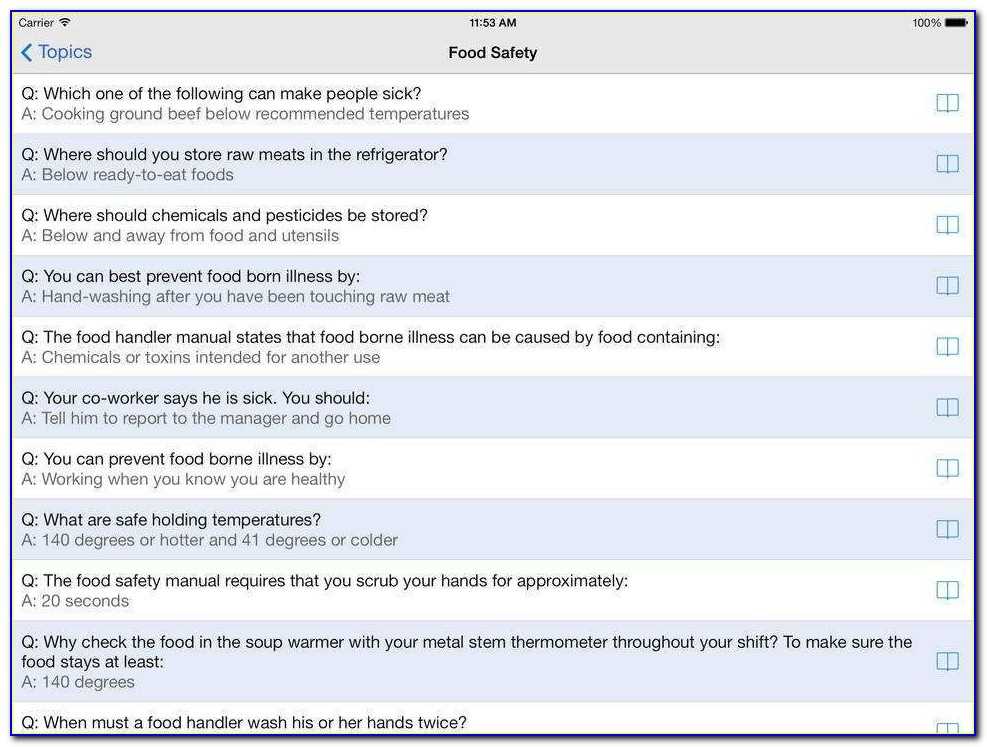
Are you preparing for your final exam in food safety? Do you want to make sure you have all the right answers before you walk into that exam room? Look no further! In this article, we will provide you with some key answers to help you ace your premier food safety final exam.
Food safety is a critical aspect of any food service establishment. It involves the proper handling, storing, and preparation of food to prevent foodborne illnesses. In your final exam, you are likely to encounter questions related to various topics such as personal hygiene, cross-contamination, temperature control, and cleaning and sanitizing procedures. Understanding the correct answers to these questions will not only help you pass your exam but also equip you with the necessary knowledge to ensure food safety in your future career.
One of the key areas you need to familiarize yourself with is personal hygiene. This includes practices such as regular handwashing, wearing clean uniforms, and avoiding jewelry or nail polish that can harbor bacteria. When it comes to cross-contamination, remember that it occurs when bacteria from one food item is transferred to another. To prevent this, you should always use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods and avoid using the same cloth to wipe different surfaces.
Premier Food Safety Final Exam Answers
In the final exam for the Premier Food Safety course, students are required to demonstrate their knowledge and understanding of key concepts related to food safety. The exam consists of a series of questions that cover various topics, such as foodborne illnesses, cross-contamination, proper food handling and storage, and HACCP principles.
One of the questions in the exam may ask students to identify the most common symptoms of foodborne illnesses. Students should be able to recognize symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. It is important for students to understand the importance of reporting these symptoms and seeking medical attention.
Another question in the exam may ask students to explain the concept of cross-contamination and provide examples. Cross-contamination occurs when harmful bacteria or allergens are transferred from one food or surface to another. Students should be able to explain that cross-contamination can happen through direct contact, such as when raw poultry comes into contact with ready-to-eat foods, or through indirect contact, such as when cutting boards or utensils are used for multiple types of foods without proper cleaning.
Students may also be asked to describe proper food handling and storage practices. They should be able to explain the importance of washing hands before and after handling food, storing food at proper temperatures, and using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods. Students should also be familiar with the proper procedures for thawing, cooking, and reheating food to prevent foodborne illnesses.
Lastly, the final exam may include questions about HACCP principles, which is a system designed to identify and control potential hazards in food production. Students should be able to explain the seven HACCP principles, which include conducting a hazard analysis, identifying critical control points, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, and implementing corrective actions.
In conclusion, the Premier Food Safety final exam assesses students’ knowledge of food safety concepts and their ability to apply them in real-life situations. By understanding the causes of foodborne illnesses, practicing proper food handling and storage techniques, and implementing HACCP principles, individuals can contribute to maintaining a safe and healthy food environment.
Understanding Food Safety Regulations
Food safety regulations are a set of standards and guidelines that are established by governments to ensure the safety and quality of food products. These regulations are put in place to protect consumers from potential health risks associated with contaminated or improperly handled food.
Food safety regulations cover a wide range of areas, including food handling and storage, personal hygiene of food handlers, temperature control, and sanitation practices. These regulations also require food establishments to have proper documentation and record-keeping systems in place to track the source of their food products and ensure traceability.
One of the key aspects of food safety regulations is the Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system. This system identifies potential hazards in the food production process and establishes critical control points to prevent, eliminate, or reduce these hazards to acceptable levels. The HACCP system is widely recognized and implemented in the food industry as an effective approach to food safety management.
Food safety regulations are not only important for the protection of consumers but also for the success and reputation of food establishments. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in fines, closures, and damage to the company’s brand. Therefore, it is crucial for food establishments to have a thorough understanding of the food safety regulations that apply to their operations and to implement and maintain proper food safety practices.
- Proper staff training and education
- Regular inspections and audits by regulatory authorities
- Effective communication and collaboration with suppliers
- Investing in appropriate equipment and infrastructure
In conclusion, understanding and complying with food safety regulations is of utmost importance for the food industry. It helps to ensure the health and well-being of consumers and contributes to the overall success and sustainability of food establishments. By following these regulations, food establishments can demonstrate their commitment to safety and quality, build trust with consumers, and mitigate the risks associated with foodborne illnesses.
Principles of Proper Food Storage
Proper food storage is essential to prevent the growth of bacteria, maintain the quality and freshness of food, and prevent foodborne illnesses. There are several key principles to follow when it comes to storing food safely.
1. Temperature Control:
Controlling the temperature of stored food is crucial to inhibit the growth of bacteria. Perishable foods, such as meat, poultry, dairy products, and cooked leftovers, should be kept at temperatures below 40°F (4°C) to slow down bacterial growth. On the other hand, frozen foods should be stored at 0°F (-18°C) or below to maintain their quality and safety.
2. Proper Packaging:
Using appropriate packaging materials is essential to preserve the freshness and prevent contamination of food. Foods should be stored in airtight containers or sealed bags to prevent moisture loss and exposure to air, which can lead to spoilage. Additionally, it is important to label all containers with the contents and date of storage to ensure proper rotation and avoid consuming expired food.
3. Separation and Organization:
Properly separating and organizing food in storage is crucial to prevent cross-contamination and ensure easy access. Raw meats and seafood should be stored separately from ready-to-eat foods to avoid the risk of bacterial contamination. It is also important to keep different types of food, such as raw poultry and raw beef, separated to prevent the spread of bacteria. Furthermore, organizing the storage area with clear labels and a system for first-in, first-out (FIFO) rotation can help ensure that older items are used first to minimize food waste.
4. Proper Use of Refrigeration and Freezing:

Refrigeration and freezing play a vital role in food storage. Refrigerators should be kept at or below 40°F (4°C) to prevent the growth of bacteria in perishable foods. It is important to divide food into smaller portions before refrigerating or freezing to promote faster and more even cooling. Additionally, frozen foods should be thawed in the refrigerator or using the microwave, rather than at room temperature, to prevent bacterial growth.
By following these principles of proper food storage, individuals and food establishments can ensure the safety and quality of the food they consume and serve. Proper storage practices are essential for preventing foodborne illnesses and maintaining the integrity of stored food products.
Hygiene Practices in the Kitchen
Hygiene practices are crucial in maintaining a safe and clean kitchen environment. Keeping the kitchen clean and practicing proper hygiene not only prevents the spread of harmful bacteria and contamination, but also ensures the safety and well-being of those consuming the food prepared in the kitchen.
Personal hygiene is of utmost importance when working in a kitchen. All kitchen staff should maintain a high standard of personal hygiene by washing their hands frequently with soap and warm water. This should be done before handling food, after handling raw meat or poultry, after using the restroom, and after any other activities that may contaminate the hands. Hair should be tied back and covered with a hat or hairnet, and any jewelry should be removed to prevent the risk of them falling into the food.
Cleaning and sanitizing surfaces in the kitchen is also essential for maintaining good hygiene. All surfaces, including countertops, cutting boards, and utensils, should be cleaned thoroughly with hot soapy water after each use. Additionally, sanitizing solutions, such as a mixture of bleach and water, should be used to disinfect surfaces regularly to kill any remaining bacteria or germs. It is important to avoid cross-contamination by using separate cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods.
Proper food storage is another important aspect of maintaining hygiene in the kitchen. Perishable foods should be stored at the appropriate temperature to prevent bacterial growth. Refrigerators should be kept clean and organized, with raw meats stored separately from other foods to avoid cross-contamination. Food should be labeled with the date of preparation to ensure that older items are used first and not left to spoil.
In conclusion, practicing good hygiene in the kitchen is essential for food safety and the prevention of illness. By maintaining personal hygiene, ensuring cleanliness of surfaces, and proper food storage, we can create a safe environment in which to prepare and consume food.
Contamination Prevention and Control
Contamination prevention and control are critical aspects of ensuring food safety in the premier food industry. Contamination can occur at various stages of the food production process, including during handling, processing, packaging, and transportation. It is essential to have robust measures in place to prevent contamination and ensure that only safe and high-quality food products reach the consumers.
Good hygiene practices are the foundation of contamination prevention. This includes proper handwashing techniques, wearing appropriate protective clothing such as gloves and aprons, and maintaining clean and sanitized workspaces. Employees should receive regular training on hygiene practices to ensure they understand the importance of maintaining hygiene standards.
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic approach that identifies and controls hazards throughout the food production process. It involves conducting a thorough assessment of potential hazards, implementing control measures, and regularly monitoring and reviewing the effectiveness of these measures. HACCP provides a proactive strategy to prevent food safety hazards and minimize the risk of contamination.
- Effective cleaning and sanitation procedures are crucial in preventing contamination. All surfaces, utensils, and equipment should be properly cleaned and sanitized to remove any potential contaminants. Regular inspections and audits should be conducted to ensure compliance with cleaning and sanitation protocols.
- Proper storage and handling of ingredients are essential to prevent contamination. Ingredients should be stored separately to avoid cross-contamination, and perishable items should be stored at the appropriate temperature to prevent the growth of bacteria. All ingredients should be inspected for quality and freshness before use.
- The use of approved suppliers is vital in ensuring the safety of food products. Suppliers should be carefully selected based on their compliance with food safety standards and their ability to provide safe and high-quality ingredients. Regular audits and inspections should be conducted to verify the compliance of suppliers.
In conclusion, contamination prevention and control are crucial in the premier food industry to ensure food safety. Good hygiene practices, HACCP, effective cleaning and sanitation procedures, proper storage and handling of ingredients, and the use of approved suppliers are all key components of preventing contamination. Implementing these measures and regularly monitoring their effectiveness is essential to guarantee the production of safe and high-quality food products.
Proper Handling and Cooking of Food
Ensuring proper handling and cooking of food is essential to prevent foodborne illnesses and maintain food safety. It is crucial to follow correct practices throughout the entire food preparation process, from the moment you purchase the ingredients to the moment you serve the final dish.
Proper handling: When purchasing groceries, it is important to check for any signs of spoilage or damage to the packaging. Store perishable foods, such as meats and dairy products, in the refrigerator or freezer as soon as possible. Keep raw and cooked foods separate to avoid cross-contamination. This includes using different cutting boards and utensils for raw and cooked foods. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water before and after handling food to prevent the spread of bacteria.
Proper cooking: Cooking food to the correct temperature is critical for killing harmful bacteria. Use a food thermometer to ensure that meats, poultry, and seafood are cooked to the appropriate internal temperature. For example, poultry should reach a minimum of 165°F (74°C), while steak should be cooked to at least 145°F (63°C) for medium-rare. Avoid partially cooking food and finishing it later, as this can lead to uneven cooking and the growth of bacteria.
- When reheating leftovers, make sure they reach a temperature of 165°F (74°C) to kill any bacteria that may have multiplied during storage.
- When serving food buffet-style, use chafing dishes, hot plates, or other methods to keep hot foods hot (at least 140°F or 60°C) and cold foods cold (below 40°F or 4°C).
- Properly storing leftovers is also crucial. Refrigerate or freeze leftover food within two hours of cooking and consume within a few days.
By following these practices and prioritizing proper handling and cooking of food, you can reduce the risk of foodborne illnesses and ensure the safety of your meals. Remember to always stay informed about food safety guidelines and stay vigilant in creating a clean and safe cooking environment.