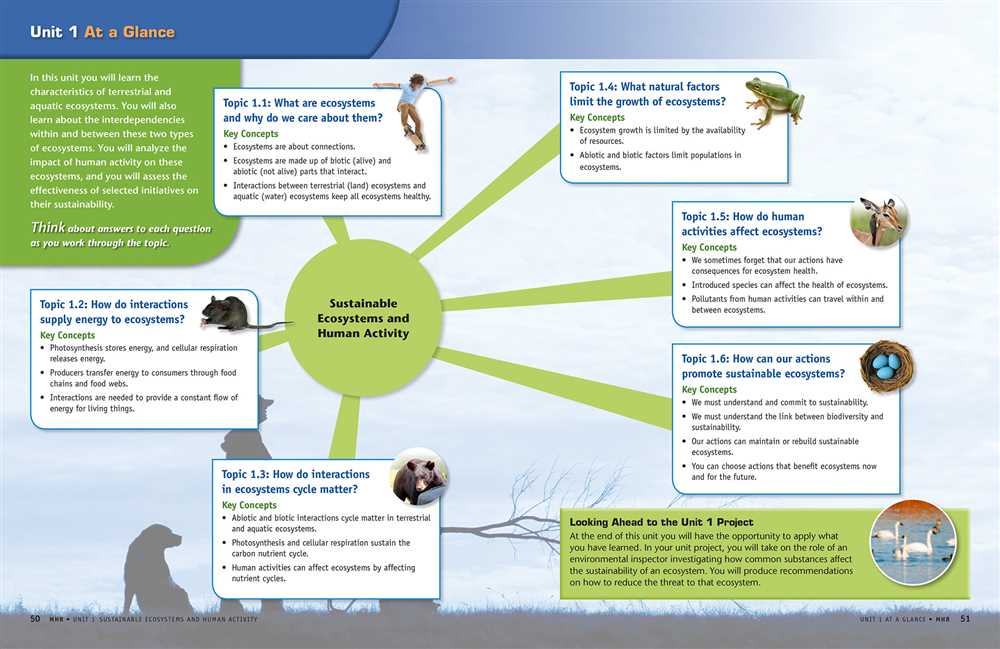
The forest ecosystem is a complex and fascinating subject to study. From the variety of plant and animal species that call it home to the intricate relationships between these organisms, there is much to learn and discover. This exploration is especially valuable for students, as it allows them to gain a deeper understanding of the natural world and the important role that forests play in maintaining a balanced environment.
As students delve into the forest ecosystem, they encounter various questions and challenges. An answer key is an invaluable resource that helps them navigate through their exploration. By providing correct answers to questions and explanations for different phenomena, the answer key serves as a guide, enabling students to enrich their understanding and further their learning.
The answer key for student exploration of the forest ecosystem covers a wide range of topics. It includes information on the different layers of the forest, such as the canopy, understory, and forest floor, and the unique plants and animals that inhabit each layer. Students can learn about the role of decomposers in breaking down organic matter, the process of photosynthesis, and the interdependence of various organisms within the ecosystem.
Furthermore, the answer key helps students understand the impact of human activities on the forest ecosystem. It highlights the importance of sustainable practices and conservation efforts to protect forest biodiversity. By exploring the answer key, students can gain a comprehensive understanding of the forest ecosystem and develop a sense of responsibility towards its preservation.
Student Exploration Forest Ecosystem Answer Key
Exploring the forest ecosystem is an exciting way for students to learn about the intricate relationships and interactions within this unique environment. The Student Exploration Forest Ecosystem Answer Key provides a comprehensive guide to understanding and interpreting the data and observations gathered during the exploration.
The answer key starts by introducing the students to the different components of the forest ecosystem, such as plants, animals, and non-living factors like soil and water. It then guides the students through the various activities and investigations conducted during the exploration, providing them with the correct answers and explanations.
Activity 1: Forest Layers
- Students learn about the different layers of the forest, including the canopy, understory, and forest floor.
- They identify various plants and animals that inhabit each layer and understand how they are adapted to their specific environment.
- Students are then provided with the answer key, allowing them to verify their observations and learn more about the plants and animals they encountered.
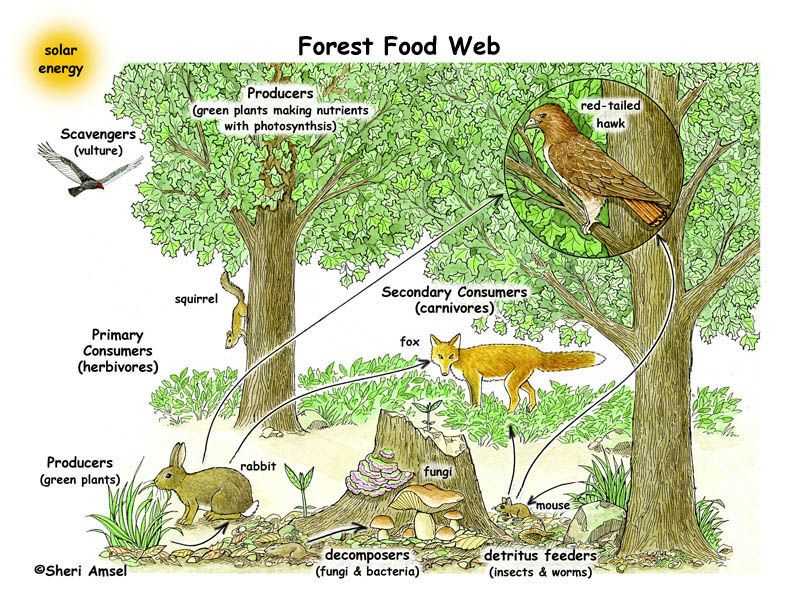
Activity 2: Food Chains and Webs
- Students explore the concept of food chains and webs within the forest ecosystem and understand the flow of energy from producers to consumers.
- They identify different organisms and their roles as producers, consumers, or decomposers.
- The answer key provides detailed information about each organism’s position within the food chain or web, helping students understand the complexity and interconnectedness of the ecosystem.
Activity 3: Biotic and Abiotic Factors
- Students examine the biotic and abiotic factors that influence the forest ecosystem.
- They identify and classify organisms as biotic or abiotic and understand the impact of these factors on the ecosystem’s balance.
- The answer key helps students confirm their classifications and provides additional information about the importance of these factors in maintaining a healthy forest ecosystem.
By using the Student Exploration Forest Ecosystem Answer Key, students can solidify their understanding of the various concepts explored during the activity and gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate web of life within the forest ecosystem.
About the Forest Ecosystem
A forest ecosystem is a complex system that includes various living organisms and their surrounding environment. It comprises a diverse range of plant and animal species, as well as countless microorganisms that all interact and depend on each other for survival. Forest ecosystems can be found throughout the world and are characterized by their dense vegetation, trees, and abundant wildlife.
Forests play a vital role in maintaining the global ecosystem. They act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing large amounts of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, thus helping to mitigate climate change. Additionally, forests provide habitat for numerous species, including mammals, birds, insects, and plants, promoting biodiversity and supporting the balance of natural ecosystems.
In a forest ecosystem, plants play a fundamental role as the primary producers. They use photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into food and energy. These plants provide food and shelter for other organisms, such as herbivores that feed on their leaves, fruits, and seeds. This creates a chain of energy transfer, where energy flows from one organism to another through predation and consumption.
- Forest ecosystems also rely on decomposers, such as fungi and bacteria, that break down organic matter and recycle nutrients back into the soil.
- Furthermore, forests contribute to the water cycle by intercepting rainfall, allowing water to infiltrate into the soil and replenish groundwater reserves.
- They also help prevent soil erosion by stabilizing the soil with their root systems.
Overall, forest ecosystems are incredibly important for both the environment and humanity. They provide us with essential resources, such as timber, food, and medicine. They also offer recreational opportunities, including hiking, camping, and wildlife observation. Protecting and preserving forest ecosystems is crucial for the sustainability of our planet and future generations.
The Importance of Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems play a critical role in maintaining the balance of our planet’s biodiversity and overall ecosystem health. These complex systems provide habitat for countless organisms, including plants, animals, and microorganisms, and support a wide range of ecological functions and processes.
Biodiversity: Forests are home to an incredible array of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic and unique to specific forest ecosystems. The rich diversity of species found in forests helps to maintain the stability and resilience of ecosystems, as different species interact and depend on each other for survival.
Climate Regulation: Forests are often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth” because they absorb carbon dioxide, a major greenhouse gas, and release oxygen through the process of photosynthesis. This helps to regulate the Earth’s climate and mitigate the effects of climate change. Forests also act as natural carbon sinks, which means they store carbon in trees and soil, preventing it from entering the atmosphere as carbon dioxide.
Water Cycle: Forests play a crucial role in the water cycle by intercepting rainfall, reducing soil erosion, regulating stream flow, and replenishing groundwater. The roots of trees help to stabilize soil, preventing erosion and landslides, and the shade provided by the canopy helps to regulate water temperature and reduce evaporation.
Economic Value: Forests provide a wide range of economic benefits, including timber and non-timber forest products, such as food, medicine, and materials for construction. Forests also support a variety of industries, including tourism and recreation, which contribute to local economies.
In conclusion, forest ecosystems are of immense importance for maintaining biodiversity, regulating climate, sustaining the water cycle, and providing valuable economic benefits. These ecosystems must be preserved and managed sustainably to ensure their continued existence and the well-being of both humans and other species that depend on them.
Components of a Forest Ecosystem
A forest ecosystem is a complex web of living organisms, abiotic factors, and ecological processes that interact with one another within a forested area. Understanding the components of a forest ecosystem is crucial for studying and conserving these diverse habitats.
1. Trees: Trees are the dominant and defining feature of a forest ecosystem. They provide shelter, food, and habitat for a wide variety of organisms, from birds and mammals to insects and fungi. Trees also play a crucial role in regulating the climate and water cycle, as they absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen through photosynthesis.
2. Understory Plants: Underneath the canopy of trees, a layer of understory plants thrives. These may include shrubs, ferns, mosses, and small flowering plants. Understory plants provide additional food and shelter for wildlife, as well as help prevent soil erosion and promote nutrient recycling.
3. Animals: Forest ecosystems are home to a vast array of animal species. These include mammals like deer, bears, and squirrels, birds such as owls and woodpeckers, reptiles and amphibians like snakes and frogs, and a multitude of insects and arachnids. These animals rely on the forest for food, shelter, and breeding grounds.
4. Soil: The soil in a forest ecosystem is crucial for supporting plant growth and providing nutrients. It is composed of organic matter, minerals, water, air, and microorganisms. The decomposition of dead plants and animals adds nutrients to the soil, creating a rich and fertile environment.
5. Abiotic Factors: Abiotic factors in a forest ecosystem include temperature, precipitation, sunlight, wind, and soil type. These factors determine the overall climate and availability of resources in the forest, influencing the types of organisms that can thrive in the ecosystem.
6. Ecological Processes: Forest ecosystems are characterized by a complex series of ecological processes. These include photosynthesis, nutrient cycling, predation, competition, and succession. These processes drive the interactions between organisms and shape the structure and function of the forest ecosystem over time.
Biotic Interactions in the Forest
In the forest ecosystem, various biotic interactions occur between different organisms, contributing to the complexity and balance of the ecosystem. These interactions involve relationships between plants, animals, and microorganisms, and play a crucial role in maintaining the health and functionality of the forest.
One of the important biotic interactions in the forest is mutualism, where two species benefit from their association. An example of mutualism in the forest is the relationship between certain plants and pollinators. Plants rely on pollinators like bees and butterflies to transfer pollen from one flower to another, enabling reproduction and fruit production. In return, the pollinators receive nectar or pollen as a food source.
Another common biotic interaction in the forest is predation. Predation involves a predator capturing and consuming its prey. In the forest, predators such as carnivorous animals and birds hunt and feed on smaller animals, regulating population sizes and controlling species diversity. This interaction is vital for maintaining a balanced ecosystem and preventing any one species from becoming dominant.
Additionally, competition is a significant biotic interaction in the forest, as different species compete for resources such as food, water, and space. For example, trees in a forest compete for sunlight, leading to the development of different growth strategies and adaptations. This competition can affect the distribution and abundance of species within the ecosystem.
The forest ecosystem is also influenced by symbiotic relationships, where two different species live in close association with each other. An example of symbiosis in the forest is mycorrhizal associations between trees and fungi. The fungi help trees absorb essential nutrients from the soil, while the trees provide the fungi with carbohydrates. This mutualistic relationship enhances the nutrient availability and uptake, promoting the overall health and growth of the forest.
In conclusion, biotic interactions in the forest ecosystem are diverse and play a critical role in maintaining the balance and functionality of the ecosystem. Mutualism, predation, competition, and symbiosis are key interactions that shape the dynamics and biodiversity of the forest. Understanding these interactions is essential for effective conservation and management of forest ecosystems.
Abiotic Factors in the Forest Ecosystem
The forest ecosystem is influenced by a variety of abiotic factors that play a crucial role in shaping its structure and functions. These abiotic factors include climate, soil composition, topography, and water availability. Each of these factors has a significant impact on the plants, animals, and other organisms that inhabit the forest ecosystem.
Climate is one of the most important abiotic factors in the forest ecosystem. It encompasses a range of variables such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, and sunlight. These factors determine the type of forest that can thrive in a particular area. Forests in tropical regions, for example, are characterized by high temperatures, abundant rainfall, and high humidity, whereas forests in temperate regions experience cooler temperatures and moderate rainfall.
The soil composition also plays a crucial role in the forest ecosystem. Different types of soil, such as clay, sand, and loam, have varying levels of fertility and drainage capacity. These factors affect the types of plants that can grow in the forest and the availability of nutrients for their growth. Additionally, soil composition influences the water retention capacity, which is essential for the survival of both plants and animals in the ecosystem.
Topography, or the physical features of the land, also influences the forest ecosystem. Slope and elevation affect factors such as water drainage, sunlight exposure, and wind patterns. Steep slopes, for example, can lead to soil erosion and affect the distribution of plants and animals. Similarly, elevation influences temperature, with higher elevations being generally cooler than lower ones.
Water availability is another critical abiotic factor in the forest ecosystem. Forests require a sufficient supply of water for the survival of plants, animals, and other organisms. Precipitation and water sources such as rivers, lakes, and groundwater play a vital role in maintaining the water balance in the ecosystem. Droughts or water scarcity can have severe consequences for the forest ecosystem, leading to reduced plant growth, increased vulnerability to forest fires, and overall biodiversity loss.
In conclusion, abiotic factors such as climate, soil composition, topography, and water availability have a significant impact on the forest ecosystem. Understanding these factors is crucial for studying and managing forest ecosystems and ensuring their long-term sustainability.