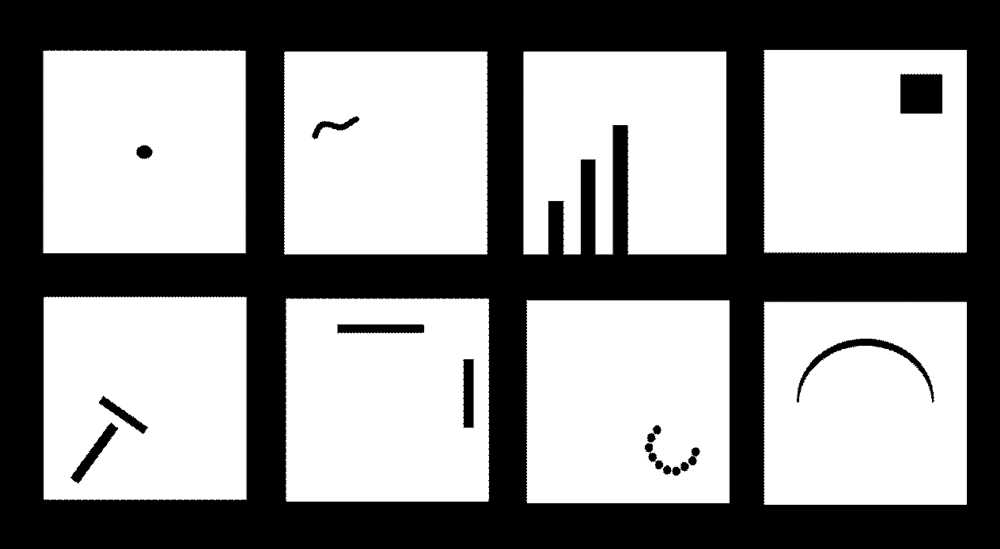
The Wartegg test is a projective drawing test that originated in the early 20th century. It consists of eight boxes, each with an incomplete picture. The test taker is asked to complete the picture in any way they choose. These completed drawings are then analyzed to gain insight into the test taker’s thoughts, emotions, and personality traits.
The Wartegg test has been used in various fields, such as psychology, counseling, and employment screening. It can provide valuable information about a person’s problem-solving skills, creativity, and emotional state.
One of the main advantages of the Wartegg test is its versatility. It can be used with individuals of different ages and cultural backgrounds, making it a valuable tool for cross-cultural research and assessment. Additionally, the open-ended nature of the test allows for a wide range of responses, providing a rich source of data for interpretation.
In conclusion, the Wartegg test is a useful tool for gaining insights into a person’s thoughts, emotions, and personality traits. Its versatility and open-ended nature make it a valuable method for research and assessment purposes. Whether used in psychology, counseling, or employment screening, the Wartegg test offers a unique perspective on an individual’s inner world.
What is the Wartegg test?
The Wartegg test is a projective psychological assessment tool that is used to evaluate an individual’s personality traits, attitudes, and cognitive functioning. It was developed by the German psychologist Ehrig Wartegg in the 20th century as a way to gain insight into a person’s unconscious thoughts and feelings.
The test consists of eight blank boxes arranged in a specific pattern on a piece of paper. Each box represents a different aspect of a person’s personality or cognitive processes. The individual is instructed to draw pictures or complete patterns within each box, based on specific instructions provided by the test administrator.
Each completed box is then analyzed to reveal underlying psychological patterns and traits. For example, the size, placement, and content of the drawings can provide information about the individual’s level of anxiety, impulsiveness, problem-solving abilities, and interpersonal skills. The test aims to uncover unconscious conflicts, desires, and motivations that may influence the individual’s behavior and decision-making process.
The Wartegg test has been widely used in clinical and research settings to assess personality characteristics, identify potential psychological issues, and guide therapy. It can also be used in various professional contexts, such as employee selection and career counseling, to gain insights into an individual’s suitability for a specific role or profession.
It is important to note that the Wartegg test is just one tool in the realm of psychological assessments and should be interpreted by trained professionals in conjunction with other assessment measures. It is not a definitive or diagnostic tool but rather a means to gather additional information about an individual’s personality and cognitive functioning.
History of the Wartegg Test
The Wartegg test, also known as the Wartegg Zeichen Test or the WZT, is a projective personality test that was developed by the German psychologist Ehrig Wartegg in 1939. It was initially designed as a tool to assess personality characteristics and psychological functioning. The test consists of eight empty boxes arranged in a two-by-four grid, each containing a stimulus or incomplete figure. The individual is then instructed to complete the figure or add any details that come to mind, and their responses are interpreted to reveal underlying personality traits.
Ehrig Wartegg was influenced by the ideas of Gestalt psychology, which emphasized the importance of understanding the whole rather than just the individual parts. He believed that by examining the way individuals completed the incomplete figures, it would be possible to gain insights into their unconscious desires, conflicts, and motivations. The test was originally intended to be used for diagnostic purposes, but over time it has also been used for vocational guidance, selection procedures, and even artistic expression.
One of the unique aspects of the Wartegg test is its emphasis on the individual’s creative abilities. By asking the individual to complete the figures in their own way, the test allows for a wide range of responses and interpretations. This flexibility has made the Wartegg test popular among psychologists and clinicians, as it provides a window into the individual’s thought processes and personality functioning.
Despite its widespread use, the Wartegg test has also been subject to criticism. Some argue that the test lacks sufficient empirical evidence to support its validity and reliability. Others suggest that the test may be influenced by cultural factors, leading to biased interpretations. Nevertheless, the Wartegg test continues to be used in various contexts and offers valuable insights into the complexities of human personality.
How does the Wartegg test work?
The Wartegg test is a psychological assessment tool used to evaluate an individual’s personality and emotional functioning. Developed in the 20th century by the German psychologist Ehrig Wartegg, this test consists of a series of abstract drawings, each composed of eight boxes with incomplete lines and shapes. The test-taker is instructed to complete each drawing using their imagination and creativity.
The purpose of the Wartegg test is to gain insights into the test-taker’s unconscious mind and inner thoughts. By interpreting the way the individual completes the drawings, psychologists can identify patterns and symbols that reflect their personality traits, emotional states, and cognitive processes. The test allows for a subjective interpretation of the drawings, providing a rich source of information about the test-taker’s psychological makeup.
In the Wartegg test, each box in the drawings has a specific meaning and is associated with different aspects of the individual’s personality. For example, the upper-left box represents the test-taker’s self-perception, while the upper-right box reflects their interpersonal relationships. By analyzing the content, placement, and style of the drawings, psychologists can draw conclusions about the individual’s self-image, social skills, emotional stability, and other psychological factors.
It is important to note that the Wartegg test is not designed to diagnose mental disorders or provide a definitive assessment of an individual’s psychological state. Instead, it serves as a tool for self-reflection and understanding. The results of the test can help individuals gain insight into their own personality traits, strengths, and areas for personal growth. Additionally, the test can also be used in therapeutic settings to facilitate discussions about personal experiences and emotions.
In conclusion, the Wartegg test is a unique psychological assessment tool that utilizes abstract drawings to explore an individual’s personality and emotional functioning. Through the interpretation of these drawings, psychologists can uncover valuable insights into the test-taker’s subconscious mind and provide a framework for self-reflection and personal growth.
Benefits of the Wartegg test
The Wartegg test, also known as the Wartegg Zeet strategy is a popular psychological assessment tool that provides valuable insights into an individual’s personality and cognitive functioning. This test consists of eight boxes or grids, each containing a unique stimulus. The individual is then instructed to complete the image using their own interpretations and imagination.
1. Self-awareness: One of the main benefits of the Wartegg test is that it helps individuals gain a deeper understanding of themselves. By interpreting the stimulus images in their own unique way, individuals can uncover their thoughts, emotions, and desires that may be hidden or unconscious. This increased self-awareness can lead to personal growth and development.
2. Problem-solving skills: The Wartegg test also assesses an individual’s problem-solving skills. By analyzing how individuals complete the image and the strategies they use, psychologists can gain insights into an individual’s ability to think creatively, critically, and solve problems. This information can be useful in various real-life situations, such as decision-making or overcoming obstacles.
3. Emotional intelligence: Another benefit of the Wartegg test is its ability to measure an individual’s emotional intelligence. Emotional intelligence refers to the ability to recognize, understand, and manage one’s own emotions, as well as the emotions of others. By examining the interpretations and responses to the stimuli, psychologists can evaluate an individual’s emotional intelligence and provide feedback for further development.
4. Personalized feedback: The Wartegg test provides individuals with personalized feedback. Psychologists can interpret the completed images and provide detailed insights into an individual’s personality traits, strengths, weaknesses, and potential areas for improvement. This feedback can be instrumental in self-reflection and personal growth.
5. Career guidance: The Wartegg test can also be used as a tool for career guidance. By analyzing an individual’s interpretation of the stimuli and their problem-solving strategies, psychologists can identify specific career paths or areas of interest that align with the individual’s strengths and personality traits. This information can assist individuals in making informed decisions about their future career choices.
- In conclusion, the Wartegg test offers numerous benefits to individuals seeking self-awareness, personal growth, and career guidance. By using their imagination to complete the stimuli, individuals can gain insights into their underlying thoughts, emotions, and problem-solving skills. This test provides personalized feedback and can be a valuable tool in the journey towards self-discovery and personal development.
Common interpretations of the Wartegg test
The Wartegg test is a popular projective test used to assess individuals’ personality traits, emotional functioning, and thought processes. The test consists of eight boxes with incomplete geometric figures, and the task of the participant is to complete the drawings. There are various interpretations of the Wartegg test based on the responses and completion of the drawings.
1. Emotional stability: One interpretation of the Wartegg test focuses on evaluating an individual’s emotional stability. Responses that depict balanced and structured completions of the figures may indicate emotional stability and a well-integrated personality. On the other hand, erratic or distorted responses may suggest emotional instability or underlying psychological issues.
2. Cognitive functioning: Another interpretation of the Wartegg test revolves around assessing an individual’s cognitive functioning. The way the drawings are completed can provide insights into a person’s thinking patterns, problem-solving abilities, and creativity. For example, organized and detailed completions may indicate logical thinking and analytical skills, while abstract or unconventional responses may suggest imaginative thinking and unconventional problem-solving approaches.
The Wartegg test does not have a fixed scoring system, but instead relies on the interpretation of the test administrator or psychologist. It is essential to consider the overall context, cultural background, and other factors that may influence the individual’s responses. Additionally, it is important to note that the Wartegg test is just one tool among many used in psychological assessments and should be used in conjunction with other assessment methods for a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s personality and psychological well-being.
Interpretation Examples:

- A person who completes the figures with symmetrical and detailed patterns may be perceived as organized and methodical in their thinking.
- Responses that include fragmented or distorted figures may suggest a lack of clarity in thoughts or possible cognitive impairments.
- Drawings that incorporate unconventional or abstract elements may indicate a creative and imaginative thinker.
- If a person avoids completing certain figures or provides minimal responses, it could suggest avoidance or reluctance to confront certain emotions or issues.
Limitations of the Wartegg test
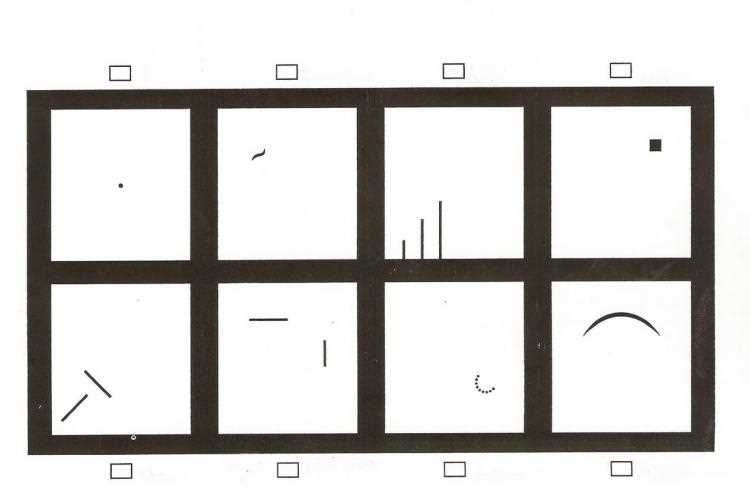
The Wartegg test is a projective drawing test that is widely used in psychology to assess an individual’s personality traits and psychological functioning. However, like any psychological assessment tool, the Wartegg test has its limitations. Understanding these limitations is crucial for the accurate interpretation of the results and avoiding potential misinterpretations.
1. Subjective interpretation: One of the main limitations of the Wartegg test is the subjective interpretation of the drawings. Since the test relies on the individual’s interpretation of the abstract shapes, symbols, and lines, there is a high degree of subjectivity involved. Different psychologists may interpret the drawings differently, leading to varying conclusions about the individual’s personality traits.
2. Lack of standardization: Another limitation of the Wartegg test is the lack of standardized scoring criteria. Unlike other psychological tests that have established norms and scoring procedures, the Wartegg test lacks standardized scoring guidelines. This lack of standardization can make it difficult to compare results across different individuals and populations, limiting the test’s reliability and validity.
3. Cultural and language bias: The Wartegg test may also be subject to cultural and language biases. The test was developed based on European and Western cultural norms, which may not be applicable or relevant to individuals from different cultural backgrounds. Additionally, language barriers can affect the individual’s understanding and interpretation of the test instructions, potentially biasing the results.
4. Limited scope: The Wartegg test focuses primarily on the individual’s emotional and interpersonal functioning, neglecting other important aspects of personality and psychological functioning. The test does not provide a comprehensive assessment of all personality traits and may only offer limited insights into the individual’s overall psychological profile.
In conclusion, while the Wartegg test can be a useful tool for assessing certain personality traits and psychological functioning, it is important to recognize and consider its limitations. Relying solely on the results of the Wartegg test may lead to incomplete or inaccurate conclusions about an individual’s personality and psychological well-being.