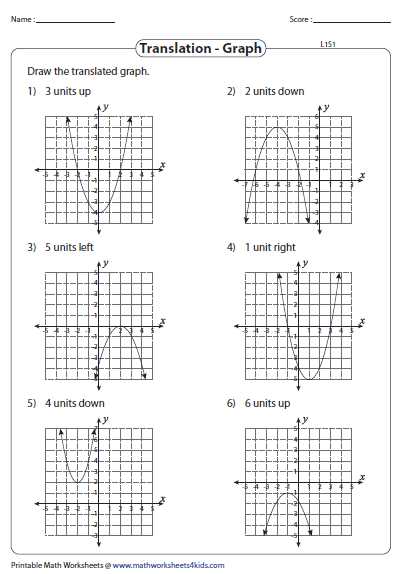
Understanding quadratic transformations is essential for mastering the concept of quadratic functions. A quadratic transformation worksheet is a valuable resource that allows students to practice and reinforce their knowledge of these transformations. This article will provide detailed explanations of the answers to a quadratic transformation worksheet, helping students to deepen their understanding and improve their problem-solving skills.
In a quadratic transformation worksheet, students are presented with a series of quadratic functions and asked to identify the transformations that have been applied to the parent function. These transformations include translations, stretches or compressions, and reflections. By analyzing the equation and graph of each quadratic function, students can determine the specific transformations that have occurred.
One common type of transformation is a translation, where the graph of a quadratic function is shifted horizontally or vertically. In the worksheet, students may be asked to identify how much the function has been shifted and in what direction. This could involve determining the value of h in the equation f(x) = a(x-h)^2 + k, or analyzing the graph to see how it has been moved.
Another type of transformation is a stretch or compression, where the graph of a quadratic function is either elongated or squashed. In the worksheet, students may need to determine the value of a in the equation f(x) = a(x-h)^2 + k, or analyze the graph to see the change in shape. Additionally, students may be asked to identify if the parabola opens upward or downward based on these transformations.
By carefully examining the equations and graphs of quadratic functions, students can successfully answer the questions on a quadratic transformation worksheet. Through this practice, students will develop a solid understanding of quadratic transformations, which will greatly benefit them in future algebra and calculus courses.
Understanding Quadratic Transformations
In the study of quadratic functions, it is important to understand the concept of transformations. A transformation is a change that is made to the original function, resulting in a new function with different characteristics. In the context of quadratic functions, these transformations involve changes to the vertex, axis of symmetry, and the shape, position, and size of the graph.
One of the most common transformations in quadratic functions is the vertical shift, which involves adding or subtracting a constant term to the original function. This shifts the graph up or down along the y-axis. For example, adding a positive constant will shift the graph upward, while adding a negative constant will shift it downward. The vertical shift does not affect the axis of symmetry.
Another important transformation is the horizontal shift, which involves adding or subtracting a constant term to the variable in the original function. This shifts the graph left or right along the x-axis. Adding a positive constant will shift the graph to the left, while adding a negative constant will shift it to the right. The horizontal shift also affects the axis of symmetry, moving it in the opposite direction of the shift.
The final transformation to consider is the vertical stretch or compression, which involves multiplying the entire function by a constant. This stretches or compresses the graph vertically. If the constant is greater than 1, the graph will be compressed, making it narrower and taller. If the constant is between 0 and 1, the graph will be stretched, making it wider and shorter. The vertical stretch or compression does not affect the vertex or axis of symmetry.
By understanding these quadratic transformations, it becomes easier to analyze and interpret the graphs of quadratic functions. These transformations allow us to manipulate the shape and position of the graph, making it a powerful tool in various fields such as physics, engineering, and economics.
What are quadratic transformations?
A quadratic transformation is a mathematical concept that involves changing the shape, position, or size of a quadratic function. In mathematics, a quadratic function is a polynomial function of degree 2, meaning it has an x-squared term. Quadratic transformations allow us to manipulate these functions to better understand their properties and behaviors.
There are several types of quadratic transformations, including translations, dilations, and reflections. Each type of transformation affects the graph of the quadratic function in a specific way. It is important to understand these transformations as they play a crucial role in graphing and solving quadratic equations.
Translations:
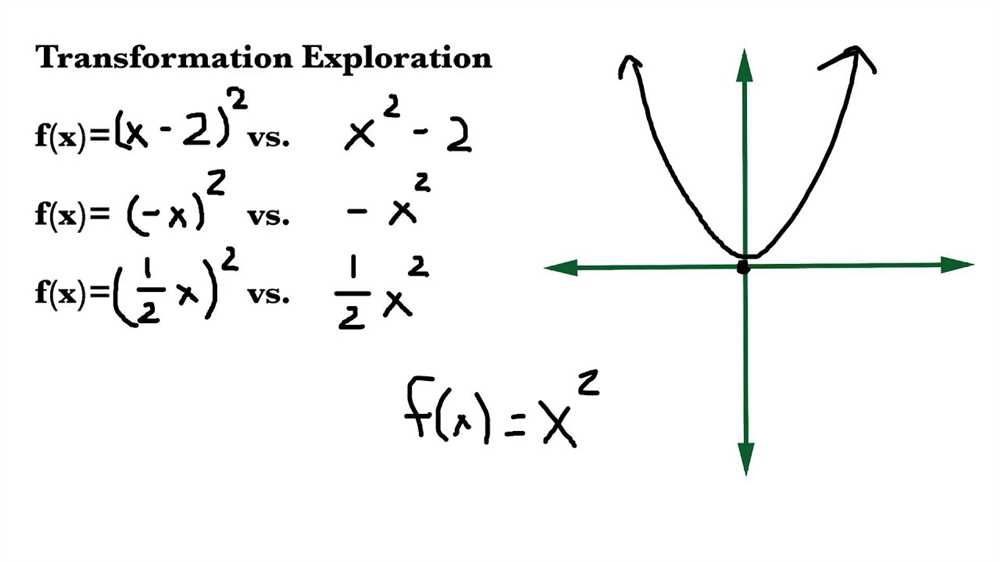
A translation is a type of quadratic transformation that shifts the graph of a quadratic function horizontally or vertically. Horizontal translations move the graph left or right, while vertical translations move it up or down. Translations are described by the equations of the form f(x) = a(x – h)^2 + k, where (h, k) represents the coordinates of the vertex after the translation.
Dilations:
A dilation is a type of quadratic transformation that changes the size of the graph of a quadratic function. It can stretch or compress the graph vertically or horizontally. Dilations are described by the equations of the form f(x) = a(x – h)^2 + k, where the value of “a” determines the scale factor of the dilation.
Reflections:
A reflection is a type of quadratic transformation that flips the graph of a quadratic function over a line. The line could be the x-axis, y-axis, or any other line. Reflections are described by the equations of the form f(x) = a(-x – h)^2 + k, where the negative sign is used to indicate the reflection.
Overall, understanding quadratic transformations is essential for analyzing and manipulating quadratic functions. These transformations allow us to visualize and solve quadratic equations more easily. By applying different transformations, we can explore different aspects of quadratic functions and gain insight into their properties.
Exploring the effects of transformations on quadratic functions
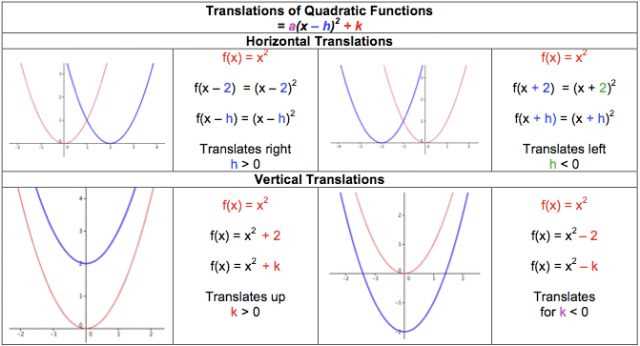
Quadratic functions are mathematical expressions that can be represented by the equation f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c, where a, b, and c are constants. These functions graph as a parabola, and by applying different transformations, we can observe how these transformations affect the shape, position, and orientation of the graph.
One common transformation is a vertical shift, where the entire graph is shifted up or down. This is achieved by adding or subtracting a constant term to the function. For example, if we have the function f(x) = x^2 and we add 2, the new function becomes f(x) = x^2 + 2. This causes the graph to shift upward by two units.
Another transformation is a horizontal shift, where the graph is shifted left or right. This is achieved by adding or subtracting a constant term inside the function. For instance, if we have the function f(x) = x^2 and we subtract 3 from the input, the new function becomes f(x – 3) = (x – 3)^2. This causes the graph to shift right by three units.
We can also stretch or compress the graph horizontally or vertically. A horizontal stretch or compression is achieved by multiplying or dividing the input by a constant. For example, if we have the function f(x) = x^2 and we double the input, the new function becomes f(2x) = (2x)^2 = 4x^2. This causes the graph to stretch horizontally by a factor of 2.
A vertical stretch or compression is achieved by multiplying or dividing the entire function by a constant. For instance, if we have the function f(x) = x^2 and we quadruple the function, the new function becomes f(x) = 4x^2. This causes the graph to stretch vertically by a factor of 4.
By applying these different transformations, we can manipulate the graph of a quadratic function to create different shapes, positions, and orientations. This allows us to explore the effects of transformations on quadratic functions and gain a deeper understanding of their properties.
Identifying Quadratic Transformations in Equations
Quadratic equations can be transformed in various ways, resulting in different shapes and positions of the parabola they represent. Understanding these transformations is crucial for analyzing and graphing quadratic functions.
One common transformation is vertical translation, which shifts the parabola up or down. This transformation is indicated by the term “q” in the quadratic equation. If q is positive, the parabola is shifted upward, and if q is negative, it is shifted downward.
Another transformation is horizontal translation, which moves the parabola left or right. This transformation is indicated by the term “p” in the quadratic equation. If p is positive, the parabola is shifted to the right, and if p is negative, it is shifted to the left.
Stretching or compressing the parabola vertically is also a possible transformation. This is determined by the coefficient of the quadratic term “a”. If a is greater than 1, the parabola is vertically compressed, and if a is between 0 and 1, it is vertically stretched.
Combining these transformations allows us to analyze quadratic equations and predict the shape and position of their graphs. By identifying the values of q, p, and a in an equation, we can easily determine how the parabola will be transformed and make accurate graphs.
Decoding Quadratic Transformations from Equations
In the study of quadratic functions, it is important to understand how different transformations affect the shape and position of the graph. By analyzing the equation of a quadratic function, we can determine the specific transformations that have been applied.
One key transformation that can be decoded from the equation is the vertical translation, or shifting, of the graph. If the equation is in the form y = ax^2 + bx + c, the value of c represents the vertical shift. Positive values of c indicate an upward shift, while negative values indicate a downward shift.
Another transformation that can be identified is the horizontal translation, or shifting, of the graph. This can be determined by examining the values of b and c in the equation. The term bx represents the horizontal shift, with positive values indicating a shift to the left and negative values indicating a shift to the right. The combination of b and c in the equation can also reveal whether the graph has been reflected horizontally.
The final transformation that can be decoded is the vertical stretching or compression of the graph. This is determined by the value of a in the equation. If a is greater than 1, the graph is compressed vertically, making it narrower. If a is between 0 and 1, the graph is stretched vertically, making it wider. If a is negative, the graph is also reflected vertically.
By analyzing the equation of a quadratic function, we can decode the specific transformations that have been applied to the graph. Understanding these transformations allows us to visualize and interpret the behavior of quadratic functions more effectively.
Interpreting the meaning of transformation coefficients
When working with quadratic transformations, it is essential to understand the meaning of the transformation coefficients. These coefficients determine how the quadratic function is stretched, compressed, or shifted in relation to the original quadratic function. They provide valuable information about the shape, position, and orientation of the graph.
The coefficient in front of the quadratic term (a) affects the vertical stretch or compression of the graph. If a > 1, the graph is stretched vertically, making it narrower. Conversely, if 0 < a < 1, the graph is compressed vertically, making it wider. When a < 0, the graph is reflected around the x-axis.
The coefficient in front of the linear term (b) determines the horizontal shift of the graph. If b > 0, the graph shifts to the left; if b < 0, it shifts to the right. This coefficient does not affect the vertical stretch or compression.
The constant term (c) influences the vertical shift of the graph. If c > 0, the graph shifts upward; if c < 0, it shifts downward. The constant term does not alter the shape or orientation of the graph.
By understanding the impact of these coefficients, we can accurately interpret the transformations and visualize how they affect the original quadratic function.
Applying Quadratic Transformations in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of quadratic transformations allows us to analyze and understand real-world scenarios more effectively. By applying these transformations, we can model and predict various phenomena and optimize our decision-making processes.
One of the key transformations in quadratic equations is the vertex transformation. This transformation shifts the vertex of a parabola either horizontally or vertically. In real-world scenarios, this transformation can be used to analyze the optimum point for a given situation. For example, in a manufacturing process, we can use the vertex transformation to determine the optimal production volume that maximizes efficiency while minimizing costs.
Another essential transformation is the stretch or compression transformation. This transformation changes the width of the parabola and affects its overall shape. In real-world scenarios, this can be applied to analyze the effect of changing a parameter on the outcome. For instance, in the field of finance, we can use the stretch transformation to understand how changes in interest rates impact the profitability of an investment.
The horizontal shift transformation is also crucial in real-world scenarios. This transformation moves the parabola horizontally without changing its shape. In practical terms, this transformation can be used to analyze the effect of time on a particular event. For example, in sports analytics, we can use the horizontal shift transformation to study how the performance of a player or a team evolves over time.
Overall, the application of quadratic transformations in real-world scenarios is instrumental in understanding complex relationships and making informed decisions. By studying these transformations, we can optimize processes, predict outcomes, and gain valuable insights into various fields such as manufacturing, finance, and sports.
Solving real-life problems using quadratic transformation concepts
Quadratic transformation concepts provide a powerful tool for solving real-life problems that involve non-linear relationships. By understanding how quadratic functions can be transformed, manipulated, and graphed, we can analyze and solve a wide range of problems in various fields.
One area where quadratic transformation concepts are particularly useful is in physics. For example, when studying the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, we often encounter quadratic relationships between variables such as time, distance, and velocity. By applying concepts such as vertex form, completing the square, and graphing techniques, we can determine the maximum height reached by a projectile, the time it takes to reach a certain distance, or the velocity at a given point in time.
Another field where quadratic transformation concepts come into play is engineering. Engineers often encounter problems that involve maximizing or minimizing certain quantities, such as the efficiency of a machine or the cost of materials. By understanding how to manipulate quadratic functions and apply optimization techniques, engineers can design more efficient systems, minimize costs, or maximize performance.
The applications of quadratic transformation concepts are not limited to physics and engineering. They can also be used in finance to model and analyze investment returns, in biology to study population growth, and in computer science to design algorithms and analyze computational complexity. In all these fields, quadratic transformation concepts provide a framework for solving complex problems and making informed decisions based on mathematical models.
Overall, understanding and applying quadratic transformation concepts allows us to solve real-life problems that involve non-linear relationships. Whether it’s modeling the motion of objects, optimizing engineering systems, analyzing financial data, or studying population growth, the ability to use quadratic transformation concepts is an essential tool in many fields of study and profession.