It is an important demographic indicator that provides insights into the structure and characteristics of a population.
Age distribution is typically represented through population pyramids, which are graphical representations showing the distribution of age groups by gender. These pyramids are shaped like triangles, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest age groups at the top.
Key phrases: Population pyramids, age groups, graphical representations, demographic indicator, youngest age groups, oldest age groups.
The age distribution of a population is influenced by various factors, including birth rates, death rates, and migration. In countries with high birth rates and limited healthcare resources, the population pyramid may have a wide base, indicating a large proportion of younger individuals. On the other hand, in countries with low birth rates and better healthcare, the population pyramid may have a more rectangular shape, indicating a more even distribution across age groups.
Understanding the age distribution of a population is crucial for policymakers, as it affects various aspects of society, such as healthcare, education, and social security. For example, an aging population with a large proportion of older adults may require increased healthcare services and retirement support. On the other hand, a population with a high proportion of younger individuals may need investments in education and employment opportunities.
Factors Affecting Age Distribution
- Birth rates: Higher birth rates lead to a larger proportion of younger individuals in the population.
- Death rates: Higher death rates, particularly among older adults, can result in a smaller proportion of older age groups.
- Migration: Immigration and emigration can influence the age distribution by introducing younger or older individuals into the population.
- Social and cultural factors: Factors such as family planning, cultural norms, and societal attitudes towards marriage and childbearing can also impact the age distribution.
Overall, analyzing and understanding the age distribution of a population is essential for policymakers and researchers to develop effective policies and programs that cater to the specific needs and characteristics of different age groups within a society.
Gender Distribution
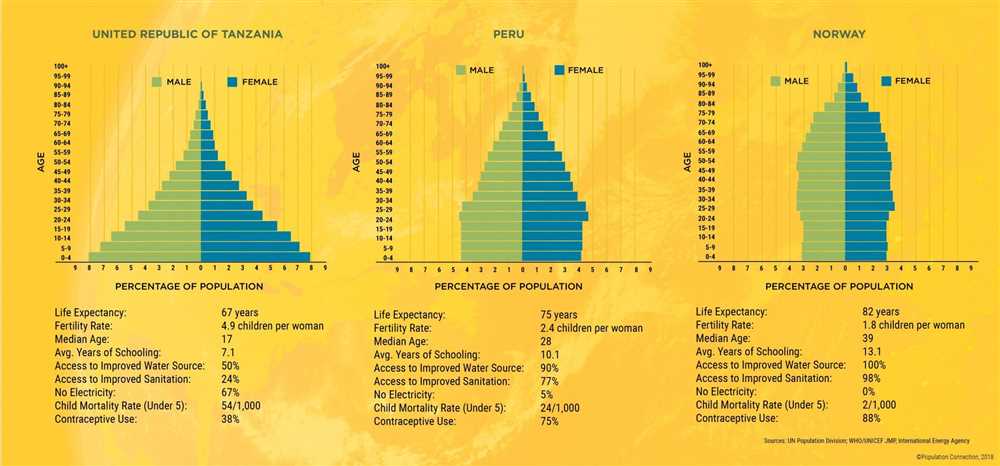
The gender distribution of a population is an important measure that provides insights into the demographic composition of a society. It refers to the distribution of males and females across different age groups within a population, as illustrated in population pyramids. Understanding the gender distribution can reveal patterns and trends in fertility rates, life expectancy, and overall population growth.
Population Pyramids: Population pyramids are graphical representations that show the age and gender distribution of a population. The pyramid shape is created by placing the percentage of population for each age group on either side of a central axis, with males on one side and females on the other. The width of each bar represents the percentage of individuals in that particular age group, while the height of the bar represents the size of the population. By examining the width and shape of the pyramid at different points in time, it is possible to discern changes in the gender distribution and population dynamics.
Key Findings: Analyzing population pyramids can reveal important insights about the gender distribution within a population. For example, a “youth bulge” is often observed in developing countries, where there is a higher proportion of young people compared to older age groups. This can indicate higher birth rates and a potential for future population growth. On the other hand, an inverted pyramid shape with a larger elderly population suggests an aging population, with implications for healthcare, social security, and labor force participation.
- Gender Imbalance: In some regions, there may be a significant gender imbalance due to various factors such as cultural preferences for male children, gender-based discrimination, or migration patterns. These imbalances can have significant social and economic consequences, impacting marriage rates, labor markets, and overall societal stability.
- Gender Equity: Monitoring the gender distribution is also important for assessing progress towards gender equity. By identifying disparities in male and female populations across different age groups, policymakers can develop targeted interventions to address issues such as education, healthcare access, and employment opportunities.
Conclusion: Understanding the gender distribution within a population is essential for effective demographic planning and policymaking. Population pyramids provide visual representations that highlight patterns and trends, allowing for informed decision-making. By analyzing the gender distribution, policymakers can address gender imbalances, promote gender equity, and ensure the overall well-being and sustainability of a population.
Population Growth and Decline

The population of a region or country is constantly changing due to various factors such as birth, death, and migration. Understanding population growth and decline is crucial for governments and policymakers in order to plan for services, resources, and infrastructure.
Population growth occurs when the number of births exceeds the number of deaths. This can lead to an increase in the overall population size and potentially put a strain on resources and infrastructure. The rate of population growth can vary significantly between regions and countries, with some experiencing rapid growth and others experiencing slower growth or even decline.
On the other hand, population decline refers to a decrease in the overall population size. This can occur due to factors such as low birth rates, high death rates, or significant outmigration. Population decline can have significant implications for a region or country, particularly in terms of economic productivity, aging population, and strain on healthcare systems.
In order to visualize population growth and decline, population pyramids are often used. Population pyramids display the age and sex distribution of a population in a particular region or country. The shape of the population pyramid can provide insights into the demographic trends and potential future population changes.
For example, a population pyramid with a larger proportion of younger individuals indicates a region or country with a higher birth rate and potentially a growing population. Conversely, a population pyramid with a larger proportion of older individuals suggests a region or country with a higher proportion of elderly population and potentially declining birth rates.
In summary, population growth and decline are important factors to consider in the study of demographics. Understanding the reasons behind population changes and visualizing them through population pyramids can help policymakers make informed decisions and plan for the future.