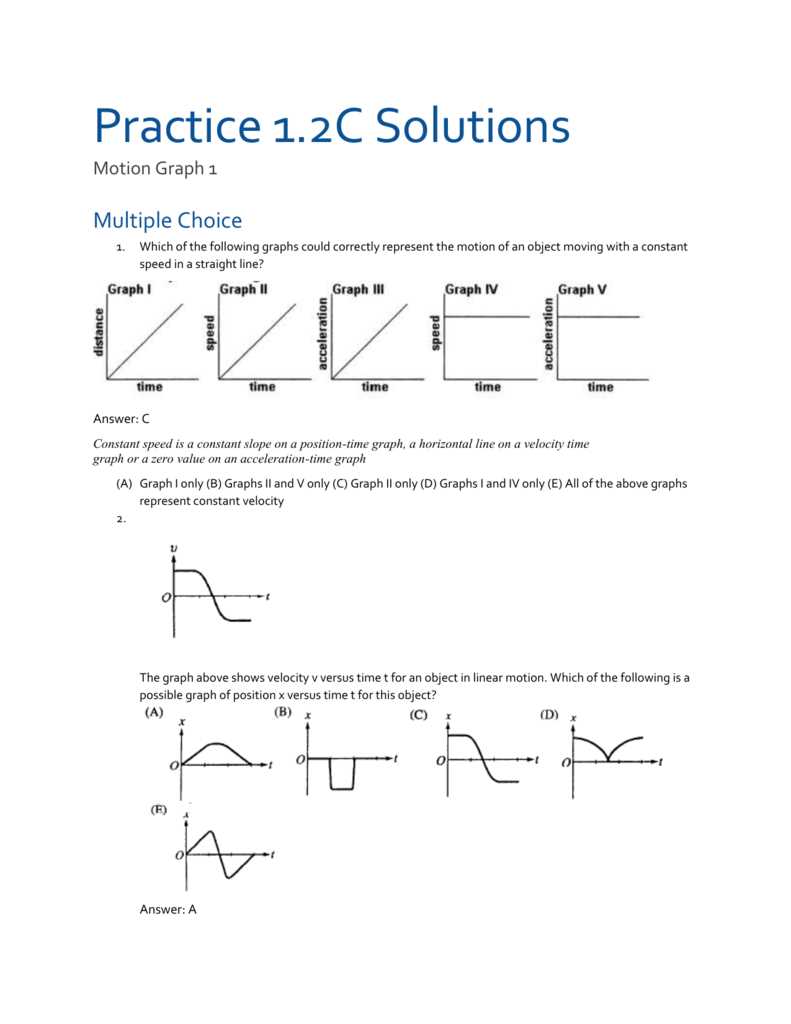
If you are studying physics or motion, chances are you will come across the concept of position vs time graphs. These graphs are a visual representation of an object’s position as it changes over time. They can be a valuable tool for analyzing and understanding how an object’s motion changes.
In this article, we will provide you with a position vs time graph worksheet with answers. This worksheet will help you practice interpreting and analyzing position vs time graphs. It will consist of several graphs, each representing a different scenario or motion. By answering the questions provided, you will be able to enhance your understanding of how to read and interpret position vs time graphs.
The worksheet will cover key concepts and skills, such as determining an object’s velocity, acceleration, and displacement from a position vs time graph. It will also include questions that test your knowledge of interpreting different shapes and patterns on the graph. By answering these questions, you will gain a deeper understanding of how changes in position over time can be represented graphically.
Whether you are a student studying physics or simply interested in learning about motion, this position vs time graph worksheet with answers will provide you with the opportunity to practice and enhance your skills. By working through the questions and checking your answers, you will be better prepared to analyze and interpret position vs time graphs in the future.
Understanding Position vs Time Graph
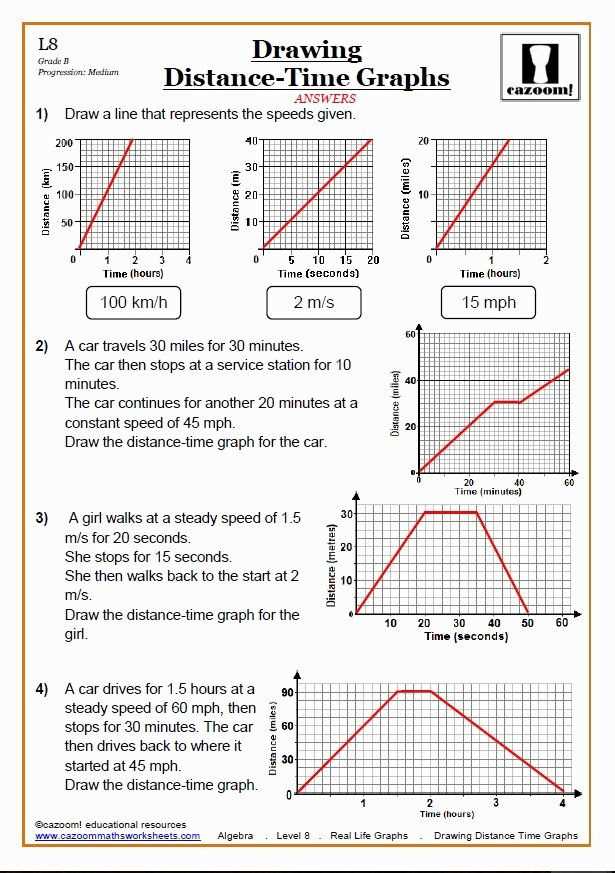
A position vs time graph is a graphical representation that shows the position of an object at different points in time. It provides valuable information about the object’s motion, including its velocity and acceleration. By studying and interpreting this graph, we can gain a better understanding of how the object is moving.
The x-axis of the graph represents time, while the y-axis represents the object’s position. The position is usually measured in meters, and time is measured in seconds. Each point on the graph represents a specific moment in time and the corresponding position of the object at that time.
An upward sloping line on the graph indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction, while a downward sloping line indicates movement in the negative direction. A horizontal line at a specific position indicates that the object is at rest.
- If the slope of the graph is positive and increasing, the object is moving with a positive velocity.
- If the slope of the graph is negative and decreasing, the object is moving with a negative velocity.
- If the slope of the graph is zero, the object is at rest.
- The steeper the slope of the graph, the greater the velocity of the object.
By analyzing the position vs time graph, we can also determine the acceleration of the object. The acceleration is represented by the curvature of the graph. If the graph is concave up, it indicates positive acceleration, while a concave down graph represents negative acceleration.
What is a position vs time graph?
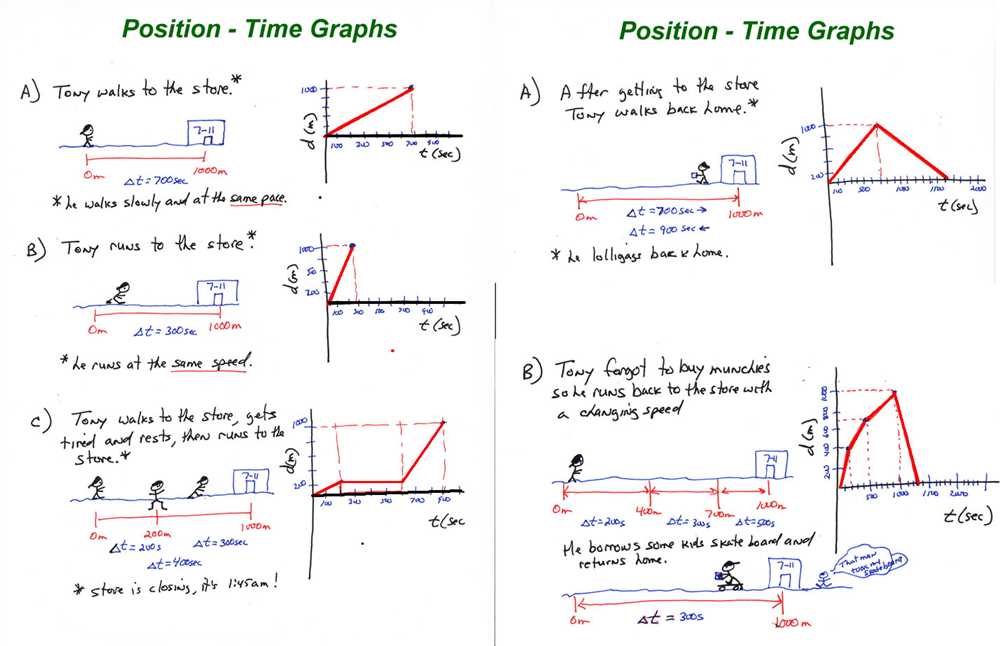
A position vs time graph is a graphical representation that shows the relationship between an object’s position and the amount of time it takes for the object to move from one position to another. The graph typically has the position of the object plotted on the y-axis, and the time on the x-axis.
In a position vs time graph, the slope of the line represents the object’s velocity. If the line is steeper, it means the object is moving faster, while a flatter line indicates slower motion. The direction of the line also indicates the direction of movement – a positive slope represents motion in one direction, while a negative slope represents motion in the opposite direction.
Here are some key features of a position vs time graph:
- Constant position: If the graph shows a horizontal line, it means the object is not changing its position over time.
- Constant velocity: A straight line with a positive or negative slope indicates constant velocity.
- Changing velocity: A curved line indicates that the object is accelerating or decelerating, as the slope of the line is changing over time.
- Zero velocity: A horizontal line at the x-axis (time) indicates that the object is at rest.
Position vs time graphs are commonly used in physics to analyze and understand the motion of objects. They provide a visual representation of an object’s position and velocity, which can help in predicting future positions or understanding the behavior of moving objects.
How is a position vs time graph interpreted?
A position vs time graph is a visual representation of an object’s position as it changes over time. The graph shows the relationship between an object’s position and the time elapsed. By analyzing the graph, we can gather information about the object’s motion and understand its behavior.
The key features of a position vs time graph are the slope of the line and its shape. The slope of the line represents the object’s velocity or speed. A steeper slope indicates a higher velocity, while a flatter slope indicates a slower velocity. A flat line indicates that the object is at rest. The shape of the graph can also provide information about the object’s motion. For example, a straight line represents uniform motion, while curved lines indicate changes in velocity or accelerated motion.
Interpreting a position vs time graph involves analyzing the different sections of the graph and understanding what they represent. By looking at the slope and shape of the graph, we can determine if the object is moving in a straight line, changing direction, speeding up, or slowing down. We can also calculate the object’s displacement by finding the area under the graph. The position vs time graph is a valuable tool for studying an object’s motion and can be used to make predictions about its future behavior.
Interpreting Position vs Time Graphs
Position vs time graphs are an essential tool for understanding the motion of an object. These graphs display how an object’s position changes over a given period of time. By analyzing the shape and slope of the graph, we can gather valuable information about the object’s velocity and acceleration.
One key feature of a position vs time graph is the slope of the line. The slope represents the object’s velocity. A positive slope indicates that the object is moving in a positive direction, while a negative slope indicates motion in the opposite direction. The steeper the slope, the greater the velocity. If the line is horizontal, it means that the object is not moving at all.
Another important aspect to consider is the shape of the graph. A straight line with a positive slope represents uniform motion, where the object is moving at a constant velocity. A curved line indicates that the object’s velocity is changing. If the curve is concave up, it means that the object is accelerating in the positive direction. On the other hand, a concave down curve indicates deceleration or acceleration in the negative direction.
By examining a position vs time graph, we can also determine the distance traveled by an object. The distance traveled is represented by the area under the graph. The larger the area, the greater the distance covered by the object.
To summarize, position vs time graphs provide valuable information about an object’s motion. By analyzing the slope, shape, and area under the graph, we can determine the object’s velocity, acceleration, and distance traveled. These graphs are a powerful tool for understanding and analyzing various types of motion.
Understanding Constant Velocity and Zero Velocity
In the study of motion, it is important to understand the concept of velocity. Velocity is a vector quantity that describes how fast an object is moving and in what direction. When analyzing the motion of an object, we often use a position vs. time graph to visualize how its position changes over time. By examining the slope of the graph, we can determine the object’s velocity.
Constant velocity refers to a situation where an object is moving at a consistent speed in a straight line. On a position vs. time graph, this is represented by a straight, diagonal line. The slope of the line represents the object’s velocity. If the slope is positive, the object is moving in the positive direction; if it is negative, the object is moving in the negative direction. A zero slope indicates that the object is at rest and not moving.
Key Points:
- Velocity is a vector quantity that describes both the speed and direction of an object’s motion.
- A position vs. time graph can be used to analyze an object’s motion and determine its velocity.
- Constant velocity refers to an object moving at a consistent speed in a straight line.
- A straight, diagonal line on a position vs. time graph represents constant velocity.
- A zero slope on the graph indicates zero velocity and that the object is at rest.
Understanding constant velocity and zero velocity is fundamental to studying the motion of objects. This knowledge allows us to analyze and interpret position vs. time graphs to determine the speed and direction of an object’s motion. By carefully examining the slope of the graph, we can gain valuable insights into the behavior and characteristics of moving objects.
Determining direction of motion from the graph
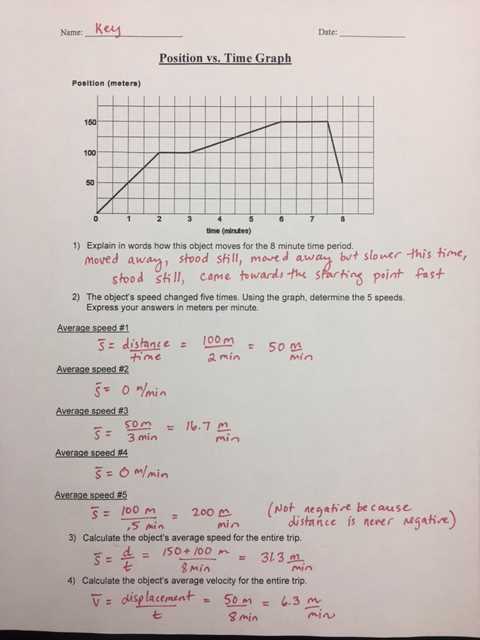
When analyzing a position vs. time graph, it is possible to determine the direction of motion by looking at the slope of the graph. The slope represents the rate of change of position over time. If the slope is positive, it indicates that the object is moving in the positive direction. If the slope is negative, it indicates that the object is moving in the negative direction.
In addition to the slope, the shape of the graph can also provide information about the direction of motion. For example, if the graph is a straight line with a positive slope, it means that the object is moving in a constant positive direction. If the graph is a straight line with a negative slope, it means that the object is moving in a constant negative direction.
However, if the graph has a curved shape, determining the direction of motion can be more complex. In this case, the direction of motion can be determined by looking at the concavity of the graph. If the graph is concave up (the slope is increasing), it means that the object is accelerating in the positive direction. If the graph is concave down (the slope is decreasing), it means that the object is accelerating in the negative direction.
Overall, analyzing a position vs. time graph can provide valuable information about the direction of motion of an object. By considering the slope and shape of the graph, it is possible to determine whether the object is moving in the positive or negative direction, as well as whether it is accelerating or decelerating.
Analyzing accelerated motion on the graph
When analyzing accelerated motion on a position vs time graph, it is important to understand the concepts of velocity and acceleration. Velocity is the rate at which an object changes its position, while acceleration is the rate at which an object changes its velocity. These concepts can be easily visualized and understood by looking at the shape and slope of the graph.
On a position vs time graph, the slope of the line represents the object’s velocity. A steeper slope indicates a higher velocity, while a flatter slope indicates a lower velocity. If the slope of the line is positive, it means the object is moving in the positive direction (e.g. to the right), and if the slope is negative, it means the object is moving in the negative direction (e.g. to the left).
Example:
For example, let’s consider a car that is accelerating uniformly. On the graph, this would be represented by a line with a steadily increasing slope. As the car accelerates, the slope of the line becomes steeper. This indicates that the car is covering more distance in less time, and therefore its velocity is increasing.
Another important aspect to analyze on the graph is the curvature of the line. If the line is curved, it means that the object’s acceleration is changing. A curved line that is concave upwards indicates that the acceleration is increasing, while a curved line that is concave downwards indicates that the acceleration is decreasing.
In conclusion, analyzing accelerated motion on a position vs time graph involves looking at the slope of the line to determine the object’s velocity, and analyzing the curvature of the line to determine how the object’s acceleration is changing. These visual representations can provide valuable insights into an object’s motion and help us better understand the concepts of velocity and acceleration.
Graphical Representations
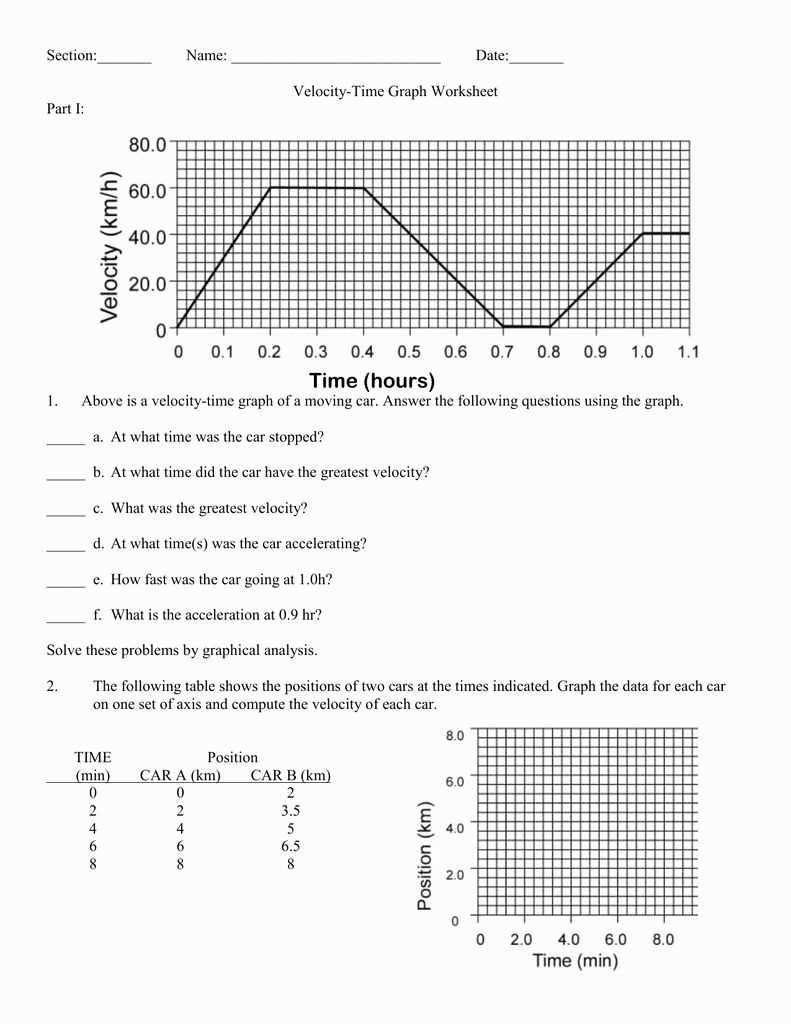
Graphical representations are visual tools used to represent data or information. They provide a clear and concise way to present complex concepts, making it easier for people to understand and interpret the information. Graphs can be used to represent various types of data, such as numbers, trends, relationships, and changes over time.
One type of graphical representation commonly used is a position vs. time graph. This graph shows the position of an object at different points in time. The x-axis represents time, while the y-axis represents position. By plotting the data points on the graph, you can see how the position changes over time and identify any patterns or trends.
In a position vs. time graph, a straight line represents constant velocity. The slope of the line indicates the velocity of the object. If the line is steep, it means the object is moving quickly, while a shallow line indicates slow movement. A horizontal line represents an object at rest, as there is no change in position over time.
When analyzing a position vs. time graph, it is also important to consider the shape of the line. A curved line may indicate an object undergoing acceleration, as the position is changing at an increasing rate. The concavity of the curve can provide additional information about the direction and magnitude of the acceleration.
In conclusion, graphical representations, such as position vs. time graphs, are valuable tools for visualizing and understanding data. They allow us to easily interpret information and identify patterns or trends. By analyzing the shape and slope of the graph, we can gain insights into the velocity and acceleration of an object.


