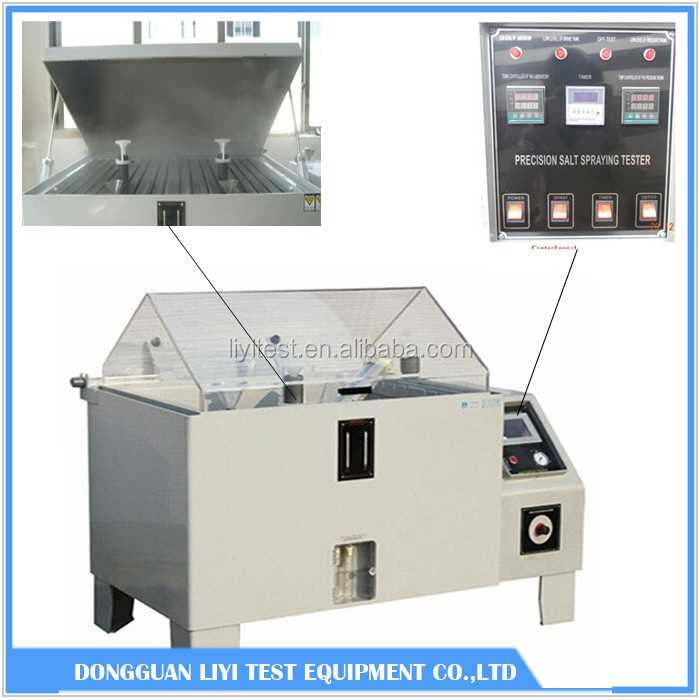

The salt spray test is a widely used method for evaluating the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. It is a controlled corrosive environment that simulates the natural conditions that cause corrosion, specifically the presence of salt in the air and water. This test is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and marine to assess the durability of materials and ensure they meet certain performance standards.
When conducting a salt spray test, it is important to follow a specific procedure to ensure accurate and reliable results. This includes preparing the test specimens, setting up the testing apparatus, and monitoring the test conditions. A detailed step-by-step procedure is typically provided in a PDF format to ensure consistency and repeatability of the test.
The PDF document for the salt spray test procedure usually includes information on the required equipment, such as the salt spray chamber, test panels, and solution preparation tools. It also provides instructions on how to properly prepare the test specimens, including cleaning and pre-treatment procedures. The document will typically outline the specific test parameters, such as the temperature, humidity, and duration of the test, as well as the criteria for evaluating the corrosion resistance.
It is important for researchers and technicians to have access to a comprehensive salt spray test procedure in PDF format to ensure they can accurately conduct the test and interpret the results. This document serves as a valuable reference for both beginners and experts in the field, providing them with the necessary guidance to perform the test effectively and efficiently.
What is Salt Spray Test?
The Salt Spray Test is a widely used method for evaluating the corrosion resistance of various materials and coatings. It simulates the harsh conditions that a product may be exposed to in coastal or industrial environments, where the presence of salt and moisture can lead to rapid corrosion.
The test involves subjecting the test specimen to a continuous atomized spray of a saltwater solution, typically composed of sodium chloride (NaCl), for a specified period of time. The test specimen is placed in a specially designed chamber that creates a controlled environment with the desired temperature, humidity, and salt concentration.
During the test, the saltwater solution creates a corrosive environment by depositing salt particles on the specimen’s surface, which accelerate the corrosion process. The test can be conducted using different salt concentrations, durations, and temperatures to simulate various corrosive conditions.
After the predetermined test duration, the specimen is removed from the test chamber and evaluated for corrosion damage. This evaluation may include visual inspection, measurement of corrosion product thickness, determination of corrosion rate, and assessment of any changes in the physical or mechanical properties of the specimen.
The Salt Spray Test is commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and coatings to assess the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. The results obtained from this test can help manufacturers evaluate their products’ suitability for use in corrosive environments and make informed decisions about materials selection and coating processes.
The Importance of Salt Spray Test
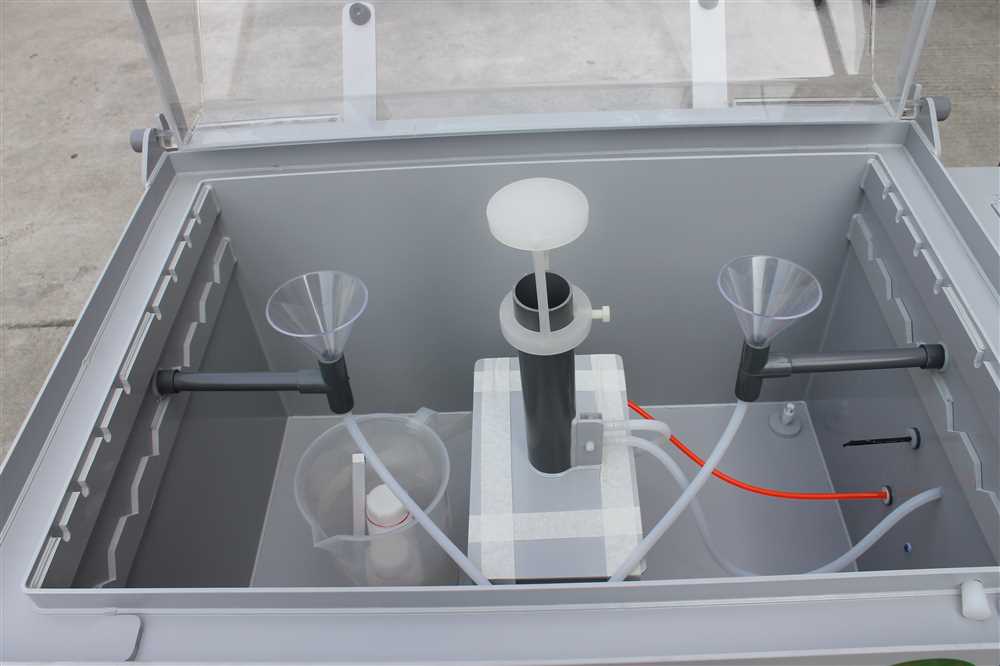

Salt spray test, also known as salt fog test, is a widely used method to determine the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. It involves subjecting the test specimens to a highly corrosive salt fog environment to accelerate the corrosion process. This test is particularly important in industries such as automotive, aerospace, marine, and electronics, where products are exposed to harsh environmental conditions containing salt, moisture, and humidity.
One of the key reasons why the salt spray test is important is its ability to predict the performance and longevity of materials and coatings in real-world corrosive environments. By exposing the specimens to a controlled salt fog environment, manufacturers and researchers can assess the effectiveness of their products’ corrosion protection measures and make necessary improvements before releasing them to the market. This helps in reducing warranty claims, improving customer satisfaction, and enhancing the overall quality of the products.
Benefits of Salt Spray Test
- Quality Assurance: The salt spray test provides a reliable and standardized method for evaluating the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings. It helps manufacturers ensure that their products meet the required quality standards and regulatory requirements.
- Comparative Analysis: By subjecting different materials or coatings to the same salt spray test conditions, manufacturers can compare their performance and select the most suitable option for their specific application. This allows for informed decision-making and optimization of product designs.
- Research and Development: The salt spray test is a valuable tool for researchers and engineers in the development of new materials and coatings. It allows them to study the corrosion behavior of different formulations, identify weaknesses, and develop innovative solutions to enhance durability and performance.
- Supplier Evaluation: The salt spray test can be used as an objective method for evaluating the corrosion resistance of products supplied by different vendors. It helps companies in selecting reliable and high-quality suppliers, thereby reducing the risk of product failures and costly recalls.
In conclusion, the salt spray test plays a crucial role in ensuring the longevity and reliability of materials and coatings in corrosive environments. It offers valuable insights into the performance of products and helps manufacturers make informed decisions regarding product design, selection of materials, and supplier evaluation. By conducting salt spray tests, companies can enhance the quality of their products, meet customer expectations, and maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Salt Spray Test Procedure
A salt spray test is a standardized test method used to determine the corrosion resistance of materials and surface coatings. It involves exposing the test specimens to a highly corrosive salt solution, typically sodium chloride, in a controlled environment. The purpose of the test is to simulate the corrosive effects of saltwater and assess the durability of the materials or coatings.
Preparation:
- Ensure that the test chamber is clean and free of any contaminants that may interfere with the test results.
- Prepare the salt solution by dissolving the appropriate amount of salt in distilled water to achieve the desired concentration. The concentration and pH level of the salt solution may vary depending on the test standard and the specific requirements of the material or coating being tested.
- Place the test specimens in the chamber, making sure they are properly secured and positioned to allow for even exposure to the salt solution.
Test Procedure:
- Set the desired test parameters, including the temperature, duration, and frequency of the salt spray cycles. These parameters should be in accordance with the test standard or specification being followed.
- Start the test by introducing the salt solution into the test chamber, ensuring that it is evenly distributed and covers the entire surface of the specimens.
- Monitor the test conditions throughout the duration of the test, including temperature, humidity, and salt solution concentration, to ensure they remain within the specified range.
- Periodically inspect the test specimens for any signs of corrosion, such as rust, discoloration, or blistering of the coating. Record and document any observations.
- Continue the test for the specified duration or number of cycles, as required by the test standard.
- After the test is complete, remove the specimens from the chamber and thoroughly clean and dry them to remove any salt residues.
Reporting and Analysis:
After the salt spray test, the recorded observations and any data collected during the test should be analyzed to determine the performance of the materials or coatings. This includes assessing the extent and severity of corrosion, evaluating the adhesion and integrity of the coatings, and comparing the test results to the specified requirements or industry standards.
The salt spray test procedure provides valuable information on the corrosion resistance of materials and coatings, helping manufacturers and engineers make informed decisions about the suitability and durability of their products in corrosive environments.
Test Setup

In order to conduct a salt spray test according to the specified procedure, a test setup must be prepared. The test setup includes the following components:
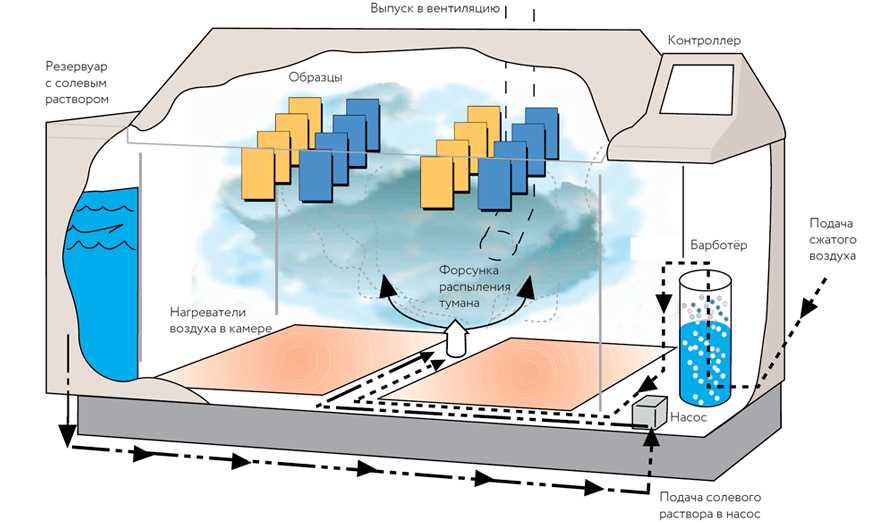
- Salt spray cabinet: A specialized chamber designed to create a controlled environment for the test. The cabinet typically consists of a chamber with a controlled temperature and humidity, a salt solution reservoir, spray nozzles, and a collection system for drainage.
- Test specimens: The materials or products being tested. These can be made of various materials, such as metals, alloys, paints, coatings, or plastics. The specimens should be carefully prepared and placed in the test cabinet in a manner that allows for exposure to the salt spray.
- Salt solution: A specific concentration of salt solution is prepared according to the test requirements. This solution is typically a mixture of sodium chloride (NaCl) and water. The concentration may vary depending on the specific test standard being followed.
- Spray duration and intervals: The test duration and spray intervals are determined based on the test standard being followed. The duration can range from a few hours to several weeks, and the intervals determine how frequently the salt spray is sprayed onto the specimens.
- Monitoring and recording equipment: Equipment such as temperature and humidity sensors, as well as corrosion measurement devices, may be used to monitor and record the test conditions and corrosion levels of the specimens over time.
It is important to carefully set up and follow the test procedure to ensure accurate and reliable results. Any deviations or inconsistencies in the test setup may affect the test outcomes and the interpretation of the results.
Test Conditions
The salt spray test is conducted in a controlled environment to simulate corrosive conditions that a product may be subjected to in real-life situations. The test conditions are carefully monitored to ensure consistent and accurate results.
Below are the key test conditions for conducting a salt spray test:
- Salt Solution: A 5% NaCl (sodium chloride) solution is used as the salt spray solution. This solution is prepared by dissolving sodium chloride in distilled water. The solution is maintained at a constant temperature to ensure accurate results.
- Spray Method: The salt solution is sprayed onto the test specimens using a spraying apparatus. The spray should be evenly distributed and cover the entire surface of the specimens.
- Temperature: The test chamber is maintained at a constant temperature of 35°C (95°F) during the test. This temperature is chosen to simulate the accelerated corrosion effect that occurs in real-life conditions.
- Humidity: The test chamber is maintained at a constant humidity of 95% during the test. This high humidity level enhances the corrosive effect of the salt spray solution on the test specimens.
By controlling these test conditions, the salt spray test accurately simulates the corrosive conditions that a product may encounter in its intended environment. This allows manufacturers to assess the durability and corrosion resistance of their products, and make necessary improvements if needed.
Test Duration
The test duration for the salt spray test is an important factor that determines the effectiveness and reliability of the test results. The duration of the test depends on various factors, including the type of material being tested, the desired level of corrosion resistance, and the requirements of the specific industry or application.
In most cases, the test duration for the salt spray test ranges from 24 to 96 hours. This duration is generally sufficient to evaluate the corrosion resistance of the material under normal operating conditions. However, in some cases, such as for high-performance materials or in extreme environments, the test duration may be extended to several hundred hours.
During the test, the samples are subjected to a continuous exposure to the salt spray, allowing the corrosive effects to develop over time. This allows for a realistic evaluation of the material’s ability to withstand corrosion in a controlled laboratory setting.
It is important to note that the test duration should be carefully chosen based on the specific requirements and expectations of the application. A longer test duration may provide more accurate and reliable results, but it also increases the time and cost associated with the testing process. Therefore, it is crucial to strike a balance between the desired level of accuracy and the practical constraints of time and cost.
In conclusion, the test duration for the salt spray test plays a crucial role in determining the effectiveness of the test results. It should be chosen based on the specific requirements of the material and application, balancing the need for accuracy with practical considerations.
Monitoring and Evaluation of Salt Spray Test Procedure

Salt spray test is a common method for assessing the corrosion resistance of coatings and materials. It is widely used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and marine. To ensure the effectiveness of the test, it is important to establish a systematic monitoring and evaluation process.
Monitoring:
- Regular Inspection: The salt spray test chamber should be visually inspected on a regular basis to ensure proper functioning. The temperature, humidity, and concentration of salt solution should be monitored and maintained at the specified levels.
- Sampling: Samples should be taken at regular intervals during the test to assess the corrosion resistance of the coating. The samples should be carefully selected to represent the overall performance of the materials being tested.
- Visual Evaluation: The samples should be visually inspected to determine the extent of corrosion. This can be done using a magnifying glass or microscope to examine the surface for any signs of blistering, peeling, or discoloration.
Evaluation:
- Rating System: A rating system should be established to quantify the level of corrosion observed on the samples. This can be done using a numerical scale or a descriptive system, such as “none,” “slight,” “moderate,” or “severe” corrosion.
- Data Analysis: The data collected from the monitoring process should be analyzed to identify any trends or patterns in the corrosion resistance of the coatings. This can help in identifying potential issues or improvements in the materials or coating process.
- Comparative Analysis: The results of the salt spray test should be compared with the expected performance of the coatings or materials. This can be done by referencing industry standards or specifications to determine if the test results meet the required criteria.
By establishing a robust monitoring and evaluation process for the salt spray test procedure, manufacturers can ensure the reliability and consistency of their coatings and materials. This can help in identifying any potential issues early on and making necessary improvements to enhance the corrosion resistance of the products.