Understanding the scientific method is essential for anyone involved in scientific research. Whether you are a student conducting a laboratory experiment or a seasoned scientist exploring a complex hypothesis, the scientific method provides a systematic approach for conducting experiments and analyzing results. In this study guide, we will delve into the key components and steps of the scientific method, providing an answer key to help you master this fundamental process.
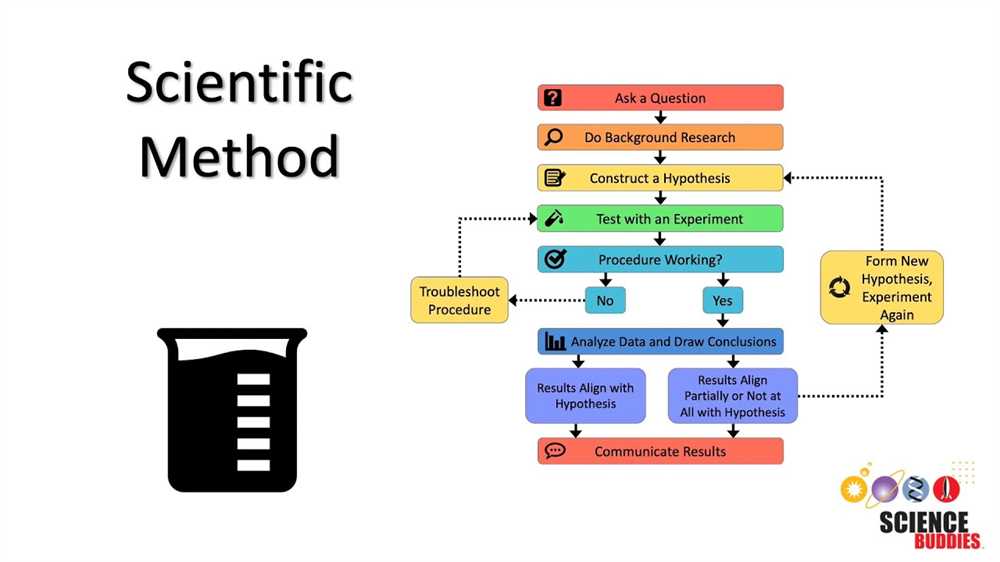
Step 1: Ask a question. The scientific method begins with curiosity. By asking a question, you identify the problem or phenomenon that you want to investigate. This step allows you to formulate a clear research question that can be tested through experimentation.
Step 2: Conduct background research. Before diving into experimentation, it is crucial to gather information about the topic at hand. This includes reviewing existing literature, examining previous studies, and understanding the current state of knowledge. By conducting thorough background research, you equip yourself with the necessary foundation to design an effective experiment.
Step 3: Formulate a hypothesis. A hypothesis is an educated guess or prediction about the outcome of your experiment. It should be based on the information gathered in the previous step. A well-formulated hypothesis sets the stage for testing and provides a clear direction for your research.
Step 4: Design and conduct an experiment. This step involves planning and implementing your experiment. It includes identifying the variables, establishing a control group, and developing a detailed procedure. Careful attention to experimental design ensures reliable and valid results.
Step 5: Collect and analyze data. Once the experiment is underway, you must collect and record data. This involves accurately measuring and documenting the results of your observations or measurements. Analyzing the data, through statistical methods or other techniques, allows you to draw meaningful conclusions.
Step 6: Draw conclusions. With the data in hand, you can evaluate your results and draw conclusions. Were your predictions supported by the evidence? Did your experiment provide new insights or raise new questions? This step requires critical thinking and reflection.
Step 7: Communicate findings. The final step of the scientific method is to share your findings with the scientific community. This includes writing a comprehensive research report, presenting your results at conferences, or publishing your work in scientific journals. By disseminating your findings, you contribute to the collective knowledge and encourage further scientific inquiry.
By understanding and applying the scientific method, scientists can systematically explore nature, test hypotheses, and contribute to the advancement of knowledge. This study guide provides an answer key to help you navigate each step of the scientific method, enabling you to conduct rigorous and reliable research.
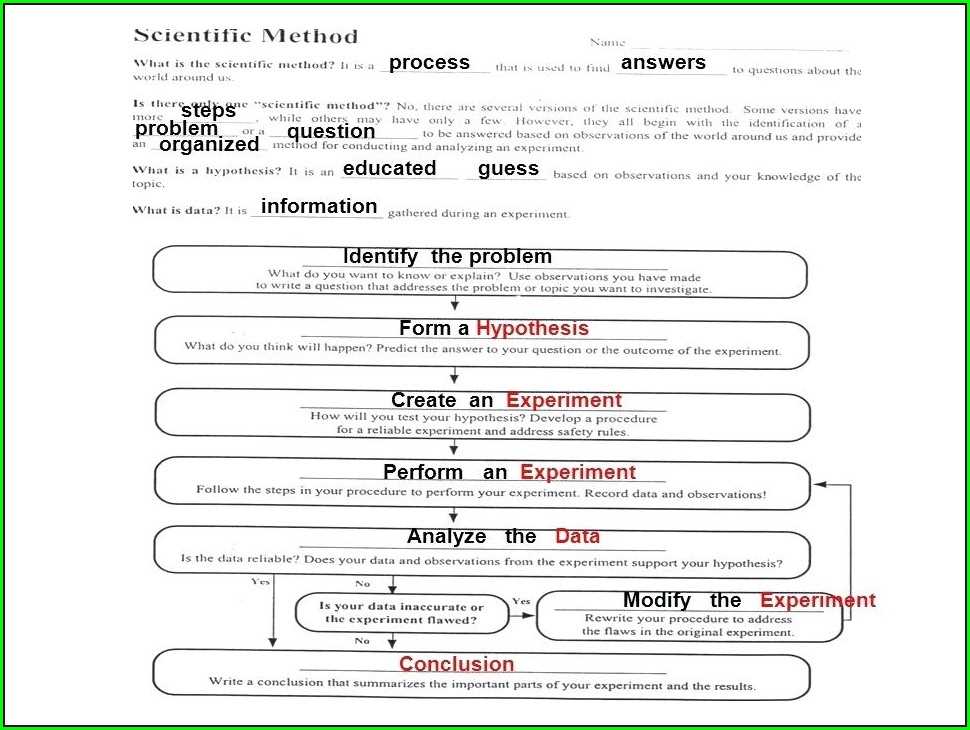
What is the scientific method?
The scientific method is a systematic approach to understanding the natural world through observation, experimentation, and analysis. It is a structured and logical process that scientists use to learn about the world around them.
The scientific method typically involves several key steps. First, scientists make observations and ask questions about a specific phenomenon or problem. These questions form the basis of the research and drive the scientific inquiry process. Once a question is formulated, scientists formulate a hypothesis, which is a proposed explanation for the observed phenomenon. A hypothesis is a testable statement that can be supported or refuted through experimentation.
Next, scientists design and conduct experiments to test their hypotheses. During experimentation, scientists manipulate variables and measure the corresponding effects or outcomes. The results of these experiments are carefully analyzed and interpreted to draw conclusions about the hypothesis. If the hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be considered a valid explanation for the observed phenomenon. However, if the data contradicts the hypothesis, scientists must revise or reject it and propose alternative explanations.
The scientific method is an iterative process, meaning that scientists repeat the steps and refine their understanding as new data and evidence become available. It is a self-correcting process that allows scientists to continually build and improve upon existing knowledge. By following the scientific method, researchers can objectively investigate and explain natural phenomena, contributing to the advancement of scientific knowledge and understanding.
Definition and explanation

The scientific method is a systematic process used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It is a way of asking questions, making observations, conducting experiments, and analyzing data in order to develop and test hypotheses and theories. The scientific method provides a framework for scientists to gather evidence and make logical, objective conclusions based on that evidence.
At its core, the scientific method is about curiosity and the desire to discover and understand how things work. Scientists begin by asking a question or identifying a problem they want to explore. They then conduct background research and gather information relevant to the question or problem. This helps them develop a hypothesis, which is a proposed explanation for the observed phenomenon.
Next, scientists design and carry out experiments or studies to test their hypothesis. This involves collecting and analyzing data, using precise and controlled methods to ensure the reliability and validity of their results. The data is then used to evaluate the hypothesis and draw conclusions.
In the scientific method, the process is not linear, but rather a cyclical loop. If the hypothesis is supported by the data, it can be further tested and refined. If the data does not support the hypothesis, scientists revise their ideas and develop new hypotheses to investigate. This iterative process is what allows scientific knowledge to advance and evolve over time.
It is important to note that the scientific method is not limited to traditional laboratory experiments. It can be applied to a wide range of disciplines, including physics, biology, chemistry, psychology, and social sciences. The scientific method is a powerful tool that helps us understand the world around us and make informed decisions based on evidence and reason.
Steps of the scientific method
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It consists of several steps that guide researchers in designing and conducting experiments, analyzing data, and drawing conclusions. Here are the key steps of the scientific method:
1. Observation: The first step in the scientific method is to carefully observe and identify a problem or question that you want to investigate. This can be done by making detailed observations or conducting experiments to gather data.
2. Research: Once you have identified the problem or question, it is important to research and gather information about the topic. This involves reviewing existing literature, conducting background research, and consulting experts in the field to gain a thorough understanding of the issue.
3. Hypothesis: After conducting research, it is time to develop a hypothesis, which is a proposed explanation or prediction for the problem or question. The hypothesis should be based on the observations and research conducted earlier.
4. Experimentation: The next step is to design and carry out an experiment to test the hypothesis. This involves identifying variables, establishing control groups, and collecting data through experiments or observations.
5. Analysis: Once the experiment is completed, the collected data needs to be analyzed and organized. This involves using statistical tools and methods to interpret the data and identify patterns or trends.
6. Conclusion: Based on the analyzed data, scientists draw conclusions and make inferences about the problem or question being investigated. The conclusions should be supported by the data and should either support or refute the original hypothesis.
7. Communication: The final step of the scientific method is to communicate the results of the study. This involves preparing a report or scientific paper summarizing the research, findings, and conclusions. Scientists also present their findings at conferences or submit them for publication in scientific journals.
In summary, the scientific method is a systematic way of investigating and understanding the natural world. It involves observing and identifying a problem or question, conducting research, developing a hypothesis, designing and conducting experiments, analyzing data, drawing conclusions, and communicating the results. By following these steps, scientists are able to gather reliable and valid information to advance our knowledge and understanding of the world around us.
Overview of the Process
The scientific method is a systematic approach used by scientists to investigate and understand the natural world. It involves a series of steps that guide researchers in formulating and testing hypotheses, collecting and analyzing data, and drawing conclusions based on evidence. The scientific method is an essential tool for conducting reproducible and objective research.
The first step in the scientific method is to make observations and ask questions about a particular phenomenon. This initial stage is crucial for identifying a problem or topic of interest that can be studied further. Once a question has been formulated, scientists develop a hypothesis, which is a proposed explanation for the observed phenomenon. The hypothesis must be testable and based on prior knowledge or evidence.
- Step 1: Observation and Question – Make observations and ask questions about a phenomenon.
- Step 2: Hypothesis – Develop a testable hypothesis that provides a possible explanation for the observed phenomenon.
- Step 3: Experiment – Design and carry out experiments to collect data and test the hypothesis.
- Step 4: Data Analysis – Analyze the collected data using statistical methods.
- Step 5: Conclusion – Draw conclusions based on the results of the experiments and evaluate the hypothesis.
- Step 6: Communication – Share the findings through scientific journals, conferences, and other means of communication.
Experiments are conducted to gather data that can either support or refute the hypothesis. The collected data is then analyzed using statistical methods to determine if it is significant and supports or rejects the hypothesis. Based on the results, scientists draw conclusions and evaluate the validity of the hypothesis.
It is important to note that the scientific method is an iterative process, meaning that it often involves repeating steps or modifying the hypothesis based on new evidence. This iterative nature of the scientific method allows for the continuous refinement and improvement of scientific knowledge. Through effective communication, scientists can share their findings with the scientific community and contribute to the collective understanding of the natural world.
Observation and question
Observation is the first step in the scientific method, and it involves using our senses to gather information about the world around us. Observations can be made using any of our senses: sight, hearing, touch, taste, and smell. Scientists often use instruments and tools to make more accurate observations, such as microscopes, telescopes, and thermometers.
During the observation stage, scientists carefully document what they observe, paying attention to details and taking notes. These observations can then be used to form a question or a hypothesis about the natural world. A question is a statement that seeks to explain a phenomenon or to understand a specific aspect of it. It is an essential part of the scientific method, as it guides the subsequent steps of the process.
- Example: An example of an observation and question could be observing that plants in a particular garden grow taller when exposed to more sunlight. The observation would be measuring the height of the plants in different areas of the garden, while the question would be: “Does sunlight affect the growth of plants?” This question would then lead to the next step in the scientific method, which is forming a hypothesis.
Importance and examples
The scientific method is a systematic approach to solving problems and answering questions through observation, experimentation, and analysis. It is an essential tool in the field of science, as it allows researchers to gather evidence, make predictions, and test hypotheses. By following the scientific method, scientists ensure that their findings are reliable and replicable, providing a solid foundation for further research and discovery.
One example of the scientific method in action is the study of genetics. Geneticists use the scientific method to investigate how traits are inherited, how genes function, and how genetic diseases can be diagnosed and treated. They begin by asking a question, such as “What causes this particular genetic disorder?” Then, they conduct research and gather information to develop a hypothesis. Next, they design and carry out experiments to test their hypothesis, collecting data and analyzing the results. Finally, they draw conclusions based on their findings and communicate their results to the scientific community.
Example 1: Study on the effects of caffeine on productivity
A researcher wants to determine if consuming caffeine can improve productivity. They begin by asking the question, “Does caffeine enhance productivity?” They then formulate a hypothesis: “If individuals consume caffeine, their productivity levels will increase.” To test this hypothesis, they design an experiment in which participants are randomly assigned to either a control group (given a placebo) or an experimental group (given caffeine). The participants’ productivity is measured and compared between the two groups. The data is analyzed, and conclusions are drawn based on the results. The researcher may find that the experimental group, which consumed caffeine, had higher productivity levels compared to the control group. This study demonstrates the scientific method in action.
Example 2: Study on the effects of exercise on mental health
A psychologist wants to investigate if regular exercise can improve mental health. They ask the question, “Does regular exercise positively impact mental well-being?” They hypothesize that individuals who engage in regular exercise will experience improved mental health. They design a study in which participants are randomly assigned to either an exercise group or a control group. The exercise group follows a structured exercise program, while the control group does not engage in regular exercise. The participants’ mental health is assessed before and after the study using validated questionnaires and measurements. The data is analyzed, and conclusions are drawn based on the results. The researcher may find that the exercise group showed significant improvements in mental health compared to the control group. This study showcases the application of the scientific method in psychology research.