When it comes to financial calculations, interest plays a crucial role in determining the growth of investments or the cost of borrowing money. Simple and compound interest are two common concepts that individuals encounter when managing their finances. Whether you are a student learning about the basics of interest or someone looking for in-depth explanations, a simple and compound interest worksheet can provide answers to your questions.
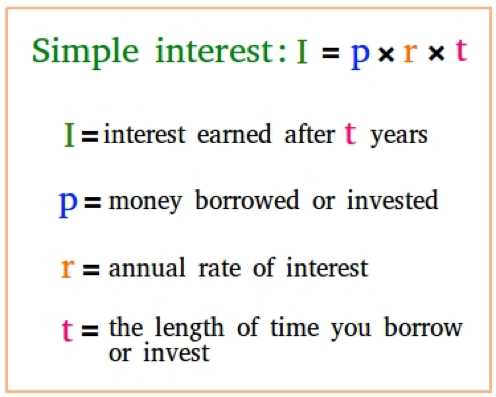
Simple interest is a straightforward concept that involves earning or paying interest only on the original principal amount. This means that the interest remains the same throughout the entire duration of the loan or investment. A simple interest worksheet can help you understand how to calculate the interest earned or paid, the total amount after interest, and the interest rate.
Compound interest, on the other hand, is more complex and involves interest being calculated not only on the original principal amount but also on the accumulated interest over time. Compound interest helps money grow exponentially, making it a powerful tool for long-term investments. The answers provided in a compound interest worksheet can help you grasp the mechanics of compound interest, including the future value of an investment, the interest rate, and the number of compounding periods.
By working through simple and compound interest worksheets and analyzing the answers, you can gain a better understanding of how interest impacts your financial decisions. Whether you are preparing for a finance exam or making important investment choices, having a clear grasp of simple and compound interest calculations is essential for financial literacy.
Understanding Simple Interest
When it comes to financial matters, it’s important to have a good understanding of simple interest. Simple interest is a basic form of interest that is calculated on the principal amount of a loan or investment. It is typically used for short-term loans or investments, and is calculated by multiplying the principal amount, the interest rate, and the time period.
Principal Amount: The principal amount refers to the initial amount of money that is borrowed or invested. This is the amount that the interest is calculated on.
Interest Rate: The interest rate is the percentage of the principal amount that is charged as interest. It determines how much interest is earned or paid on the principal amount.
Time Period: The time period is the duration for which the loan or investment is made. It is typically expressed in years, but can also be in months, days, or any other unit of time. The time period is important because it determines how long the principal amount will be earning or paying interest.
Calculating simple interest is straightforward. The formula for calculating simple interest is:
Simple Interest = Principal Amount x Interest Rate x Time Period
For example, let’s say you have a principal amount of $1,000, an interest rate of 5%, and a time period of 3 years. To calculate the simple interest, you would use the formula:
Simple Interest = $1,000 x 0.05 x 3 = $150
This means that over a period of 3 years, the initial investment of $1,000 would earn $150 in interest.
Understanding simple interest is important for managing your finances and making informed decisions about loans and investments. By knowing how to calculate simple interest, you can determine how much interest you will earn or pay, and make better financial decisions based on that knowledge.
Calculating Simple Interest
Calculating simple interest is a straightforward process that involves using a simple formula to determine how much interest is earned or owed on a principal amount over a specific period of time.
To calculate simple interest, you need three pieces of information: the principal amount, the interest rate, and the time period. The principal amount is the initial amount of money that is borrowed or invested. The interest rate is the percentage of the principal that is charged or earned as interest. The time period is the length of time that the interest is calculated for.
The formula for calculating simple interest is:
Interest = (Principal × Rate × Time) / 100
For example, let’s say you have $1,000 that you want to invest for 5 years at an interest rate of 5%. To calculate the interest earned, you would use the formula:
- Principal = $1,000
- Rate = 5%
- Time = 5 years
Interest = (1000 × 5 × 5) / 100 = $250
So, after 5 years, you would earn $250 in interest on your $1,000 investment.
It is important to note that simple interest does not take into account any compounding factors, such as the reinvestment of interest earnings. This means that the interest earned remains constant over the time period.
Overall, calculating simple interest is a simple and straightforward process that can help individuals and businesses determine the amount of interest earned or owed on an investment or loan. By understanding how to calculate simple interest, you can make informed decisions about your financial investments and obligations.
Examples of Simple Interest
Simple interest is a basic concept in finance that is used to calculate the cost or earnings of a loan or investment. It is calculated as a percentage of the principal amount, or the amount of money being borrowed or invested. Here are some examples of how simple interest can be applied in different situations:
1. Loan Repayment
Let’s say you borrow $10,000 from a bank at an annual interest rate of 5%. The bank charges simple interest on this loan. After one year, you would owe $10,500, which is the original principal ($10,000) plus the interest ($500). The interest is calculated by multiplying the principal by the interest rate and the time period (in this case, one year).
2. Fixed Deposit
If you have $5,000 that you want to invest in a fixed deposit account that offers a simple interest rate of 3% per year, you can calculate the interest earned over a certain period of time. For example, if you keep the money in the account for 2 years, you would earn $300 in interest ($5,000 * 0.03 * 2 = $300).
3. Credit Card Debt
When you have outstanding balances on your credit card, the credit card company may charge you interest on that amount. This interest is calculated based on a daily or monthly rate applied to the amount owed. For example, if you have a balance of $1,000 on your credit card with an annual interest rate of 15%, you would owe $150 in interest for one year ($1,000 * 0.15).
These are just a few examples of how simple interest can be applied in different financial scenarios. It’s important to understand how it is calculated and how it can affect your loans or investments.
Advantages of Compound Interest
Compound interest is a powerful concept in the world of finance that can offer several advantages to individuals and businesses. Unlike simple interest, which is calculated only on the initial amount of money deposited or borrowed, compound interest takes into account the accumulated interest over time. This means that the interest earned on an investment or loan is added back to the principal amount, allowing for exponential growth.
1. Higher Earnings
One of the main advantages of compound interest is that it can lead to higher earnings compared to simple interest. As the interest is calculated not just on the principal amount but also on the accumulated interest, the growth of the investment or loan accelerates over time. This compounding effect allows for the potential to earn more money without having to make additional contributions or payments.
2. Long-Term Wealth Creation
Compound interest is particularly beneficial for long-term wealth creation. By reinvesting the interest earned back into the investment or loan, individuals and businesses can harness the power of compounding to build wealth over time. This can be particularly advantageous for retirement savings, college funds, or any other financial goals that require long-term planning.
3. Increased Savings Motivation
The concept of compound interest can provide individuals with increased motivation to save and invest. Knowing that their money can grow significantly over time through compounding can incentivize people to set aside more money and make smarter financial decisions. This can help individuals achieve their financial goals faster and more effectively.
4. Flexibility
Compound interest offers flexibility in terms of investment options. With the power of compounding, individuals can choose from a variety of investment vehicles such as stocks, bonds, mutual funds, or even high-interest savings accounts. This allows for customization and diversification, giving individuals the opportunity to maximize their returns based on their risk tolerance and financial goals.
5. Business Growth
Compound interest can also be advantageous for businesses seeking growth and expansion. By reinvesting the interest earned back into the business, companies can fuel their growth through compound growth. This can lead to increased profitability, the ability to reinvest in new projects, and overall financial stability.
In conclusion, compound interest offers several advantages, including higher earnings, long-term wealth creation, increased savings motivation, flexibility, and business growth. By understanding and harnessing the power of compounding, individuals and businesses can take advantage of the exponential growth potential and achieve their financial goals.
Formula for Compound Interest
The formula for compound interest allows you to calculate the future value of an investment by taking into account both the principal amount and the interest earned over time. Compound interest is the accrual of interest on top of the interest already earned. This means that the interest is calculated not only on the initial principal, but also on the accumulated interest from previous periods.
The formula for compound interest is:
A = P(1 + r/n)nt
Where:
- A is the future value of the investment
- P is the principal amount (initial investment)
- r is the annual interest rate (expressed as a decimal)
- n is the number of times that interest is compounded per year
- t is the number of years the money is invested
This formula takes into account the frequency of compounding, which can greatly affect the final value of the investment. The more frequently interest is compounded, the greater the future value will be. By using this formula, you can determine the potential growth of your investment over time and make informed decisions for financial planning.
Benefits of Compound Interest
Compound interest is a powerful financial tool that can help individuals grow their savings and investments over time. Unlike simple interest, which only calculates interest on the initial principal, compound interest allows for the accumulation of interest on both the principal amount and any previously earned interest. This compounding effect can greatly increase the growth potential of an investment.
1. Increased ROI: One of the main benefits of compound interest is its ability to provide a higher return on investment (ROI) compared to simple interest. As interest accumulates and is reinvested, the overall value of the investment continues to grow at an accelerated rate. This means that over time, a smaller initial investment can potentially generate a larger return.
2. Long-term growth: Compound interest is particularly advantageous for long-term investments. By reinvesting earned interest back into the principal balance, the overall investment amount keeps growing exponentially. This compounding effect allows for significant wealth accumulation over extended periods of time, making it an ideal strategy for retirement savings or wealth building.
3. Passive income: Another perk of compound interest is the potential for generating passive income. As the investment grows, the interest earned can start to become a significant source of income without requiring much additional effort or active involvement. This passive income can be used to supplement one’s salary, cover expenses, or reinvest for even greater growth.
4. Diversification opportunities: Compound interest also opens up opportunities for diversification. By continuously reinvesting earned interest, investors can allocate funds to different asset classes, sectors, or markets. This diversification can help mitigate risk and increase the chances of achieving consistent returns.
5. Financial security: Lastly, compound interest can provide financial security and stability. By consistently reinvesting and allowing interest to compound, individuals can build a robust financial portfolio, which can act as a safety net during times of economic uncertainty or unexpected expenses. This can provide peace of mind and a sense of security in the face of financial challenges.
In conclusion, compound interest offers numerous benefits that can help individuals achieve their financial goals. From increased ROI and long-term growth to passive income generation and diversification opportunities, compound interest is a valuable tool for wealth creation and financial security.
Comparison of Simple and Compound Interest
When it comes to earning interest on an investment or loan, it’s important to understand the difference between simple and compound interest. Simple interest is calculated only on the original principal amount, while compound interest takes into account both the principal and any accumulated interest.
Simple Interest: With simple interest, the interest is calculated based on the initial principal amount and remains constant throughout the entire duration of the investment or loan. The formula for simple interest is: Principal x Rate x Time. This means that the interest earned or owed stays the same each period.
For example: Let’s say you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5%. After one year, you would earn $50 in interest (Simple Interest = Principal x Rate x Time = $1,000 x 0.05 x 1 = $50). After two years, you would earn a total of $100 in interest.
Compound Interest: Compound interest, on the other hand, takes into account the accumulated interest when calculating future interest. This means that the interest earned or owed is not constant, but grows as the investment or loan continues to compound over time. The formula for compound interest is: Principal x (1 + Rate)^Time. This means that the interest earned or owed increases each period.
For example: Let’s say you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded annually. After one year, you would earn $50 in interest (Compound Interest = Principal x (1 + Rate)^Time = $1,000 x (1 + 0.05)^1 = $1,050). After two years, you would earn a total of $105 in interest.
Summary:
- Simple interest is calculated based only on the initial principal amount, while compound interest takes into account both the principal and any accumulated interest.
- Simple interest remains constant throughout the entire duration of the investment or loan, while compound interest grows as the interest is added back to the principal each period.
- Simple interest is commonly used for short-term investments or loans, while compound interest is more commonly used for long-term investments or loans.
- The choice between simple and compound interest depends on the specific financial goals and time horizon of the individual or organization.