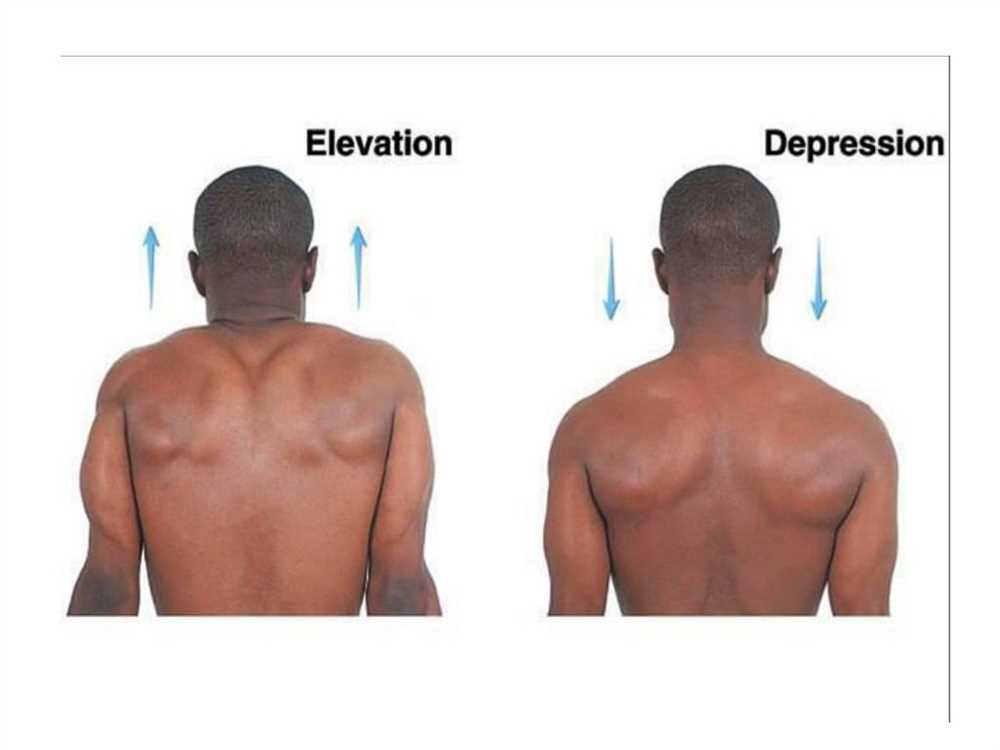
The shoulder depression test is a diagnostic tool used by healthcare professionals to assess the integrity and function of the shoulder joint. This test is commonly employed in cases where there is suspicion of nerve impingement or injury to the brachial plexus, a network of nerves that control movement and sensation in the upper limbs.
During the shoulder depression test, the patient is placed in a seated or lying position, and their affected shoulder is gently pushed downwards towards the floor. The healthcare provider applies a controlled amount of pressure to assess for any abnormal pain, weakness, or instability in the shoulder joint. This test specifically targets the lower trapezius muscle, which plays a pivotal role in maintaining proper shoulder alignment and stability.
The shoulder depression test is particularly useful in evaluating conditions such as thoracic outlet syndrome, rotator cuff injuries, and cervical radiculopathy, among others. It helps to identify any compression or impingement of the nerves in the shoulder area, which can cause symptoms like pain, weakness, tingling, or numbness in the upper extremities.
It is important to note that the shoulder depression test is just one component of a comprehensive clinical examination. It should be used in conjunction with other diagnostic tools, such as imaging studies or additional physical tests, to arrive at an accurate diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan for the patient.
What is the Shoulder Depression Test?
The Shoulder Depression Test is a diagnostic test used by healthcare professionals to evaluate the strength and function of the shoulder muscles. It is primarily used to assess the integrity of the trapezius muscle, which plays a crucial role in shoulder movement and stability.
During the Shoulder Depression Test, the patient is instructed to sit or stand with their arms relaxed at their sides. The examiner gently applies downward pressure to the patient’s shoulders, causing a depression or downward movement of the shoulders. The patient is then asked to resist this downward pressure and maintain their shoulder position.
This test helps identify any weakness or dysfunction in the trapezius muscle. If the patient is unable to resist the downward pressure or experiences pain while performing the test, it may indicate a trapezius muscle strain or weakness. The test can also be used to determine the strength and stability of other shoulder muscles, such as the deltoids and rotator cuff muscles.
The Shoulder Depression Test is commonly used in the assessment of shoulder injuries, such as rotator cuff tears, shoulder impingement, or scapular instability. It provides valuable information for healthcare professionals to develop an appropriate treatment plan and rehabilitative exercises to improve shoulder function and reduce pain.
Definition

The shoulder depression test is a diagnostic maneuver used to assess the integrity and function of the brachial plexus and surrounding structures in the shoulder region. It involves elevating and depressing the patient’s shoulder in order to evaluate the strength and sensation in the upper extremity.
During the shoulder depression test, the patient is typically seated or standing with their arms at their sides. The examiner then gently applies downward pressure on the patient’s shoulder, causing a depression or drop of the shoulder girdle. The patient is instructed to resist this downward pressure by maintaining shoulder elevation using the muscles of the upper extremity.
The shoulder depression test is commonly used in the assessment of conditions such as brachial plexus injuries, thoracic outlet syndrome, and shoulder impingement syndrome. The test is based on the principle that these conditions may cause weakness or sensory deficits in the upper extremity, which can be exacerbated by the downward pressure applied during the test.
Positive findings during the shoulder depression test may include weakness, pain, or sensory changes in the upper extremity, indicating a potential underlying pathology. However, it is important to note that a positive test result does not provide a definitive diagnosis, but rather serves as an indication for further investigation or additional diagnostic tests.
The shoulder depression test is a simple yet valuable tool in the assessment of shoulder and upper extremity conditions. It helps clinicians gather information about the functional status of the brachial plexus and surrounding structures, aiding in the formulation of an accurate diagnosis and appropriate management plan.
Purpose
The purpose of the shoulder depression test is to help diagnose a condition called thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). This test specifically assesses for the presence of neurogenic TOS, which occurs when nerves in the neck and shoulder are compressed or irritated.
Neurogenic TOS can cause symptoms such as pain, tingling, and weakness in the arm, shoulder, and hand. By performing the shoulder depression test, healthcare professionals can determine if these symptoms are due to nerve compression in the thoracic outlet region.
To perform the test, the patient is asked to sit or stand with their involved arm relaxed at their side. The examiner then applies downward pressure on the patient’s shoulder while the patient simultaneously rotates their head and neck away from the involved side. This maneuver helps to further compress the neurovascular structures in the thoracic outlet and reproduce the patient’s symptoms, confirming a positive test.
If the patient experiences an increase in symptoms during the shoulder depression test, further diagnostic tests may be recommended to determine the exact cause of their thoracic outlet syndrome. These tests could include imaging studies such as X-rays, MRIs, or nerve conduction studies to assess the extent of nerve compression and guide appropriate treatment options.
How to Perform the Shoulder Depression Test?
The shoulder depression test is a physical examination technique used to assess the integrity of the suprascapular nerve. This test can help identify nerve compression or injury that may be causing pain or weakness in the shoulder or upper limb. The test involves positioning the patient’s arm in a specific way to stress the suprascapular nerve.
To perform the shoulder depression test, follow these steps:
- Have the patient sit upright with their arms at their sides.
- Instruct the patient to depress their shoulder on the side being tested by pulling the scapula downwards.
- Apply a downward pressure on the patient’s arm just above the elbow to assist with the shoulder depression.
- Ask the patient to maintain the shoulder depression while you palpate the suprascapular notch.
- If the patient experiences pain or discomfort during the test, it may indicate suprascapular nerve compression or injury.
It is important to note that the shoulder depression test should be performed by a trained healthcare professional, such as a physical therapist or orthopedic specialist, who is familiar with the anatomy and mechanics of the shoulder joint. If the test results are positive for nerve compression or injury, further diagnostic tests such as imaging studies or nerve conduction tests may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis and determine the appropriate treatment.
Preparations
Before performing the shoulder depression test, it is important to make certain preparations in order to ensure accurate results. These preparations involve positioning the patient correctly and ensuring the necessary equipment is available.
Positioning the Patient: The patient should be positioned in a seated or supine position, depending on their comfort. They should be relaxed and have their shoulders and neck in a neutral position. It is important to instruct the patient to maintain this position throughout the test.
Equipment: The necessary equipment for this test includes a plinth or examination table and a beaded curtain or other device to provide privacy for the patient. Additionally, the healthcare professional conducting the test should have gloves, measuring tape, and a pen to make the necessary measurements and record the results.
Once the patient is appropriately positioned and the necessary equipment is available, the healthcare professional can proceed with performing the shoulder depression test. This test is a useful diagnostic tool to assess whether there is impingement or compression of the structures within the subacromial space. By following these preparations, accurate and reliable results can be obtained, aiding in the diagnosis and management of shoulder pathologies.
Execution
The shoulder depression test is a physical examination maneuver that is used to assess the integrity of the nerve supply to the muscles responsible for depression of the shoulder girdle. It is performed by the healthcare professional by asking the patient to sit or stand while observing the movements of the shoulder girdle.
To execute the shoulder depression test, the healthcare professional instructs the patient to relax their shoulder muscles and then actively depress their shoulder girdle by pulling the affected shoulder down towards the opposite hip. The patient may be asked to perform this movement against resistance or without resistance, depending on the purpose of the test.
The healthcare professional carefully observes the movement of the shoulder girdle during the test. They look for any signs of weakness or inability to depress the shoulder girdle fully. If the patient experiences pain or if the movement is limited or asymmetrical, it may indicate an issue with the nerve supply to the muscles involved in shoulder depression.
In some cases, the healthcare professional may also palpate the muscles and nerves in the area to further evaluate any abnormalities or discomfort. The results of the shoulder depression test, along with other diagnostic tests and assessments, help the healthcare professional determine the underlying cause of shoulder dysfunction and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Interpreting the Results of the Shoulder Depression Test
The shoulder depression test, also known as the Scalenus Test or Adson’s Test, is performed to assess the presence of thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS). This test involves the patient sitting or standing while the examiner passively depresses the shoulder, stretching the scalene muscles and putting pressure on the brachial plexus. Interpreting the results of the shoulder depression test requires a careful analysis of the patient’s response and understanding of the potential implications.
If the patient experiences pain, numbness, tingling, or the reproduction of their symptoms during the shoulder depression test, it may indicate a positive result. A positive result suggests compression or irritation of the nerves or blood vessels in the upper extremity, which can occur due to compression from the scalene muscles or other structures in the thoracic outlet.
A positive shoulder depression test does not provide a definitive diagnosis of thoracic outlet syndrome on its own. Further diagnostic tests, such as imaging studies or nerve conduction studies, may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis. Additionally, other clinical assessment tools, such as the Roos Test or Wright Test, may be used in conjunction with the shoulder depression test to gather more comprehensive information.
It is important to note that a negative result on the shoulder depression test does not necessarily rule out the presence of thoracic outlet syndrome. False-negative results can occur, especially in cases where the compression or irritation of the nerves or blood vessels is intermittent or the patient’s symptoms are not reproduced during the test. Therefore, clinical judgment and consideration of the patient’s entire clinical presentation are crucial in interpreting the results of the shoulder depression test.
Positive Result
When performing the shoulder depression test, a positive result is indicated when the patient experiences pain or discomfort in the affected shoulder or arm. This indicates the presence of impingement or compression of the structures within the shoulder joint, such as the rotator cuff tendons or the subacromial bursa.
Important information to note during a positive result are:
- The location and intensity of the pain or discomfort
- The specific movements or positions that aggravate the symptoms
- Any associated weakness or loss of range of motion
These findings can help healthcare professionals determine the underlying cause of the shoulder pain and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Common diagnoses associated with a positive result of the shoulder depression test include rotator cuff tendinopathy, subacromial impingement syndrome, or bicipital tendinopathy.
Negative Result
When performing the shoulder depression test, a negative result indicates that there is no impingement or compression of the brachial plexus or axillary artery. The patient does not experience any pain or discomfort during the test, and there are no signs of weakness or limited range of motion in the affected shoulder.
In a negative result, the examiner applies downward pressure on the patient’s shoulder while the arm is fully extended and the head is rotated away from the affected side. The patient should be able to resist the pressure and maintain normal strength in the shoulder muscles. There should be no tingling or numbness in the arm or hand, and the pulses in the affected arm should remain strong and regular.
If the test is negative, it is likely that the patient does not have any issues with nerve or vascular compression in the shoulder. However, it is important to note that the shoulder depression test alone may not be sufficient to rule out all potential causes of shoulder pain or dysfunction. Additional tests and evaluations may be necessary to fully assess the patient’s condition and determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Possible Causes of Positive Shoulder Depression Test
The shoulder depression test is a physical examination technique used to assess the integrity and function of the shoulder joint. A positive test result indicates the presence of pathology or dysfunction in the shoulder. There are several possible causes that can give rise to a positive shoulder depression test.
Rotator Cuff Pathology:
One possible cause of a positive shoulder depression test is rotator cuff pathology. The rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that surround and support the shoulder joint. If there is damage or inflammation in the rotator cuff, it can affect the stability and movement of the shoulder joint, leading to a positive test result. Common conditions that can cause rotator cuff pathology include rotator cuff tears, tendinitis, and impingement syndrome.
Glenohumeral Instability:
Glenohumeral instability refers to an abnormal movement or looseness in the ball-and-socket joint of the shoulder. This can occur due to ligamentous laxity, repetitive stress, trauma, or congenital factors. When the shoulder joint is unstable, it can lead to increased movement and subluxation, which can be detected by a positive shoulder depression test.
Shoulder Impingement:
Shoulder impingement occurs when the space between the acromion (a bony prominence on the shoulder blade) and the humeral head (the ball of the upper arm bone) is narrowed, resulting in compression and irritation of the structures within the shoulder joint. This can cause pain, inflammation, and limited range of motion in the shoulder. A positive shoulder depression test can indicate the presence of shoulder impingement.
Labral Tears:
The labrum is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint, providing stability and cushioning. Labral tears can occur due to trauma, repetitive overhead activities, or degenerative changes. A positive shoulder depression test can suggest the presence of a labral tear, as it can cause pain, instability, and abnormal movement in the shoulder joint.
Other Possible Causes:
Other potential causes of a positive shoulder depression test include biceps tendinitis, bursitis, arthritis, muscle strains, or nerve impingement. These conditions can affect the structures around the shoulder joint, leading to pain and dysfunction that can be detected through a positive shoulder depression test.
In summary, a positive shoulder depression test can indicate various underlying causes, including rotator cuff pathology, glenohumeral instability, shoulder impingement, labral tears, and other shoulder-related conditions. It is important to consider these possible causes and conduct further diagnostic tests to confirm the exact source of the positive test result and develop an appropriate treatment plan.